A Historical Journey: Mapping the French Colonial Legacy
Related Articles: A Historical Journey: Mapping the French Colonial Legacy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Historical Journey: Mapping the French Colonial Legacy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Historical Journey: Mapping the French Colonial Legacy
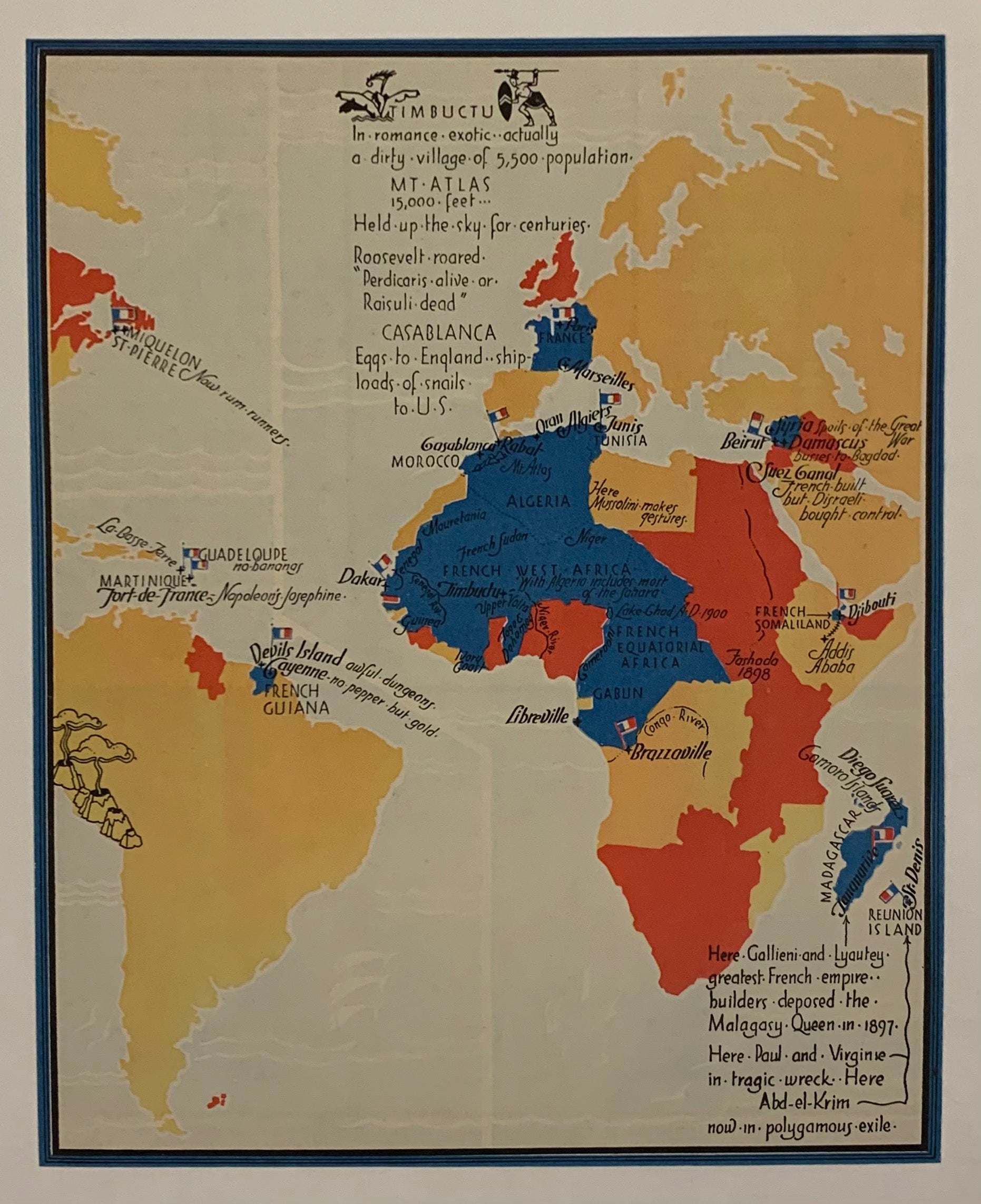
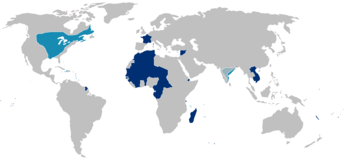
The French colonial empire, spanning centuries and continents, left an indelible mark on the global landscape. Understanding its evolution and impact requires a comprehensive view, one best provided by a map. This exploration delves into the intricacies of the French colonial map, revealing its historical significance and the lasting consequences of its presence.
The Rise and Fall of a Colonial Power:
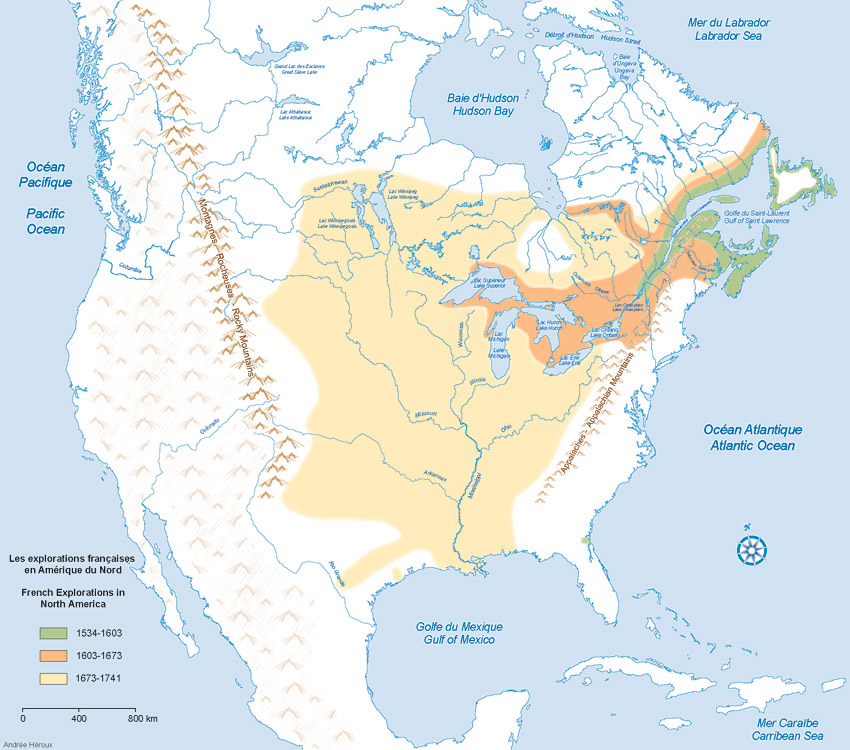
The French colonial adventure began in the 16th century, fueled by the insatiable European thirst for resources and expansion. Early ventures focused on North America, with settlements established in what is now Canada and the United States. The 17th and 18th centuries saw the French colonize vast territories in the Caribbean, Africa, and Asia, fueled by the lucrative trade in sugar, coffee, and spices.
A Visual Chronicle of Expansion:
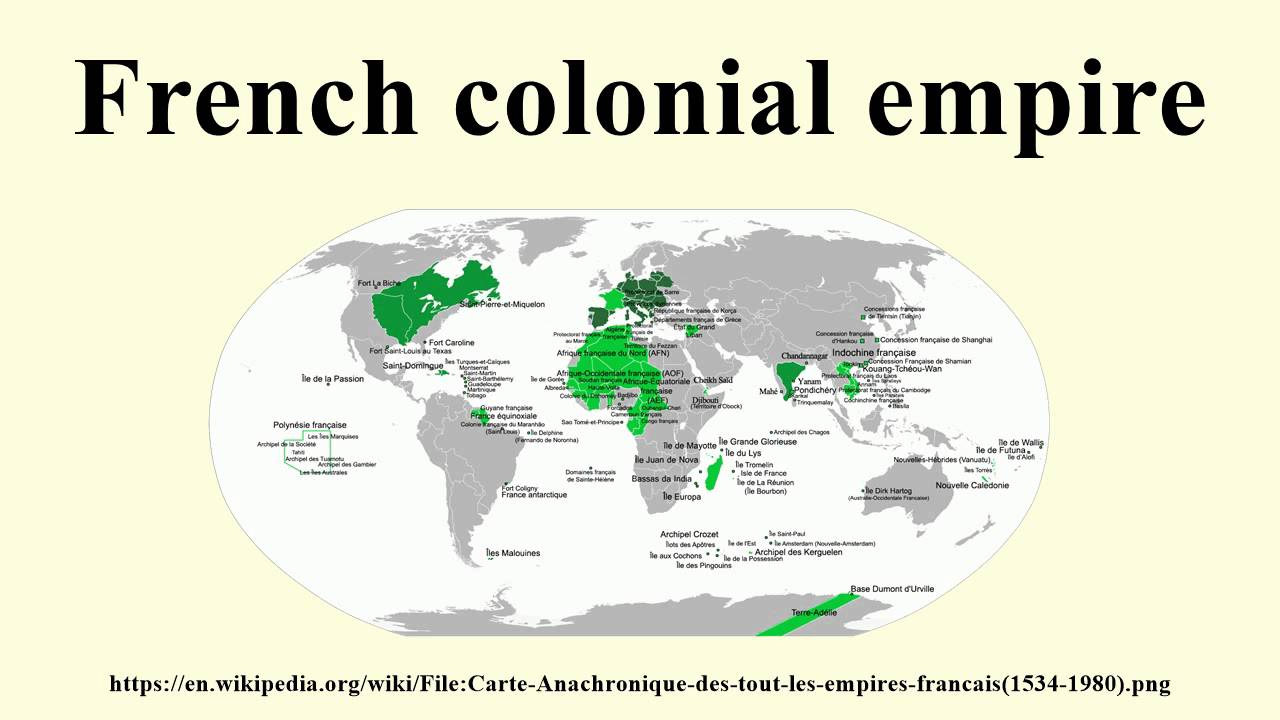
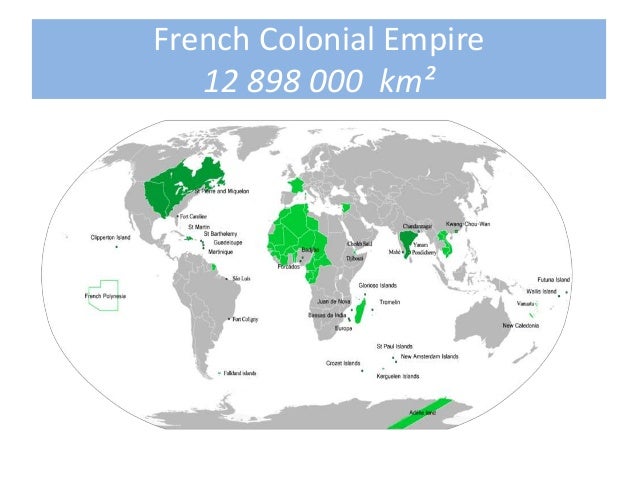
A map of French colonies, meticulously tracing the boundaries of their dominion, offers a powerful visual narrative. It reveals the extent of their influence, highlighting the diverse regions they controlled:
- North America: From the St. Lawrence River to the Mississippi Valley, French settlements dotted the landscape, establishing trade routes and laying the foundation for a vibrant fur trade.
- Caribbean: The islands of Martinique, Guadeloupe, and Haiti became key sugar producers, contributing significantly to the French economy.
- Africa: French influence stretched across the continent, encompassing regions like Senegal, Ivory Coast, and Algeria. These territories served as sources of raw materials, particularly for the burgeoning industrial revolution in Europe.
- Asia: The French established trading posts and colonies in Southeast Asia, including Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. They also gained control of the strategically important port of Pondicherry in India.
The Legacy of Colonialism:
The French colonial map, while showcasing the vastness of their empire, also underscores the complexities of its impact. The legacy of French colonialism is a multifaceted one, encompassing both positive and negative consequences:
Positive Impacts:
- Infrastructure Development: The French invested in infrastructure projects, building roads, railways, and ports. These developments facilitated trade and communication within their colonies.
- Education and Healthcare: The introduction of French education and healthcare systems, albeit often limited to the elite, contributed to the development of human capital in certain regions.
- Cultural Exchange: The interaction between French colonists and local populations led to cultural exchange, with the transmission of ideas, customs, and languages.
Negative Impacts:
- Exploitation of Resources: French colonialism was primarily driven by economic interests, leading to the exploitation of natural resources and the subjugation of local populations.
- Political and Social Disruption: The imposition of French laws and administration often disrupted traditional social structures and political systems, leading to resentment and resistance.
- Forced Labor and Slavery: The French utilized forced labor and slavery in their colonies, particularly in the Caribbean, to maximize profits from plantations.
The Decolonization Process:
The 20th century witnessed the dismantling of the French colonial empire. Following World War II, a wave of decolonization swept across the globe, fueled by nationalist movements and the changing political landscape. Many French colonies gained independence, leading to the redrawing of the colonial map.
Understanding the Map’s Significance:
The map of French colonies serves as a powerful tool for understanding the past and its enduring impact on the present. It allows us to:
- Visualize the Scope of Colonialism: The map provides a clear visual representation of the extent of French influence, highlighting its global reach.
- Analyze the Dynamics of Power: By studying the map, we can gain insights into the power dynamics between colonizers and colonized populations.
- Recognize the Consequences of Colonialism: The map serves as a reminder of the lasting consequences of French colonialism, including political, economic, and social structures that persist today.
FAQs about the Map of French Colonies:
Q: What was the largest French colony?
A: Algeria was the largest French colony in terms of land area, encompassing a vast region in North Africa.
Q: When did France lose its colonies?
A: The process of decolonization began after World War II and continued throughout the 20th century. Most French colonies gained independence between the 1950s and the 1970s.
Q: What are the lasting impacts of French colonialism?
A: The legacy of French colonialism is complex and multifaceted. It has influenced the languages, cultures, and political systems of many former colonies. The economic disparities and social inequalities that persist in many post-colonial societies can be traced back to the colonial era.
Q: How does the map help us understand French colonialism?
A: The map provides a visual representation of the extent of French influence and the diversity of regions under their control. It allows us to analyze the dynamics of power, the economic motivations behind colonialism, and the consequences of colonization.
Tips for Studying the Map of French Colonies:
- Focus on Regional Differences: Pay attention to the different types of colonies and their unique characteristics. For example, the Caribbean colonies were primarily agricultural, while the African colonies were more diverse in terms of economic activities.
- Consider the Timeline: Track the evolution of the French colonial map over time, noting the periods of expansion, consolidation, and decline.
- Connect the Map to Historical Events: Relate the map to key historical events, such as the French Revolution, World War I, and World War II, to understand how these events influenced the colonial landscape.
Conclusion:
The map of French colonies is a powerful tool for understanding the complex history of colonialism. It provides a visual record of the extent of French influence and the lasting impact of their presence on the world. By studying the map, we can gain insights into the dynamics of power, the economic motivations behind colonialism, and the consequences of colonization that continue to shape the global landscape today. The legacy of French colonialism remains a subject of ongoing debate and scrutiny, prompting us to reflect on the complexities of history and the enduring impact of imperial ambitions.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Historical Journey: Mapping the French Colonial Legacy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!