Deciphering the Language of Learning: A Guide to Understanding MAP Test Scores
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Learning: A Guide to Understanding MAP Test Scores
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Learning: A Guide to Understanding MAP Test Scores. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Learning: A Guide to Understanding MAP Test Scores
The Measures of Academic Progress (MAP) tests are a valuable tool for educators and parents to assess student learning and track academic growth. However, navigating the complex world of MAP scores can be daunting. This comprehensive guide will provide a clear and informative breakdown of how to interpret these scores, empowering you to understand their significance and utilize them effectively.
Understanding the Basics: The MAP Test and its Structure
The MAP test is a computer-adaptive assessment that measures students’ progress in reading, language usage, and mathematics. Unlike traditional standardized tests, MAP tests are not designed to compare students to a national average. Instead, they focus on individual student growth and provide a personalized snapshot of their strengths and areas for improvement.
The Key Components of MAP Scores:
MAP test scores are presented in three key components:
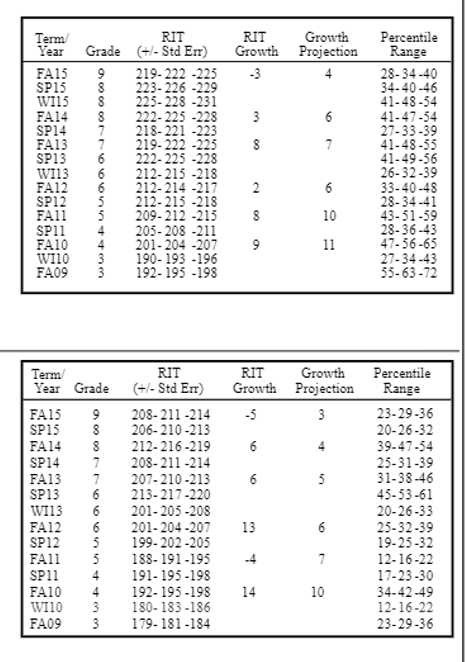
- RIT Score: The RIT score represents a student’s current academic level. It is a numerical score that reflects their performance on the test, with higher scores indicating a higher level of proficiency.
- Growth Percentile: This metric measures a student’s academic growth over time. It indicates their progress compared to other students who started at a similar RIT level. A higher growth percentile suggests a faster rate of learning.
- Stanine Score: The stanine score is a standardized score that ranges from 1 to 9. It helps compare a student’s performance to a national sample, with higher scores indicating stronger performance.
Deciphering the RIT Score: A Window into Academic Proficiency
The RIT score is the cornerstone of MAP test results. It provides a snapshot of a student’s current academic proficiency in a specific subject area. Here’s how to interpret RIT scores:
- Lower RIT Scores: Lower RIT scores indicate a lower level of proficiency in the tested subject. This might suggest a need for additional support or interventions.
- Higher RIT Scores: Higher RIT scores indicate a higher level of proficiency. These students may be ready for more challenging material or advanced learning opportunities.
- RIT Score Ranges: RIT scores are organized into ranges that correspond to different grade levels. This allows for a clear comparison of a student’s performance to their peers in the same grade.
Understanding Growth Percentile: Measuring the Pace of Learning
The growth percentile provides valuable insights into a student’s academic progress over time. It indicates how their learning trajectory compares to other students who started at a similar RIT level. Here’s a breakdown:
- High Growth Percentile: A high growth percentile indicates that a student is making significant progress in their learning. They are likely exceeding expectations and demonstrating a strong rate of growth.
- Average Growth Percentile: An average growth percentile suggests that a student is making typical progress in their learning. They are likely on track with their peers and demonstrating a steady rate of growth.
- Low Growth Percentile: A low growth percentile indicates that a student’s growth rate is below average. This might suggest areas where additional support or interventions are needed to accelerate their learning.
The Stanine Score: A Broader Perspective on Performance
The stanine score provides a broader perspective on a student’s performance by comparing it to a national sample. It allows educators and parents to understand how a student’s performance aligns with national norms. Here’s a breakdown:
- Stanine Scores 1-3: These scores indicate performance below the national average.
- Stanine Scores 4-6: These scores indicate performance at or near the national average.
- Stanine Scores 7-9: These scores indicate performance above the national average.
Interpreting MAP Scores: A Holistic Approach
It is crucial to interpret MAP scores holistically, considering all three components – RIT score, growth percentile, and stanine score – in conjunction with other available data, such as classroom performance and teacher observations. This comprehensive approach provides a more accurate and nuanced understanding of a student’s academic progress.
Utilizing MAP Scores: Empowering Educators and Parents
MAP scores are valuable tools that can be used to:
- Identify areas of strength and weakness: By analyzing the RIT scores across different subject areas, educators can identify areas where students excel and areas where they need additional support.
- Monitor student progress over time: Tracking changes in RIT scores and growth percentiles allows educators and parents to gauge a student’s learning trajectory and identify areas where interventions may be necessary.
- Tailor instruction to individual needs: MAP scores can help teachers differentiate instruction and provide individualized support to meet the unique needs of each student.
- Communicate student progress to parents: MAP scores can be used to provide parents with a clear and concise picture of their child’s academic performance and progress.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How often should students take the MAP test?
A: The frequency of MAP testing varies depending on the school and student’s grade level. Typically, students take the test two to three times per year to track their progress effectively.
Q: What are the implications of a low RIT score?
A: A low RIT score suggests that a student may need additional support or interventions to improve their proficiency in the tested subject. Educators may implement strategies such as individualized tutoring, small group instruction, or differentiated learning activities to address the student’s specific needs.
Q: What can parents do to support their child’s academic progress based on MAP scores?
A: Parents can use MAP scores to understand their child’s strengths and areas for improvement. They can work with their child on specific skills identified as needing improvement and provide a supportive learning environment at home. Open communication with teachers is crucial to understand how to best support their child’s academic growth.
Q: Can MAP scores be used to predict future academic success?
A: While MAP scores can provide insights into a student’s current academic performance, they are not a perfect predictor of future success. Other factors, such as motivation, work ethic, and life experiences, also play a significant role in a student’s overall academic trajectory.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing MAP Scores:
- Attend parent-teacher conferences: These meetings provide an opportunity to discuss your child’s MAP scores in detail with their teacher and gain valuable insights into their academic progress.
- Review your child’s MAP report: Take the time to carefully review the report and understand the different components of the scores. Discuss any questions or concerns you have with your child’s teacher.
- Focus on individual growth: Remember that MAP scores are designed to measure individual growth, not compare students to each other. Celebrate your child’s progress and support their continued learning.
- Use scores as a starting point: MAP scores can be a valuable tool for identifying areas for improvement, but they should not be the sole measure of your child’s academic success.
Conclusion: Empowering Students and Fostering Success
MAP test scores provide a valuable window into student learning and offer insights that can be used to empower educators and parents to support academic growth. By understanding the different components of these scores and utilizing them effectively, we can create a more personalized and effective learning environment for all students. Remember, MAP scores are not a definitive measure of a student’s potential but rather a tool to guide and support their academic journey.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Learning: A Guide to Understanding MAP Test Scores. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!