Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales
Maps are powerful tools that allow us to visualize and navigate the world around us. They compress vast distances and complex landscapes into manageable representations, making them indispensable for a multitude of purposes, from planning road trips to understanding global events. However, the true value of a map lies in its ability to accurately depict the real world, and this accuracy hinges on a critical element: the map scale.
What is a Map Scale?
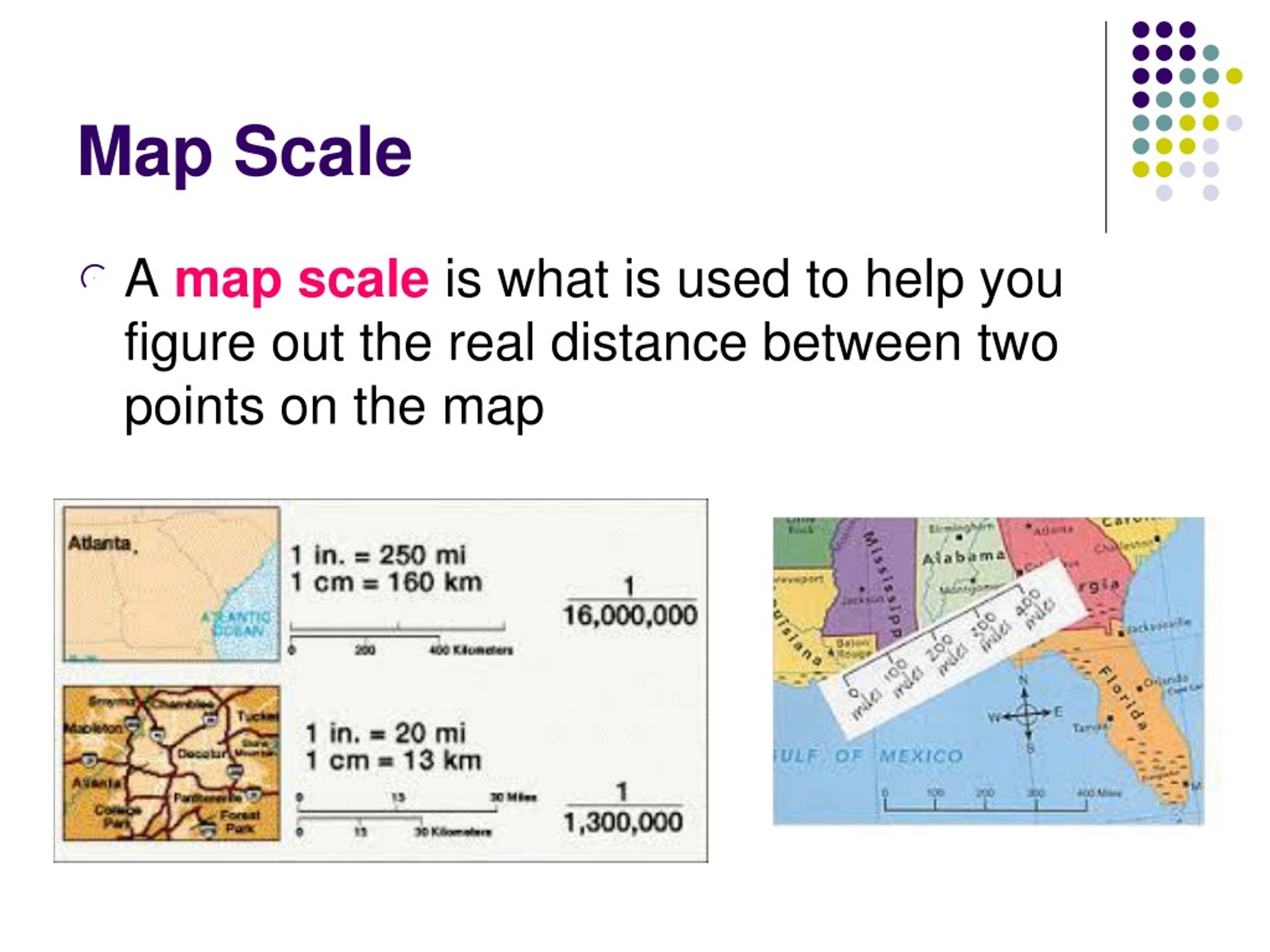
A map scale is a numerical ratio that represents the relationship between distances on a map and the corresponding distances on the ground. It provides a crucial key to interpreting the map, allowing users to translate the distances depicted on the map into real-world measurements.
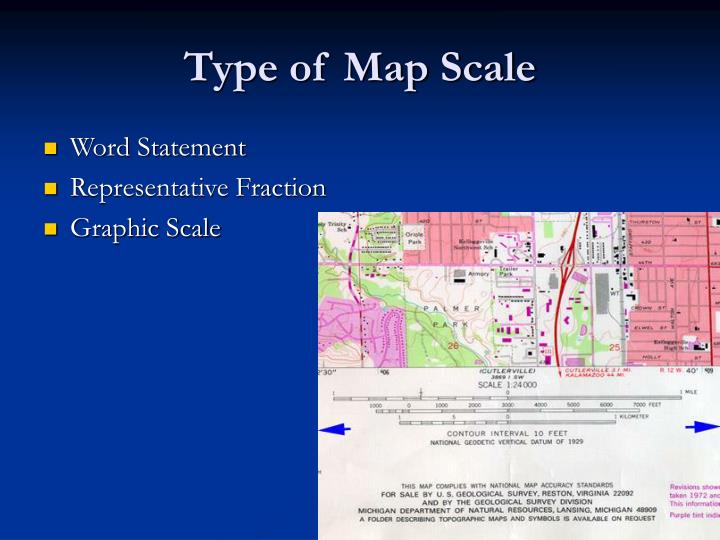
Types of Map Scales
Map scales are expressed in various forms, each offering a unique way to understand the relationship between the map and reality:
- Verbal Scale: This is the most straightforward way to express a map scale. It uses words to describe the ratio, such as "1 centimeter on the map represents 10 kilometers on the ground." This format is easy to understand but can be cumbersome for precise measurements.
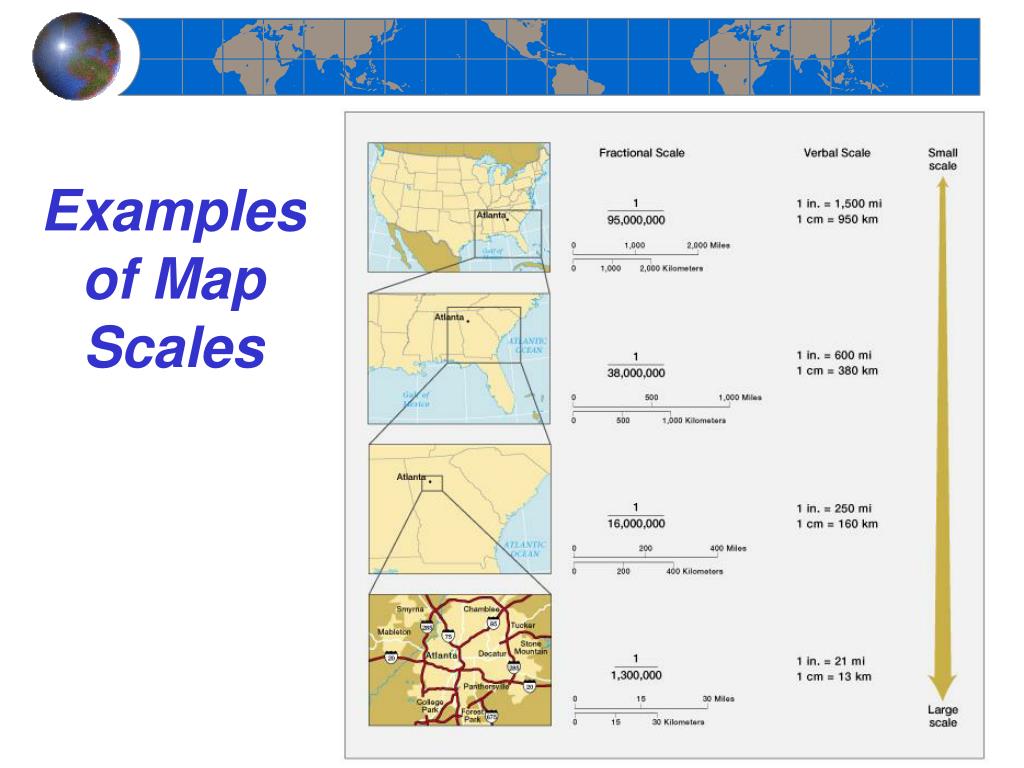
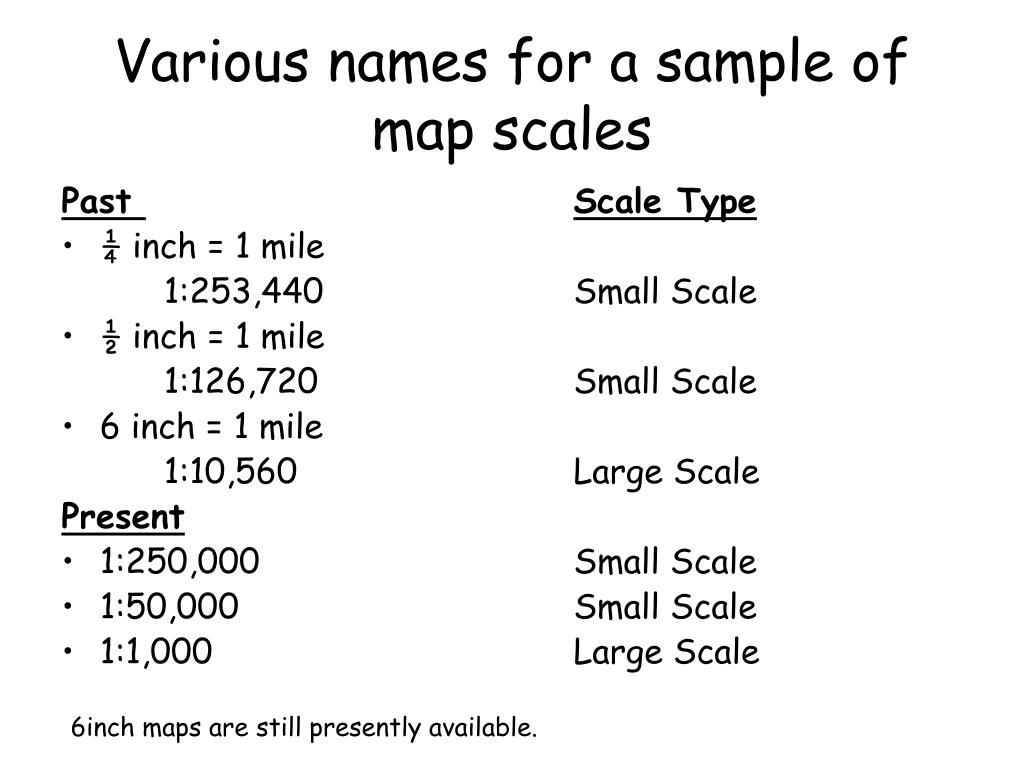
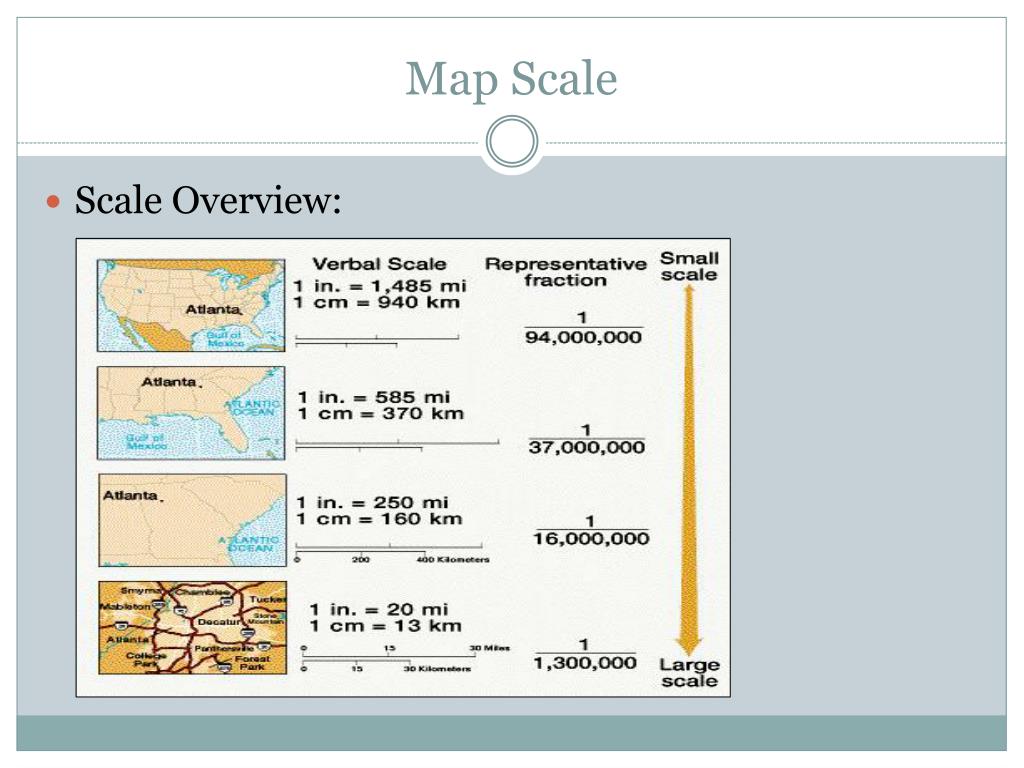
- Representative Fraction (RF): This scale uses a numerical ratio to express the relationship. For example, a scale of 1:100,000 indicates that one unit on the map represents 100,000 units on the ground. This format is widely used due to its clarity and precision.
- Graphic Scale: This scale uses a line segment divided into smaller units, each representing a specific distance on the ground. It allows for quick visual comparisons of distances on the map.
Understanding the Significance of Map Scale
The map scale is crucial for several reasons:
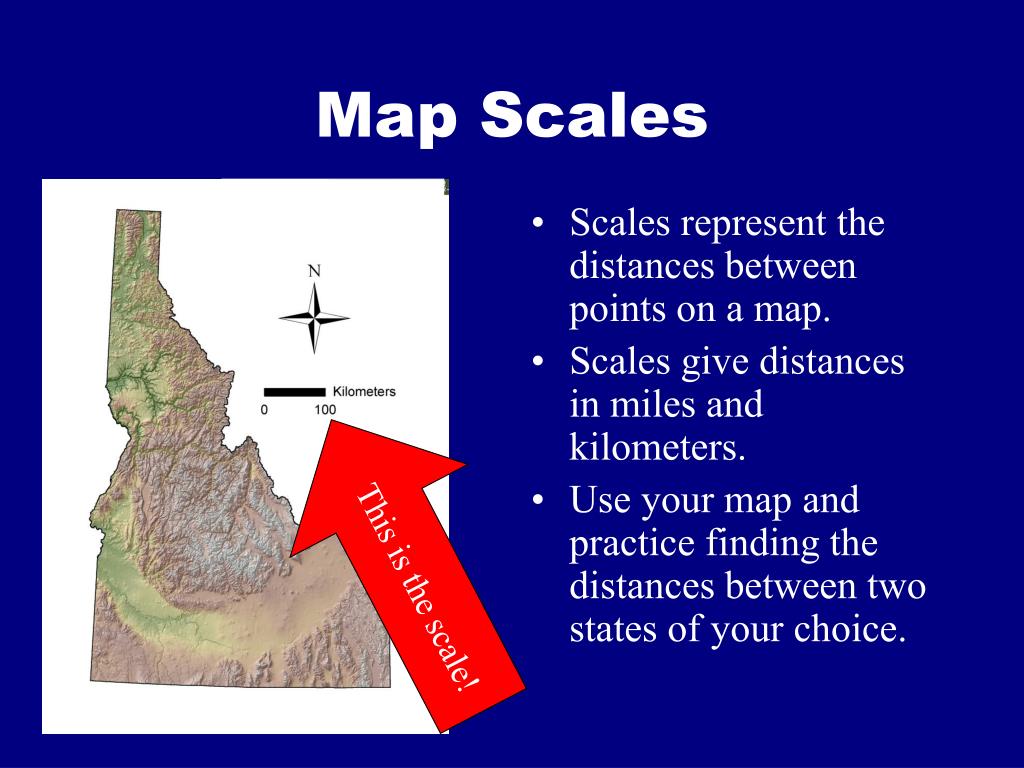
- Accurate Distance Measurement: It allows users to accurately determine distances between points on the map and translate them to real-world measurements. This is essential for planning journeys, calculating travel times, and understanding the spatial relationships between different locations.
- Interpreting Geographic Features: The scale determines the level of detail that can be displayed on a map. Larger scale maps (1:10,000 or larger) show greater detail, making them ideal for urban planning, site surveys, and detailed mapping of smaller areas. Smaller scale maps (1:1,000,000 or smaller) depict larger areas with less detail, suitable for regional planning, global analysis, and broad overviews.
- Comparing Maps: Understanding the scale of different maps allows for accurate comparisons of geographic features and their relative sizes. This is essential for analyzing spatial patterns, understanding the scale of environmental changes, and comparing the development of different regions.
Using Map Scales Effectively
To utilize map scales effectively, it is essential to:
- Identify the Scale: Always locate the map scale before interpreting any distances or features.
- Understand the Scale Units: Be aware of the units used for both the map and the ground distances (e.g., centimeters, meters, kilometers).
- Utilize Tools: Use rulers, compasses, and other tools to accurately measure distances on the map.
- Consider the Purpose: Choose a map with a scale appropriate for the intended purpose, whether it is for detailed planning or a general overview.
FAQs on Map Scales
Q: Why are there different map scales?
A: Different map scales are used to represent different levels of detail and geographic areas. Larger scale maps are used for detailed representations of smaller areas, while smaller scale maps provide a broader overview of larger regions.
Q: How do I calculate real-world distances from a map?
A: To calculate real-world distances, measure the distance on the map using a ruler, then multiply it by the scale factor. For example, if the map scale is 1:100,000 and the distance on the map is 5 centimeters, the real-world distance would be 5 cm x 100,000 = 500,000 centimeters or 5 kilometers.
Q: What happens if I use the wrong scale?
A: Using the wrong scale can lead to inaccurate distance measurements, misinterpretations of geographic features, and flawed planning decisions.
Q: Can I change the scale of a map?
A: While it is possible to digitally resize a map, this will not change the actual scale. Resizing a map only alters the visual representation, not the actual relationship between the map and the ground.
Tips for Understanding and Using Map Scales
- Practice Measuring: Regularly measure distances on maps using different scales to develop a sense of scale and improve accuracy.
- Compare Scales: Analyze maps with different scales to understand the differences in detail and representation.
- Utilize Online Tools: Several online tools can help calculate distances and convert between different map scales.
- Consult Professionals: If you are working with maps for specific purposes, consult with cartographers or other professionals for guidance on appropriate scales and techniques.
Conclusion
The map scale is a fundamental concept in cartography, providing a crucial link between the map and the real world. Understanding and utilizing map scales effectively is essential for accurate distance measurement, interpretation of geographic features, and informed decision-making. By mastering this essential skill, we can unlock the full potential of maps as powerful tools for exploration, analysis, and understanding our world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of Maps: Understanding Map Scales. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!