Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Military Maps
Related Articles: Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Military Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Military Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Military Maps

Military maps are not mere illustrations; they are powerful tools that translate the complexities of the terrain into a language understood by soldiers, commanders, and strategists. Their importance lies in their ability to provide a detailed and accurate representation of the landscape, enabling informed decision-making in diverse operational environments. This guide will delve into the intricacies of reading military maps, equipping readers with the knowledge to navigate, plan, and execute missions effectively.
Understanding the Foundation: Elements of a Military Map
Military maps are meticulously crafted, incorporating a diverse array of symbols and conventions to convey a wealth of information. The key elements include:
1. Map Sheet and Margin Information:
- Map Sheet Number: This unique identifier distinguishes each map sheet, facilitating organization and retrieval.
- Date of Survey and Revision: This indicates the map’s accuracy and relevance, highlighting any updates or changes made to the original survey.
- Map Series and Edition: This specifies the map’s purpose, scale, and version, aiding in selecting the appropriate map for a particular mission.
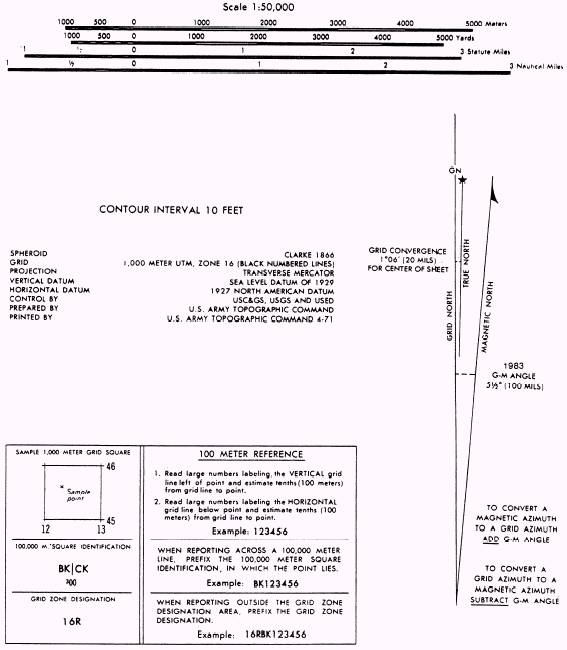
- Grid System: The grid system provides a precise coordinate reference for locating points on the map.
- Legend: The legend explains the meaning of symbols used on the map, ensuring clarity in interpreting features and objects.
- Marginal Information: This includes details such as elevation data, magnetic declination, and map projection information, crucial for accurate calculations and navigation.
2. Topographic Features:
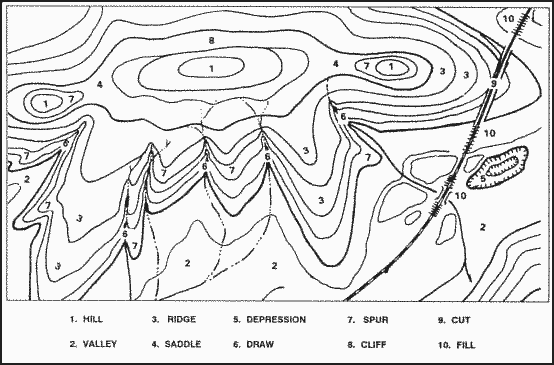
- Relief: The map depicts the elevation and shape of the terrain using contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation.
- Hydrography: Water features like rivers, lakes, and streams are represented on the map, providing insights into water availability and potential obstacles.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation are indicated on the map, revealing potential cover and concealment opportunities.
- Cultural Features: Structures, roads, and settlements are depicted on the map, offering information about infrastructure and potential targets.
3. Military Symbols:
- Unit Symbols: These symbols represent different military units, such as infantry, armor, and artillery, aiding in understanding troop dispositions.
- Operational Symbols: These symbols indicate various military activities, including attacks, defenses, and logistical operations.
- Equipment Symbols: These symbols depict specific military equipment, such as tanks, aircraft, and artillery pieces.
- Tactical Symbols: These symbols represent tactical elements like fire support areas, observation posts, and communication nodes.
Mastering the Art: Reading a Military Map
Reading a military map involves a systematic approach, ensuring accurate interpretation and efficient utilization of the information presented.
1. Orientation and Scale:
- Orientation: The first step is to orient the map with the terrain, aligning the map’s north with the actual north direction. This can be achieved using a compass or by identifying prominent features on the map and in the field.
- Scale: Understanding the map’s scale is crucial for accurate distance measurements. Military maps typically use a representative fraction (RF), which indicates the ratio between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
2. Interpreting Contour Lines:
- Contour Intervals: The vertical distance between contour lines is known as the contour interval. This interval determines the degree of detail in the map’s representation of elevation changes.
- Contour Patterns: The spacing and shape of contour lines reveal the terrain’s slope and features. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentle slopes.
3. Identifying Features:
- Relief: Contour lines, spot elevations, and hachures are used to represent the terrain’s elevation and shape.
- Hydrography: Water features are depicted using blue lines and symbols. Rivers, lakes, and streams are important for understanding water availability, potential obstacles, and potential routes.
- Vegetation: Green symbols and patterns represent different types of vegetation, providing insights into potential cover and concealment opportunities.
- Cultural Features: Black symbols and lines represent man-made features such as roads, buildings, and communication infrastructure.
4. Using the Grid System:
- Grid Coordinates: Military maps use a grid system to provide precise location references. Each grid square is identified by a unique combination of letters and numbers, enabling accurate targeting and navigation.
- Grid References: To locate a specific point on the map, a six-digit grid reference is used, consisting of two letters and four numbers. The first two digits represent the grid square, while the next two digits represent the horizontal position within the square, and the final two digits represent the vertical position.
5. Understanding Military Symbols:
- Unit Symbols: Different units are represented by unique symbols, allowing for quick identification of troop dispositions and capabilities.
- Operational Symbols: These symbols depict military activities, such as attacks, defenses, and logistical operations, providing a clear understanding of the operational context.
- Equipment Symbols: Symbols represent specific military equipment, aiding in assessing the capabilities and vulnerabilities of opposing forces.
- Tactical Symbols: These symbols represent tactical elements like fire support areas, observation posts, and communication nodes, essential for planning and executing operations.
The Importance of Military Maps: Applications and Benefits
Military maps are indispensable tools for a wide range of military operations, enabling effective planning, execution, and coordination.
1. Navigation and Orientation:
- Terrain Awareness: Maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the terrain, enabling soldiers to navigate effectively and avoid potential hazards.
- Route Planning: Military maps facilitate route planning, ensuring the selection of optimal paths considering terrain, obstacles, and enemy positions.
- Orientation: Maps aid in orienting soldiers in unfamiliar environments, ensuring they remain aware of their location and surroundings.
2. Planning and Execution:
- Situational Awareness: Maps provide a clear picture of the battlefield, enabling commanders to assess the situation and make informed decisions.
- Target Identification: Maps aid in identifying potential targets and assessing their vulnerabilities, contributing to effective targeting strategies.
- Mission Planning: Maps are essential for planning missions, ensuring the allocation of resources, coordination of units, and effective execution of tasks.
3. Communication and Coordination:
- Common Ground: Military maps provide a common language for communication and coordination between units, ensuring everyone shares the same understanding of the operational environment.
- Shared Information: Maps enable the sharing of information and intelligence, facilitating collaboration and synchronized efforts.
- Effective Command and Control: Maps support effective command and control, allowing commanders to monitor the situation, issue orders, and track the progress of operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Military Maps:
1. What are the different types of military maps?
Military maps come in various types, each tailored to specific purposes and scales. Some common types include:
- Tactical Maps: Designed for tactical operations at the battalion and company levels, typically at a scale of 1:50,000 or 1:25,000.
- Operational Maps: Used for planning and conducting operations at the brigade and division levels, typically at a scale of 1:100,000 or 1:250,000.
- Strategic Maps: Employed for planning and conducting operations at the corps and army levels, typically at a scale of 1:500,000 or 1:1,000,000.
- Air Navigation Charts: Designed for aerial navigation, providing information about terrain, airspace, and navigational aids.
2. How are military maps updated?
Military maps are constantly updated to reflect changes in the terrain, infrastructure, and operational environment. Updates are typically made through:
- Reconnaissance: Military units conduct reconnaissance missions to gather data about changes in the terrain and update maps accordingly.
- Aerial Photography: Aerial photographs provide a comprehensive overview of the terrain, enabling accurate updates to map features.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellite imagery offers high-resolution data about the terrain, facilitating the identification of changes and updates to maps.
3. What are the benefits of using digital military maps?
Digital military maps offer several advantages over traditional paper maps:
- Real-time Updates: Digital maps can be updated in real-time, providing soldiers with the most current information.
- Enhanced Functionality: Digital maps offer advanced functionality, such as route planning, terrain analysis, and target identification.
- Portability and Accessibility: Digital maps are easily portable and accessible on a wide range of devices, enabling soldiers to access information from anywhere.
Tips for Reading Military Maps Effectively:
- Practice Makes Perfect: Regularly practice reading and interpreting military maps to develop proficiency and speed.
- Use a Compass: A compass is essential for orienting the map with the terrain, ensuring accurate navigation.
- Identify Key Features: Focus on identifying prominent features on the map and matching them with the corresponding features in the field.
- Understand the Legend: Thoroughly review the map legend to understand the meaning of symbols and conventions used.
- Use a Protractor: A protractor is helpful for measuring angles and determining bearings, essential for accurate navigation and targeting.
- Work with a Team: Collaborate with others to interpret maps and share information, ensuring a common understanding of the operational environment.
Conclusion:
Military maps are vital tools for military operations, enabling effective navigation, planning, execution, and coordination. By understanding the elements of a military map, mastering the art of reading it, and utilizing its information effectively, soldiers and commanders can gain a decisive advantage in any operational environment. Continued practice and a commitment to continuous learning are essential for maximizing the utility of these powerful tools, ensuring success in the challenging and dynamic world of military operations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Reading Military Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!