Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding Vegetation Zone Maps: A Glimpse into Earth’s Green Tapestry
- 3.2 The Genesis of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Journey of Exploration and Mapping
- 3.3 The Unfolding Applications of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Multifaceted Tool for Research and Management
- 3.4 The Importance of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Cornerstone for Sustainable Development
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions About Vegetation Zone Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Using Vegetation Zone Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Managing Earth’s Ecosystems
- 4 Closure
Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

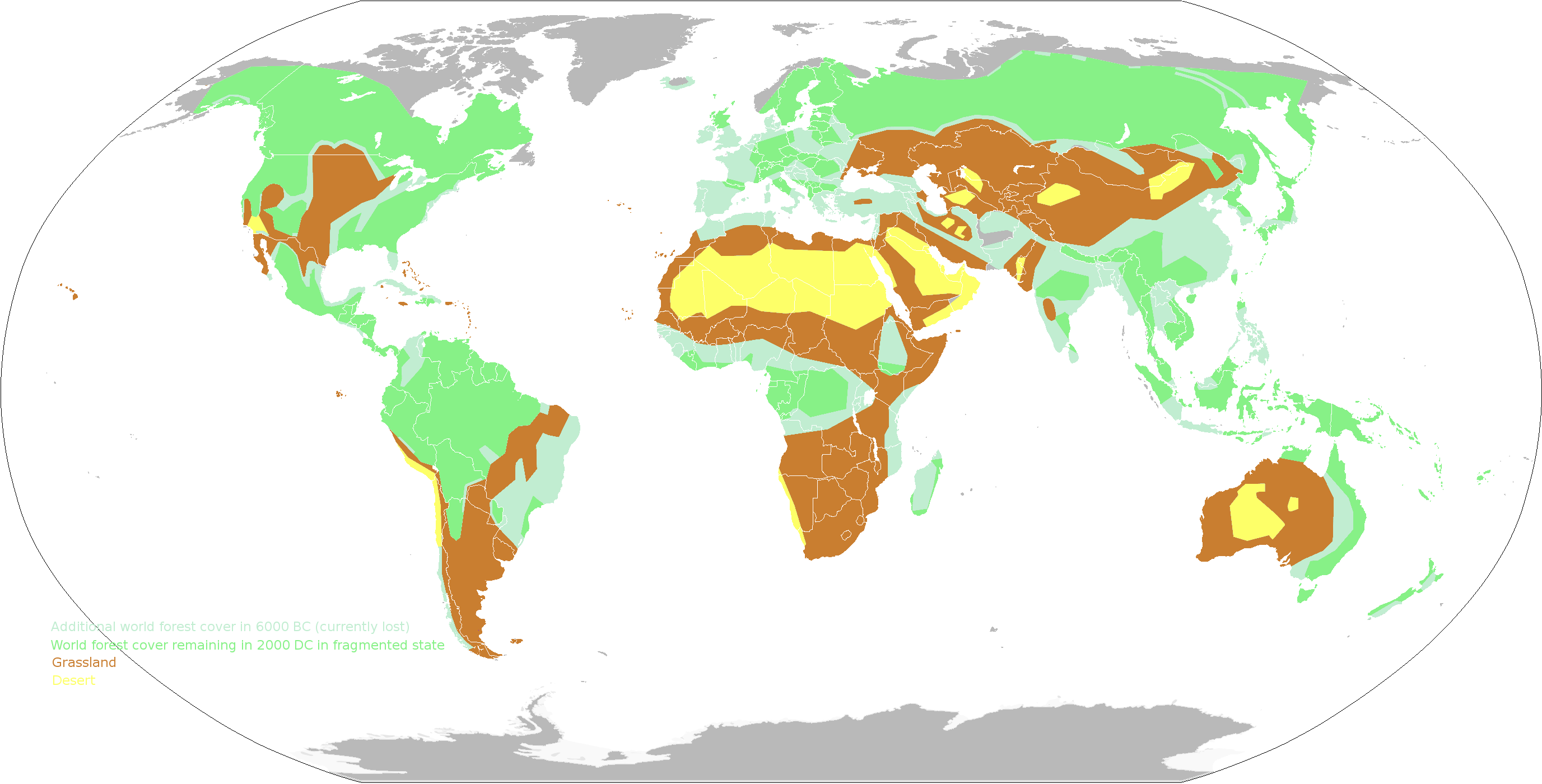
Vegetation zone maps, also known as biogeographic maps, are essential tools for understanding and managing the Earth’s diverse ecosystems. These maps visually represent the distribution of different plant communities across the globe, providing invaluable insights into the intricate interplay between climate, geography, and plant life. This comprehensive guide explores the nuances of vegetation zone maps, their creation, applications, and significance in various fields.
Understanding Vegetation Zone Maps: A Glimpse into Earth’s Green Tapestry
Vegetation zone maps are graphical representations that depict the spatial distribution of distinct plant communities based on their dominant species, growth forms, and overall structure. They offer a simplified yet powerful depiction of the complex tapestry of vegetation that covers the Earth’s surface. Each zone is characterized by specific climate conditions, soil types, and ecological factors that influence the types of plants that thrive within its boundaries.
Key Elements of Vegetation Zone Maps:
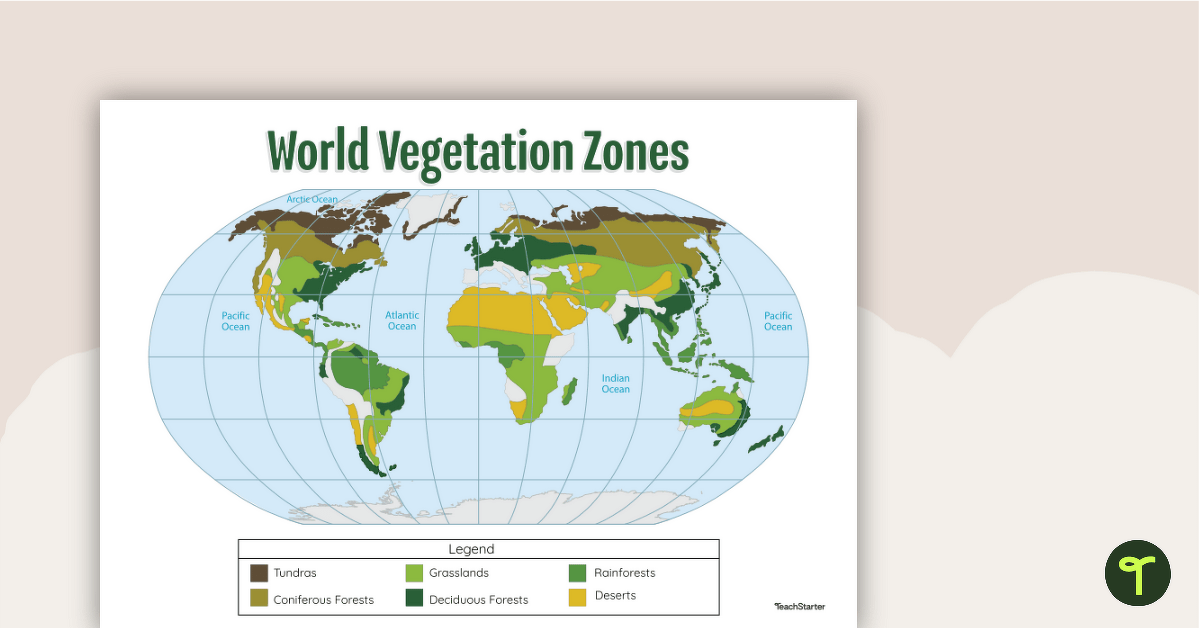
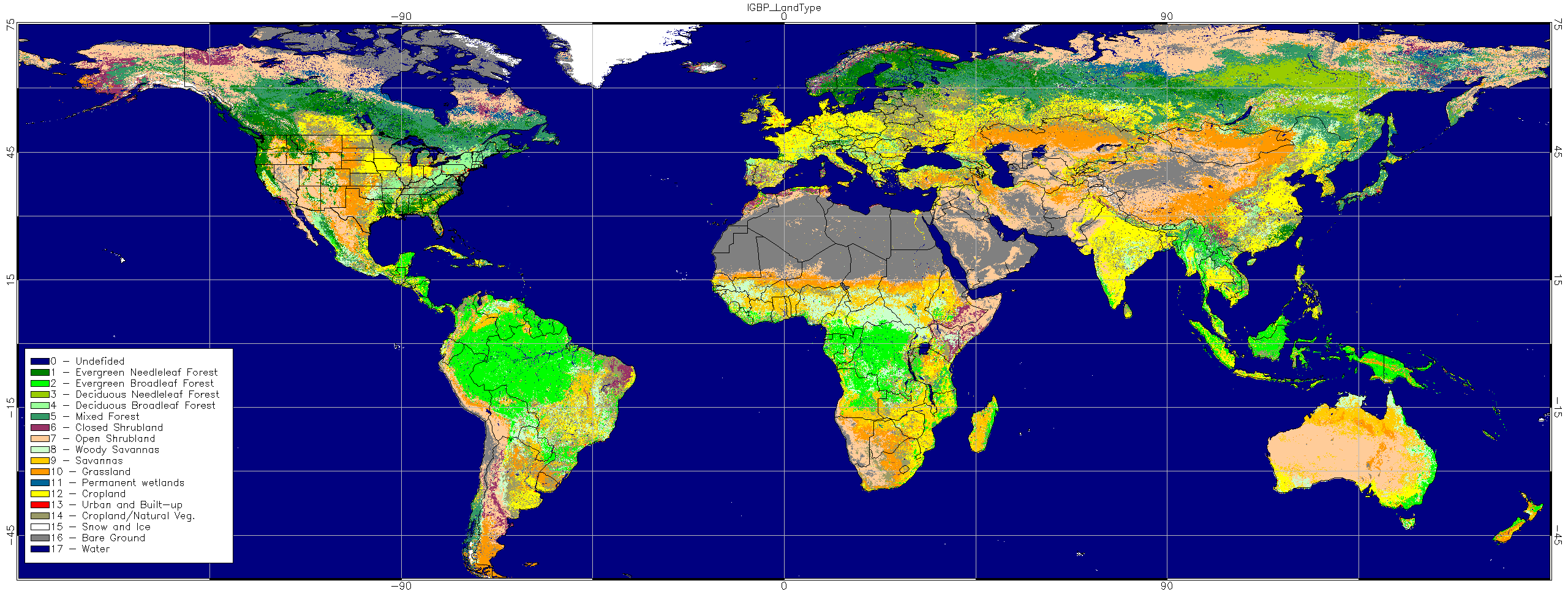
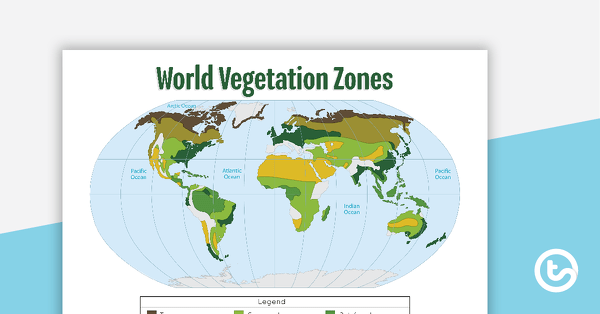
- Vegetation Types: These maps classify plant communities into broad categories, such as forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras, and wetlands. Each category is further subdivided based on specific species composition and ecological characteristics.
- Geographic Boundaries: Vegetation zones are delineated by distinct boundaries, often coinciding with significant changes in climate, elevation, or soil conditions. These boundaries are not always sharp and can exhibit gradual transitions between zones.
- Spatial Distribution: The maps depict the spatial distribution of different vegetation types across the globe, highlighting areas with similar plant communities. This spatial information is crucial for understanding the global patterns of biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Climate and Environmental Factors: Vegetation zone maps incorporate information about climate variables such as temperature, precipitation, and seasonality. These factors play a crucial role in determining the type and distribution of plant communities.
- Soil and Topography: Soil characteristics, including nutrient content, drainage, and texture, also influence the types of vegetation that can thrive in a particular region. Topographic features such as elevation and slope can further modify vegetation patterns.
The Genesis of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Journey of Exploration and Mapping
The development of vegetation zone maps has been a gradual process, driven by scientific curiosity and the need to understand the complex relationships between plants and their environment. Early attempts at mapping vegetation relied on qualitative observations and descriptions, but advancements in technology and ecological knowledge have led to more sophisticated and accurate maps.
Key Milestones in Vegetation Zone Mapping:
- Early Exploration and Description: Explorers and naturalists of the 18th and 19th centuries documented plant communities based on their observations and collected specimens. These early descriptions laid the foundation for later mapping efforts.
- Development of Biogeographical Concepts: The emergence of biogeography as a scientific discipline in the late 19th century provided a theoretical framework for understanding the distribution of plant and animal life. This led to the development of the first formal vegetation zone maps.
- Advancements in Remote Sensing and GIS: The advent of remote sensing technologies, particularly satellite imagery, revolutionized vegetation mapping. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provided powerful tools for analyzing and visualizing spatial data, enabling the creation of detailed and accurate maps.
- Integration of Ecological Data: Modern vegetation zone maps are increasingly incorporating data from ecological surveys, climate models, and soil databases. This integrated approach provides a more comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence vegetation patterns.
The Unfolding Applications of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Multifaceted Tool for Research and Management
Vegetation zone maps are not merely static representations of plant communities; they serve as vital tools for various disciplines, offering valuable insights and supporting crucial decision-making processes.
Applications in Research and Conservation:
- Biodiversity Assessment: Vegetation zone maps provide a framework for understanding the distribution of biodiversity across different ecosystems. They help identify areas with high species richness and endemism, guiding conservation efforts and habitat protection.
- Ecosystem Services Mapping: These maps are essential for mapping and quantifying ecosystem services, such as carbon sequestration, water filtration, and pollination. This information is crucial for sustainable land management and policy decisions.
- Climate Change Impacts: Vegetation zone maps can be used to model the potential impacts of climate change on vegetation distribution, helping predict shifts in plant communities and their associated ecosystem services.
- Species Distribution Modeling: The maps provide valuable data for species distribution modeling, predicting the potential range of species based on their ecological requirements and climate conditions.
Applications in Management and Planning:
- Land Use Planning: Vegetation zone maps are essential for land use planning, helping identify areas suitable for different land uses, such as agriculture, forestry, and urban development.
- Natural Resource Management: These maps inform the management of natural resources, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, ensuring sustainable utilization and conservation.
- Disaster Risk Assessment: Vegetation zone maps can be used to assess the risk of natural disasters, such as wildfires and floods, by identifying areas with specific vegetation types that are susceptible to these hazards.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: These maps are valuable tools for assessing the environmental impacts of development projects, helping to identify potential risks and mitigation strategies.
The Importance of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Cornerstone for Sustainable Development
Vegetation zone maps are indispensable tools for understanding and managing the Earth’s ecosystems. They provide a framework for:
- Understanding Biodiversity: These maps are crucial for understanding the distribution and diversity of plant life across the globe, highlighting areas of high biodiversity and endemism.
- Assessing Ecosystem Services: They help quantify and map the crucial services provided by different ecosystems, such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and pollination.
- Managing Natural Resources: Vegetation zone maps inform sustainable resource management practices, ensuring the long-term health and productivity of forests, grasslands, and other ecosystems.
- Mitigating Climate Change: These maps play a vital role in understanding the potential impacts of climate change on vegetation distribution and in developing strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
- Supporting Sustainable Development: By providing a framework for understanding and managing the Earth’s ecosystems, vegetation zone maps contribute to sustainable development goals, ensuring the long-term well-being of both human societies and the natural environment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vegetation Zone Maps
1. What are the different types of vegetation zones?
Vegetation zones are broadly classified into major biomes, such as forests, grasslands, deserts, tundras, and wetlands. Each biome is further subdivided based on specific species composition, climate conditions, and ecological characteristics. For example, forests can be categorized into tropical rainforests, temperate deciduous forests, and boreal forests, each with distinct plant communities and environmental factors.
2. How are vegetation zone maps created?
Modern vegetation zone maps are created using a combination of data sources, including satellite imagery, ecological surveys, climate models, and soil databases. Remote sensing technologies, such as Landsat and MODIS, provide high-resolution imagery that allows for the identification and mapping of different vegetation types. GIS software is used to analyze and visualize this data, creating accurate and detailed maps.
3. What are the limitations of vegetation zone maps?
While vegetation zone maps provide valuable insights, they also have some limitations. They are often simplified representations of complex ecosystems, and the boundaries between zones can be gradual and variable. Additionally, maps may not capture the full diversity of plant communities within a given zone, and they may not accurately reflect the dynamic nature of vegetation change over time.
4. How can vegetation zone maps be used to address climate change?
Vegetation zone maps are crucial for understanding the potential impacts of climate change on vegetation distribution and for developing adaptation strategies. By analyzing historical and projected climate data, scientists can use these maps to predict shifts in vegetation zones and their associated ecosystem services. This information can guide conservation efforts, land management practices, and policy decisions aimed at mitigating the effects of climate change.
5. What are the future directions for vegetation zone mapping?
Future advancements in vegetation zone mapping will likely focus on:
- Integration of Big Data: Incorporating large datasets from various sources, including remote sensing, ecological surveys, and climate models, to create more comprehensive and accurate maps.
- Dynamic Modeling: Developing dynamic models that account for the temporal changes in vegetation patterns, capturing the effects of climate change, land use, and other disturbances.
- Participatory Mapping: Engaging local communities in mapping efforts to incorporate traditional ecological knowledge and to ensure that maps are relevant to local needs and priorities.
Tips for Using Vegetation Zone Maps
- Consider the scale of the map: Vegetation zone maps are available at various scales, ranging from global maps to regional and local maps. Choose a map with a scale appropriate for your specific needs and research objectives.
- Understand the map legend: Familiarize yourself with the legend of the map, which explains the symbols and colors used to represent different vegetation types.
- Interpret the boundaries: Recognize that the boundaries between vegetation zones are not always sharp and can exhibit gradual transitions.
- Combine data sources: Integrate vegetation zone maps with other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and land use data, for a more comprehensive understanding of the factors influencing vegetation patterns.
- Consider the temporal aspect: Vegetation zone maps are snapshots in time, and vegetation patterns can change over time due to natural disturbances, climate change, and human activities.
Conclusion: A Vital Tool for Understanding and Managing Earth’s Ecosystems
Vegetation zone maps are essential tools for understanding and managing the Earth’s diverse ecosystems. They provide a visual representation of the distribution of plant communities, offering invaluable insights into the complex interplay between climate, geography, and plant life. These maps are used in a wide range of fields, including research, conservation, management, and planning, supporting crucial decision-making processes and contributing to sustainable development goals. As our understanding of ecosystems and their responses to global change continues to evolve, vegetation zone maps will play an increasingly important role in guiding our efforts to protect and manage the Earth’s valuable natural resources.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Realm of Vegetation Zone Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!