MAP Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price
Related Articles: MAP Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to MAP Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
MAP Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price

In the competitive landscape of retail, businesses are constantly seeking strategies to optimize pricing and maintain profitability. One such strategy, often employed by manufacturers to control the retail price of their products, is Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP), commonly referred to as MAP pricing.
What is MAP Pricing?
MAP pricing, a common practice across various industries, is a strategy where a manufacturer sets a minimum price that retailers must adhere to when selling their products. This minimum price serves as a guideline for retailers, ensuring that products are not sold below a certain threshold. While retailers are free to set prices higher than the MAP, selling below it is strictly prohibited.
Why Do Manufacturers Implement MAP Pricing?
The implementation of MAP pricing stems from a manufacturer’s desire to maintain brand value and protect their profit margins. Several key reasons drive this practice:
- Brand Image and Value: Consistent pricing across different retailers helps maintain a uniform brand image and perception of value. Selling products at significantly lower prices can devalue the brand in the eyes of consumers, leading to a negative impact on sales and brand loyalty.
- Price Competition Control: MAP pricing prevents retailers from engaging in cutthroat price wars, which can erode profit margins for both retailers and manufacturers. By setting a minimum price, manufacturers ensure that retailers remain competitive without resorting to unsustainable discounting strategies.
- Channel Management: MAP pricing helps manufacturers manage their distribution channels effectively. By setting a minimum price, they can incentivize retailers to focus on providing value-added services and a positive customer experience rather than solely competing on price.
- Product Differentiation: MAP pricing allows manufacturers to differentiate their products from competitors, particularly in markets with similar offerings. By maintaining a minimum price, they can position their products as premium or high-quality, even if the actual cost difference is minimal.
Benefits of MAP Pricing for Manufacturers:
- Increased Profitability: MAP pricing directly contributes to increased profitability by ensuring that retailers sell products at a price that covers the manufacturer’s costs and provides a reasonable margin.
- Improved Brand Image: Consistency in pricing across different retailers helps maintain a premium brand image and a perception of quality, which can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty.
- Reduced Channel Conflicts: MAP pricing helps mitigate conflicts between manufacturers and retailers by ensuring that all parties are working towards a common goal of maintaining a healthy profit margin and brand value.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: By encouraging retailers to focus on providing value-added services and a positive customer experience, MAP pricing indirectly benefits customers.
Benefits of MAP Pricing for Retailers:
- Reduced Price Competition: MAP pricing removes the pressure to engage in cutthroat price wars, allowing retailers to focus on providing value-added services, building customer relationships, and creating a positive shopping experience.
- Improved Profit Margins: MAP pricing ensures that retailers are not forced to sell products at unsustainable prices, allowing them to maintain healthy profit margins.
- Simplified Pricing Strategies: MAP pricing simplifies pricing decisions for retailers, eliminating the need to constantly monitor competitor prices and adjust their own pricing strategies.
- Access to Exclusive Products: MAP pricing can provide retailers with access to exclusive products that are not available to competitors, giving them a competitive advantage in the market.
Challenges of Implementing MAP Pricing:
While MAP pricing offers numerous benefits, it also presents certain challenges:
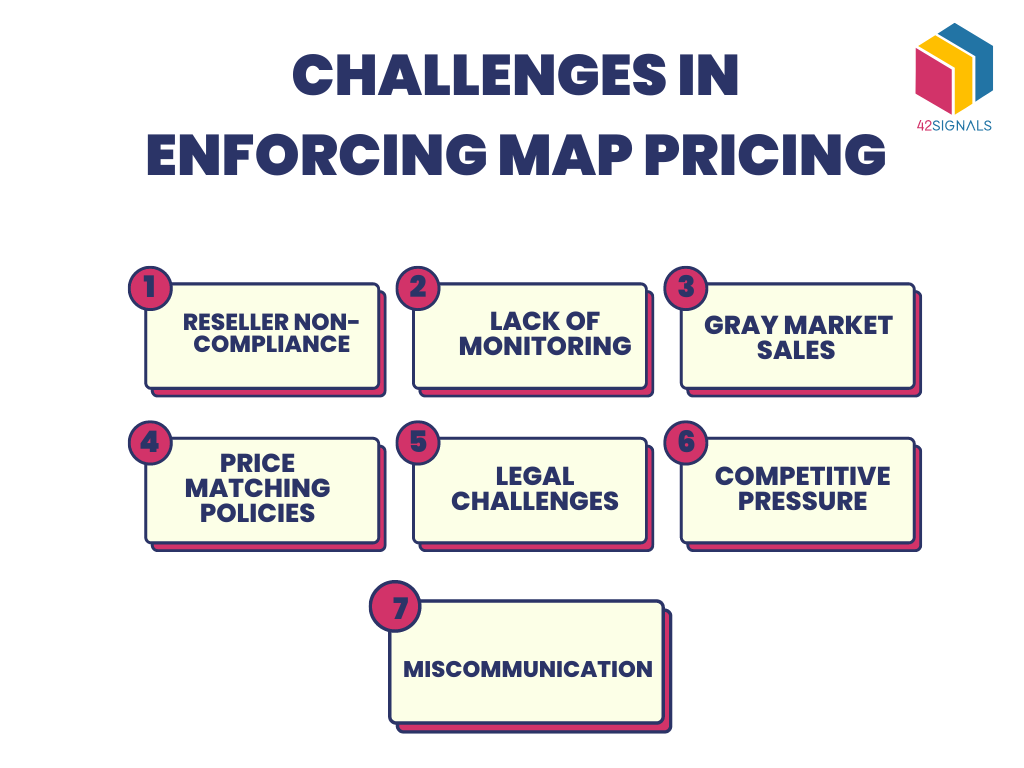
- Enforcement: Ensuring compliance with MAP pricing policies can be challenging, as retailers may be tempted to sell products below the minimum price to gain a short-term advantage. Manufacturers must actively monitor retail pricing and enforce their policies to maintain compliance.
- Retailer Resistance: Some retailers may resist MAP pricing policies, viewing them as an infringement on their pricing autonomy. Manufacturers must carefully communicate the benefits of MAP pricing to retailers and address their concerns to foster cooperation.
- Legal Considerations: MAP pricing policies must comply with antitrust laws and regulations. Manufacturers must carefully structure their MAP policies to avoid legal issues.
- Flexibility Limitations: MAP pricing can limit retailers’ flexibility in adjusting prices based on market conditions or promotions. This can be a challenge in dynamic markets where prices fluctuate frequently.
FAQs about MAP Pricing:
1. Is MAP Pricing Legal?
Yes, MAP pricing is generally legal in the United States, but it must comply with antitrust laws and regulations. Manufacturers must carefully structure their MAP policies to avoid legal issues.
2. How is MAP Pricing Enforced?
Manufacturers typically enforce MAP pricing through a combination of monitoring, communication, and enforcement actions. They may use software to monitor online pricing, contact retailers directly to address violations, and take legal action if necessary.
3. Can Retailers Sell Products Below MAP?
No, retailers are generally prohibited from selling products below the MAP set by the manufacturer. Violations of MAP pricing policies can result in various consequences, such as termination of distribution agreements or legal action.
4. Does MAP Pricing Apply to All Products?
Not all products are subject to MAP pricing. Manufacturers typically implement MAP pricing for products that are considered premium or high-value, where consistent pricing is essential to maintain brand image and value.
5. How Does MAP Pricing Affect Consumers?
MAP pricing can benefit consumers by ensuring that they are not paying inflated prices for products. It also helps maintain a consistent level of quality and service across different retailers.
Tips for Implementing MAP Pricing:
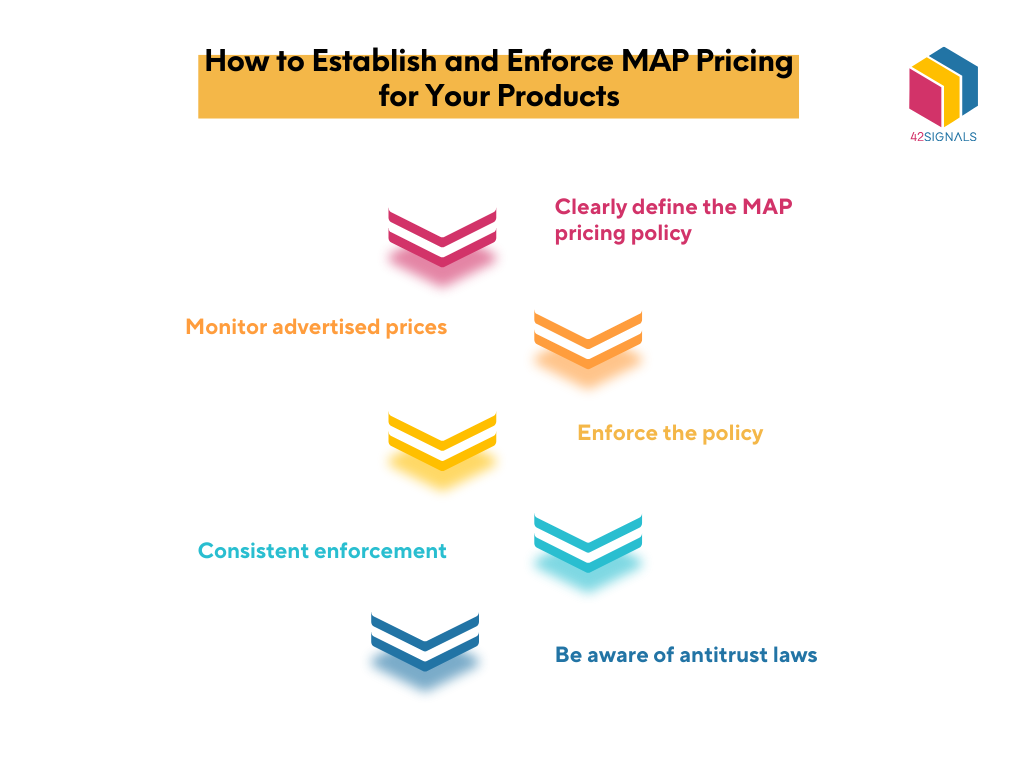
- Clearly Communicate Your MAP Policy: Ensure that your MAP policy is clearly communicated to all retailers, including the minimum price, the consequences of violating the policy, and the methods for monitoring compliance.
- Provide Incentives for Compliance: Offer incentives to retailers for adhering to your MAP policy, such as exclusive product offerings, marketing support, or loyalty programs.
- Monitor Retail Pricing Regularly: Use software or other methods to monitor retail pricing and identify any violations of your MAP policy promptly.
- Address Violations Promptly: Respond to violations of your MAP policy quickly and decisively, taking appropriate action to ensure compliance.
- Stay Informed about Legal Considerations: Consult with legal counsel to ensure that your MAP policy complies with antitrust laws and regulations.
Conclusion:
MAP pricing, when implemented strategically and ethically, can be a valuable tool for manufacturers and retailers alike. It helps maintain brand value, control price competition, manage distribution channels effectively, and ultimately contribute to a more stable and profitable retail environment. By understanding the benefits and challenges of MAP pricing, businesses can make informed decisions about whether this strategy is right for them and implement it effectively to achieve their desired outcomes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into MAP Pricing: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!