Mapping the Melodies of America: A Comprehensive Look at Dialects of American English
Related Articles: Mapping the Melodies of America: A Comprehensive Look at Dialects of American English
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Melodies of America: A Comprehensive Look at Dialects of American English. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Melodies of America: A Comprehensive Look at Dialects of American English
The United States, a nation forged from diverse origins, possesses a linguistic tapestry as vibrant and multifaceted as its cultural landscape. This tapestry is woven from the threads of regional dialects, unique variations of American English that reflect the historical, social, and geographical influences shaping each region. Understanding these dialects offers a fascinating glimpse into the evolution of the language and the cultural identity of its speakers.
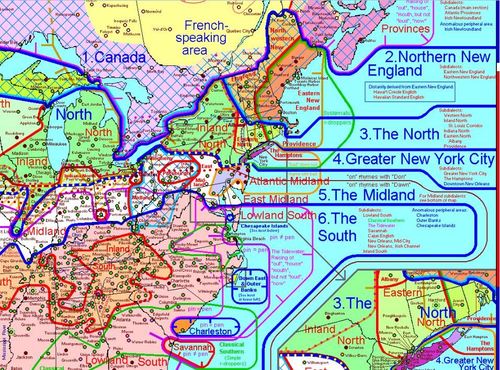
Delving into the Dialect Map: A Visual Representation of Linguistic Diversity
A dialect map, also known as an isogloss map, serves as a visual guide to the geographical distribution of linguistic features across the United States. These maps, often based on extensive linguistic surveys and data analysis, highlight the areas where specific pronunciations, vocabulary, grammar, and even intonation patterns prevail. They offer a compelling visual representation of the rich linguistic diversity that characterizes American English.
Understanding the Dynamics of Dialect Formation
Several factors contribute to the emergence and evolution of regional dialects:
- Migration Patterns: The initial settlement of the United States by immigrants from various parts of the world laid the foundation for distinct regional dialects. Early settlers brought their own linguistic traditions, which gradually blended and evolved over time, resulting in regional variations.
- Geographical Isolation: Physical barriers, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts, often acted as natural boundaries, limiting communication and fostering the development of unique linguistic features within isolated communities.
- Social and Economic Factors: The social and economic landscape of a region also plays a significant role in shaping its dialect. Urban centers, with their diverse populations and rapid pace of change, tend to exhibit more rapid linguistic evolution than rural areas.
- Linguistic Contact: Interactions between speakers of different dialects can lead to the adoption of new features and the modification of existing ones. This phenomenon, known as language contact, is particularly evident in areas where different dialect groups come into contact, such as major cities and urban centers.
Key Features Defining Regional Dialects
While the specific features of each dialect are numerous and varied, several key elements contribute to their distinctiveness:
- Pronunciation: Differences in pronunciation are perhaps the most readily recognizable feature of regional dialects. For example, the "r" sound in words like "car" and "bird" is often pronounced differently in various regions, with some speakers dropping the sound altogether.
- Vocabulary: Regional dialects often feature unique vocabulary words or phrases, reflecting the specific experiences and cultural traditions of the region. For instance, the word "pop" for "soda" is common in the Midwest, while "soda" is more prevalent in the Northeast.
- Grammar: Regional dialects can also exhibit differences in grammatical structures. For instance, the use of double negatives, such as "I don’t have no money," is more common in some regions than others.
- Intonation: The way in which speakers use their voice to convey meaning, known as intonation, can also vary significantly across regions. For example, speakers in the South often employ a "drawl," a slower and more melodic speaking style.
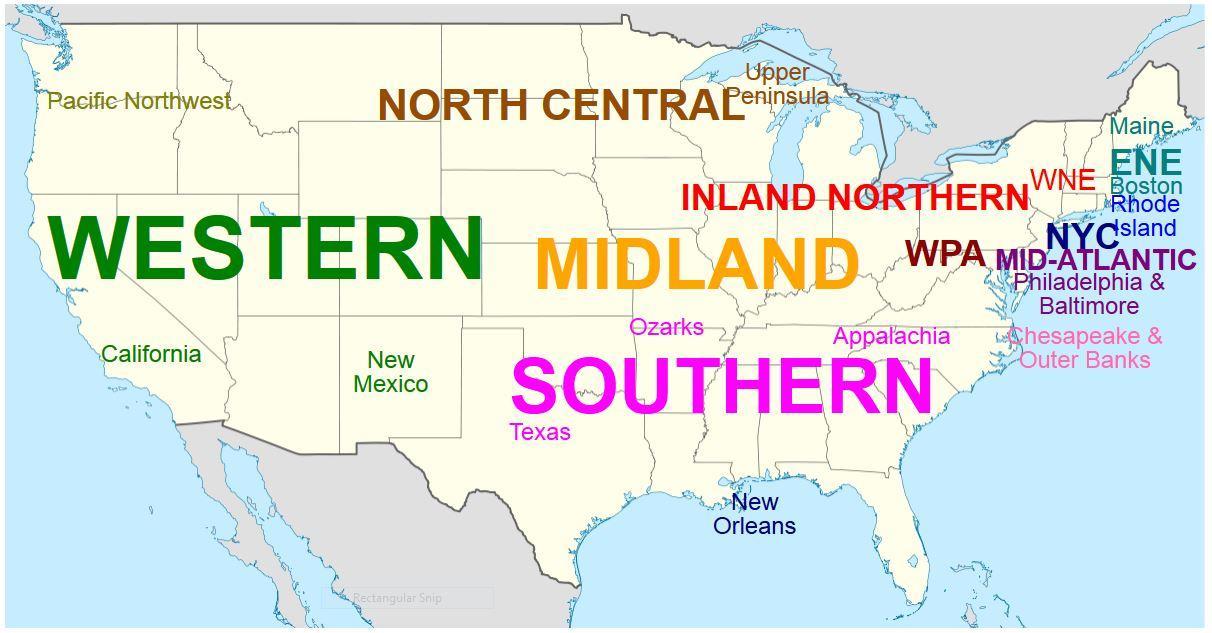
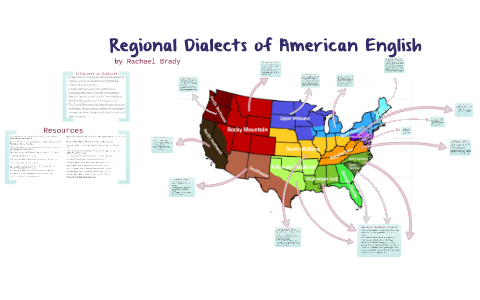
Exploring the Major Dialect Regions of the United States
While the boundaries between dialects are rarely clear-cut, linguistic scholars have identified several major dialect regions within the United States:
- New England: Characterized by a distinct "New England accent," with features like the dropping of the "r" sound in words like "car" and "bird," and the use of words like "wicked" meaning "very" or "extremely."
- Mid-Atlantic: Known for its "Mid-Atlantic accent," often associated with the speech of actors and newscasters, with features like the pronunciation of "r" as a retroflex sound, and the use of words like "hoagie" for "sub sandwich."
- Southern: Distinguished by a "Southern drawl," a slower and more melodic speaking style, with features like the pronunciation of "y’all" for "you all," and the use of words like "fixin’ to" meaning "about to."
- Midwestern: Characterized by a "Midwestern accent," often described as neutral or standard American English, with features like the pronunciation of "cot" and "caught" with the same vowel sound, and the use of words like "pop" for "soda."
- Western: Exhibiting a more diverse range of accents due to its relatively recent settlement and diverse population, with features like the pronunciation of "r" as a retroflex sound, and the use of words like "hella" meaning "very" or "extremely."
Beyond Regional Differences: The Influence of Social Factors
While geographical location plays a significant role in shaping dialects, social factors also exert a profound influence on language variation. These factors include:
- Social Class: Different social classes often exhibit distinct linguistic features, reflecting their socioeconomic status, education level, and cultural background.
- Ethnicity: Ethnic groups within the United States often maintain their own linguistic traditions, which can influence the dialects spoken by their members.
- Age: Generational differences in language use can also contribute to dialect variation. Younger speakers may adopt new words and phrases, while older speakers may retain traditional linguistic features.
The Importance of Understanding Dialect Variation
Understanding the diverse tapestry of American English dialects offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Communication: Awareness of regional differences in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar can improve communication between speakers from different regions.
- Cultural Appreciation: Dialects reflect the unique cultural heritage and identity of different communities, fostering a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of American culture.
- Linguistic Research: The study of dialects provides valuable insights into the evolution of language, the processes of language change, and the relationship between language and society.
Frequently Asked Questions about Dialects of American English
Q: Are all dialects of American English equally correct?
A: All dialects of American English are equally correct and valid forms of the language. There is no single "correct" dialect, and all dialects are equally capable of expressing thoughts and ideas effectively.
Q: Can I learn to speak a different dialect?
A: While it may be challenging to completely adopt a new dialect, it is possible to learn and incorporate features of another dialect into your own speech. Exposure to different dialects through media, travel, or interaction with speakers of other dialects can help you develop an understanding and appreciation for linguistic diversity.
Q: Does speaking a particular dialect affect my social standing?
A: In some contexts, certain dialects may be associated with specific social groups or stereotypes. However, it is important to remember that all dialects are equally valid and should be respected. Focusing on clear and effective communication, regardless of dialect, is essential.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating Dialect Variation
- Be open-minded: Approach dialects with an open mind, recognizing that they are simply different ways of speaking the same language.
- Listen attentively: Pay attention to the pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar of speakers from different regions.
- Ask questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions about words or phrases that you don’t understand.
- Be respectful: Treat all speakers with respect, regardless of their dialect.
- Engage in conversations: Seek opportunities to interact with speakers of different dialects to broaden your linguistic horizons.
Conclusion
The dialect map of the United States reveals a vibrant tapestry of linguistic diversity, reflecting the nation’s rich cultural heritage and the dynamic evolution of American English. Understanding these dialects fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexities of language, the influence of social factors on linguistic variation, and the unique cultural identities of different communities. As we continue to explore the fascinating world of American English dialects, we gain a richer understanding of the language we share and the people who speak it.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Melodies of America: A Comprehensive Look at Dialects of American English. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!