Mapping the Past: A Journey Through Mexico in 1700
Related Articles: Mapping the Past: A Journey Through Mexico in 1700
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Past: A Journey Through Mexico in 1700. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Past: A Journey Through Mexico in 1700
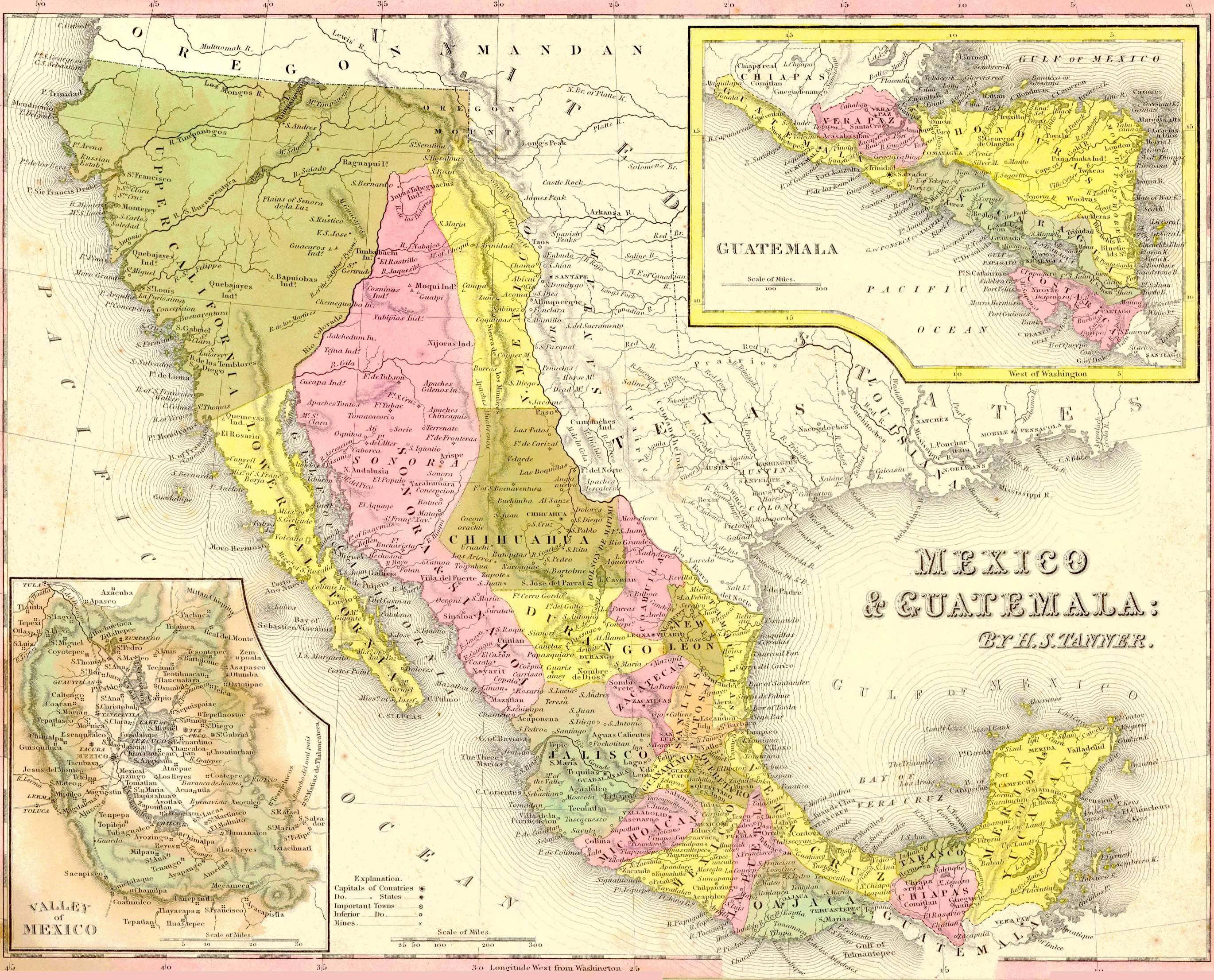
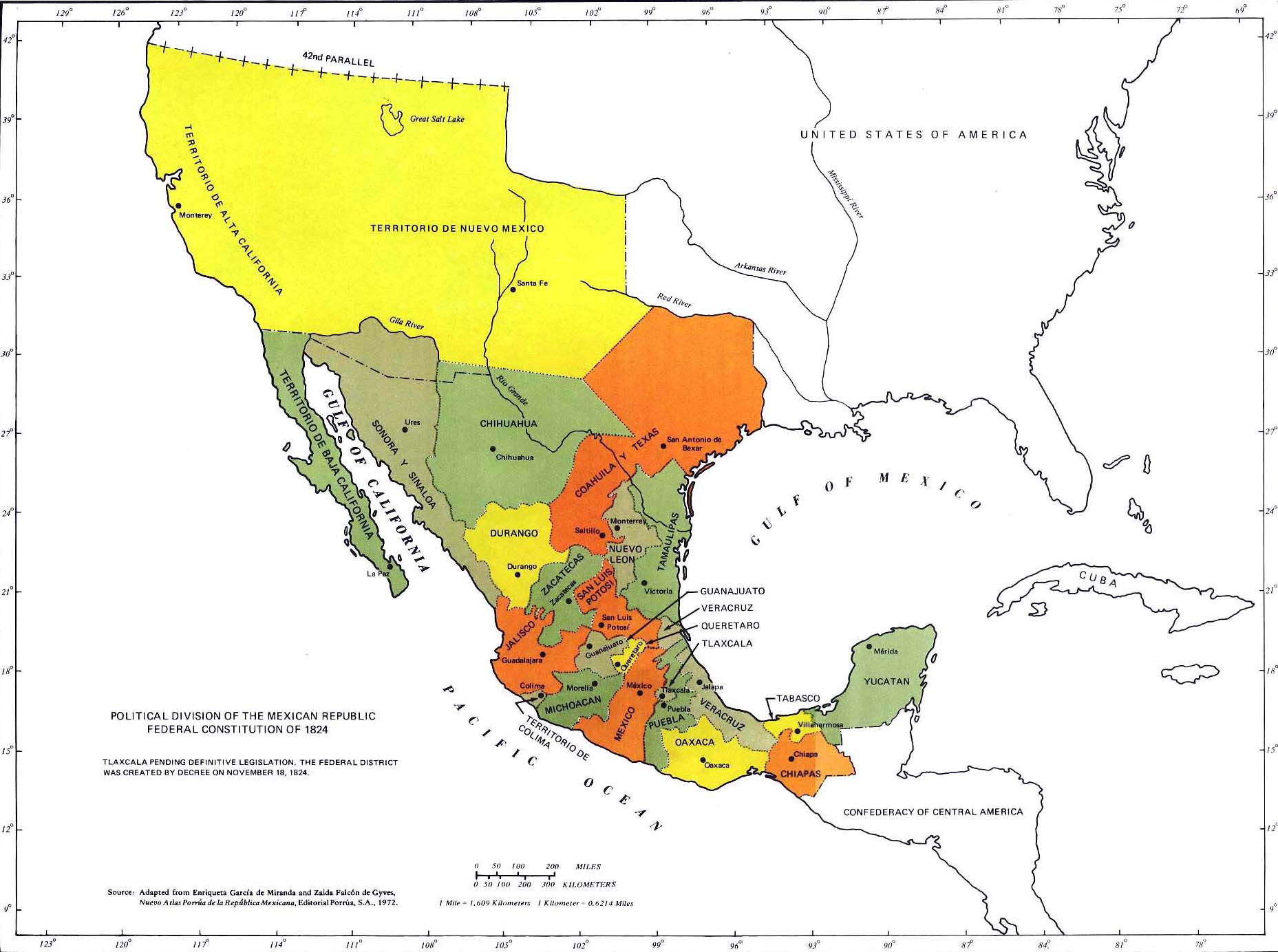
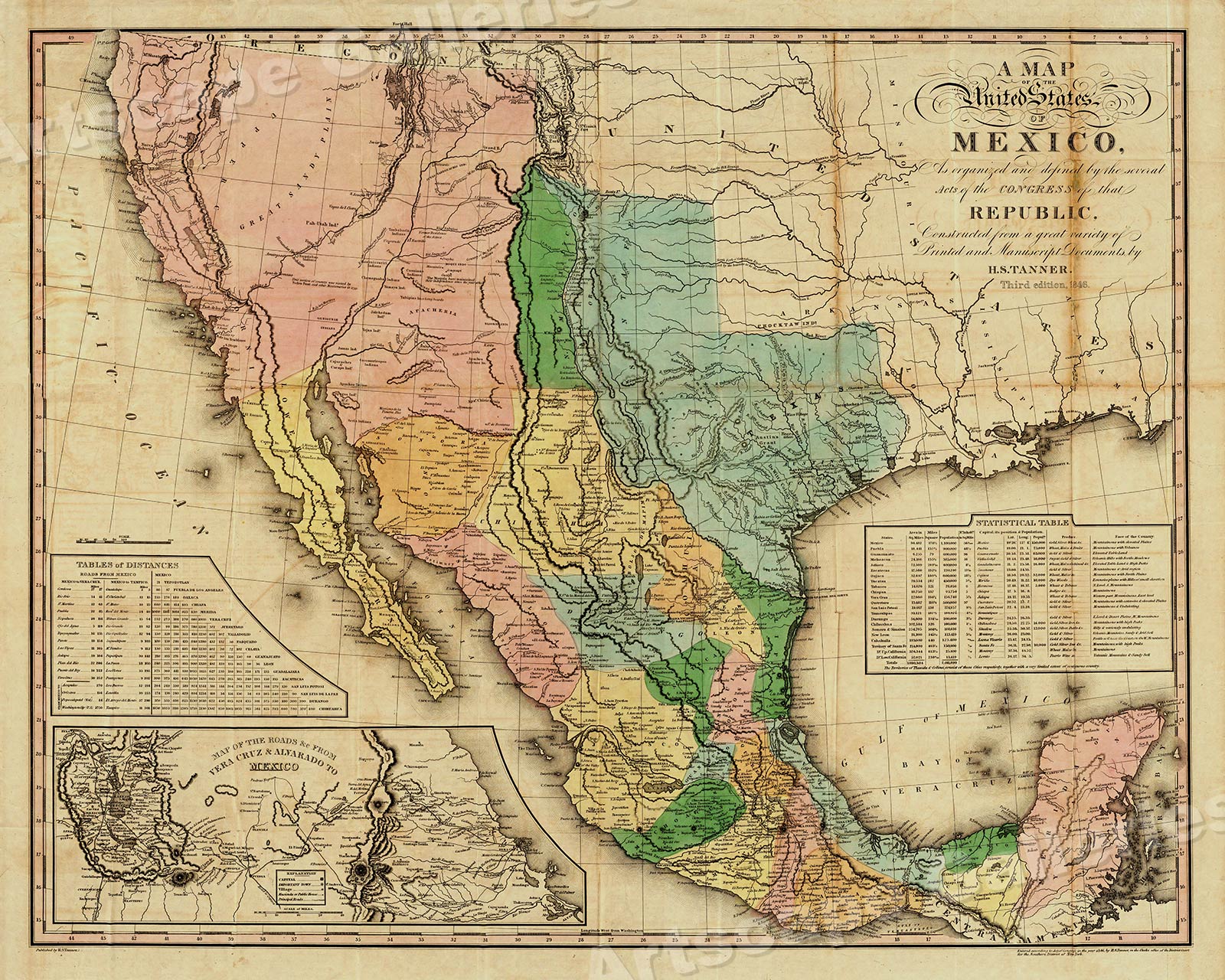
The year 1700 marks a pivotal point in Mexican history, a time of transition and transformation. As the Spanish colonial empire reached its zenith, Mexico, then known as New Spain, was a sprawling, diverse territory. Understanding the geography of this era is crucial for appreciating the complex socio-political landscape and the enduring legacy of Spanish rule.
A Tapestry of Territories:
The map of Mexico in 1700 reveals a vast expanse of land stretching from the present-day southwestern United States to the Isthmus of Panama. This territory, encompassing modern-day Mexico, parts of Central America, and the southwestern United States, was divided into distinct administrative units known as viceroyalties and captaincies general.
-
The Viceroyalty of New Spain: The heart of Spanish power in Mexico, the viceroyalty was governed by a viceroy, representing the Spanish Crown. This vast region encompassed the majority of present-day Mexico, including major cities like Mexico City, Guadalajara, and Puebla.
-
Captaincies General: Smaller administrative units, captaincies general were responsible for specific regions, often on the periphery of the viceroyalty. Notable examples include the Captaincy General of Guatemala, encompassing present-day Guatemala, Belize, and El Salvador, and the Captaincy General of Yucatán, encompassing the Yucatán Peninsula.
Beyond Political Boundaries:
The map of Mexico in 1700 goes beyond mere administrative divisions. It reveals a rich tapestry of geographical features, diverse ecosystems, and indigenous communities that played a crucial role in shaping the history of the region.
-
The Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental: These imposing mountain ranges served as natural barriers, influencing trade routes, communication, and the distribution of population.
-
The Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean: These vast bodies of water played a vital role in maritime trade, connecting Mexico to other parts of the Spanish Empire and the wider world.
-
The Diverse Landscapes: From the arid deserts of the north to the lush rainforests of the south, Mexico in 1700 boasted a remarkable array of landscapes, each supporting distinct indigenous cultures and economies.
The Legacy of Spanish Rule:
The map of Mexico in 1700 serves as a testament to the enduring impact of Spanish colonization. The administrative divisions, the infrastructure developed, and the cultural exchange that took place during this period left an indelible mark on the region.
-
Urban Development: The Spanish established major cities like Mexico City, Puebla, and Guadalajara, which became centers of commerce, culture, and administration. These cities, with their grand architecture and intricate urban planning, reflected the power and influence of the Spanish Crown.
-
Infrastructure Development: The Spanish invested heavily in infrastructure, constructing roads, bridges, and ports to facilitate trade and communication within their vast empire. These infrastructure projects, while serving the interests of the Spanish Crown, also contributed to the economic and social development of the region.
-
Cultural Exchange: The arrival of the Spanish brought about a complex cultural exchange. Spanish language, religion, and customs were introduced, while indigenous traditions and practices continued to persist, creating a unique cultural blend that continues to shape Mexican identity today.
A Window into the Past:
The map of Mexico in 1700 offers a valuable window into the past, allowing us to understand the historical context that shaped the modern nation of Mexico. It reveals the complexities of colonial rule, the resilience of indigenous cultures, and the enduring legacy of Spanish influence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Map of Mexico in 1700:
1. What were the main administrative divisions of Mexico in 1700?
Mexico in 1700 was primarily divided into the Viceroyalty of New Spain, encompassing most of present-day Mexico, and various Captaincies General, such as Guatemala, Yucatán, and others, covering specific regions within the broader territory.
2. What were the major cities in Mexico in 1700?
Major cities in Mexico in 1700 included Mexico City, the capital of the viceroyalty, as well as other important centers like Puebla, Guadalajara, Veracruz, and Oaxaca.
3. How did the geography of Mexico influence its development in 1700?
The diverse geography of Mexico, with its mountains, valleys, deserts, and coastlines, influenced trade routes, communication networks, and the distribution of population. Natural barriers like the Sierra Madre mountains shaped settlement patterns and economic activities.
4. What were the main economic activities in Mexico in 1700?
Mexico in 1700 was primarily an agricultural economy, with large haciendas producing crops like sugar, tobacco, and cacao. Mining, particularly silver, played a crucial role in the economy, fueling trade and enriching the Spanish Crown.
5. How did Spanish colonization impact the indigenous population of Mexico in 1700?
Spanish colonization had a profound impact on the indigenous population of Mexico, leading to forced labor, displacement, and cultural suppression. However, indigenous cultures and traditions persisted, shaping the cultural fabric of Mexico.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Mexico in 1700:
-
Focus on the administrative divisions: Pay attention to the boundaries of the viceroyalty and captaincies general, understanding their administrative roles and the power dynamics within the colonial system.
-
Explore the geographical features: Study the major mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines, recognizing their influence on trade routes, communication networks, and settlement patterns.
-
Consider the indigenous communities: Remember that the map of Mexico in 1700 also reflects the presence of diverse indigenous cultures, each with its own traditions, languages, and ways of life.
-
Analyze the impact of Spanish colonization: Examine how Spanish rule influenced urban development, infrastructure, and cultural exchange, recognizing both the positive and negative consequences of this period.
Conclusion:
The map of Mexico in 1700 offers a fascinating glimpse into a pivotal moment in history, a time when the Spanish colonial empire reached its zenith. It reveals a complex tapestry of political divisions, geographical features, and cultural interactions, shaping the future of Mexico and leaving an enduring legacy on the nation’s identity. By understanding the map of Mexico in 1700, we gain a deeper appreciation for the historical context that shaped the modern nation, its cultural diversity, and its enduring ties to the past.
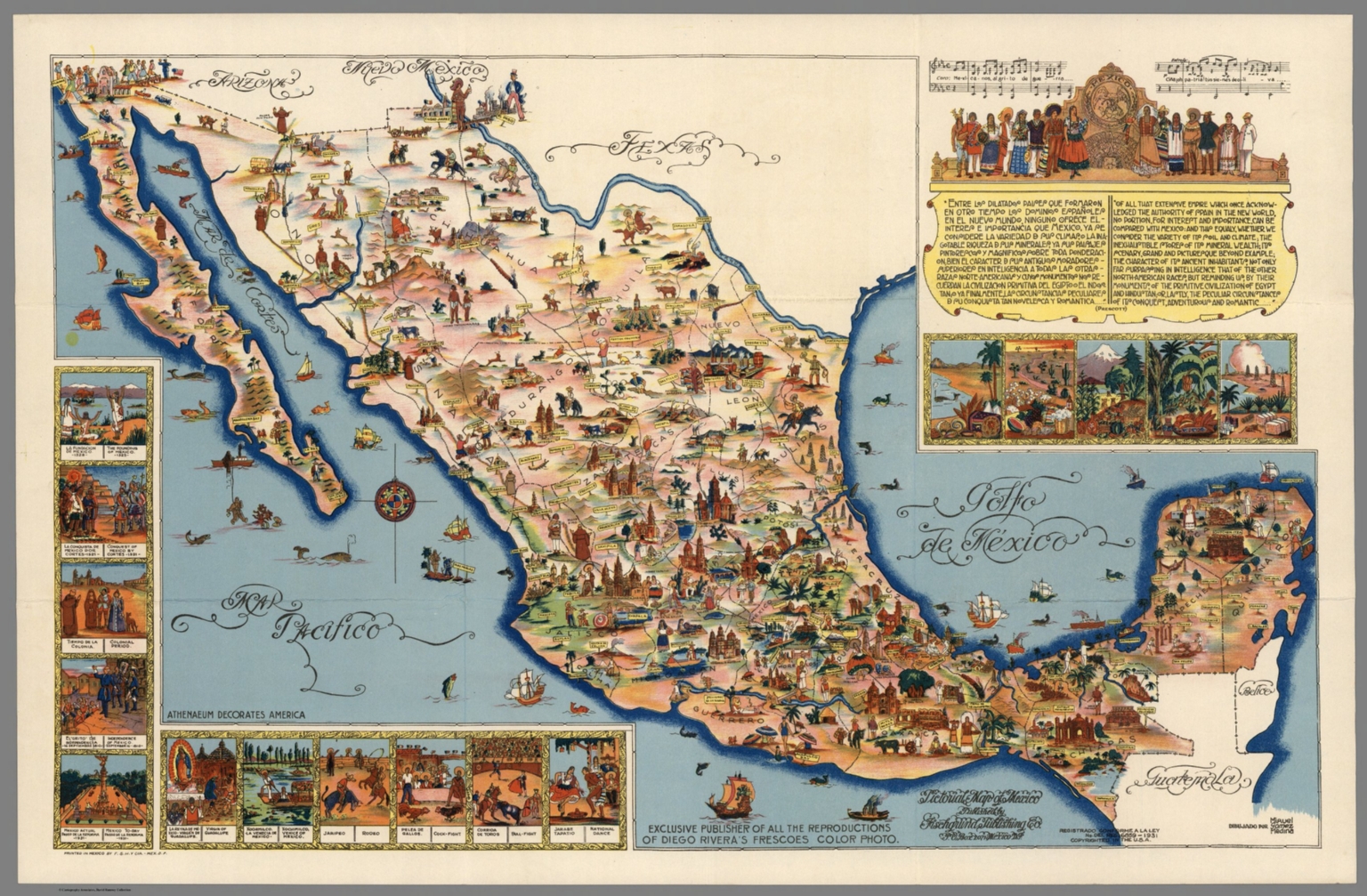



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Past: A Journey Through Mexico in 1700. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!