Navigating the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Flow Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Flow Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Flow Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Flow Maps
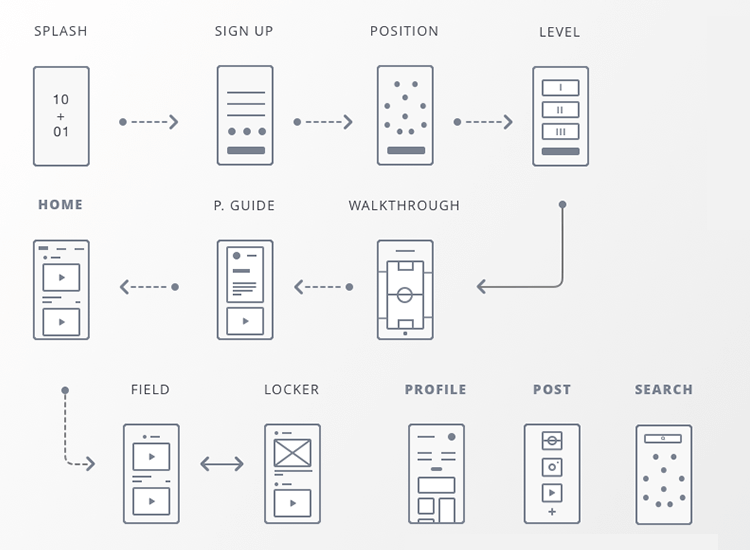
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital products and services, understanding how users interact with a website or application is paramount. This is where user flow maps emerge as indispensable tools for visualizing and optimizing the user experience. By charting the path users take to achieve their goals, these maps provide valuable insights into user behavior, identify potential roadblocks, and guide the development of intuitive and efficient digital interfaces.
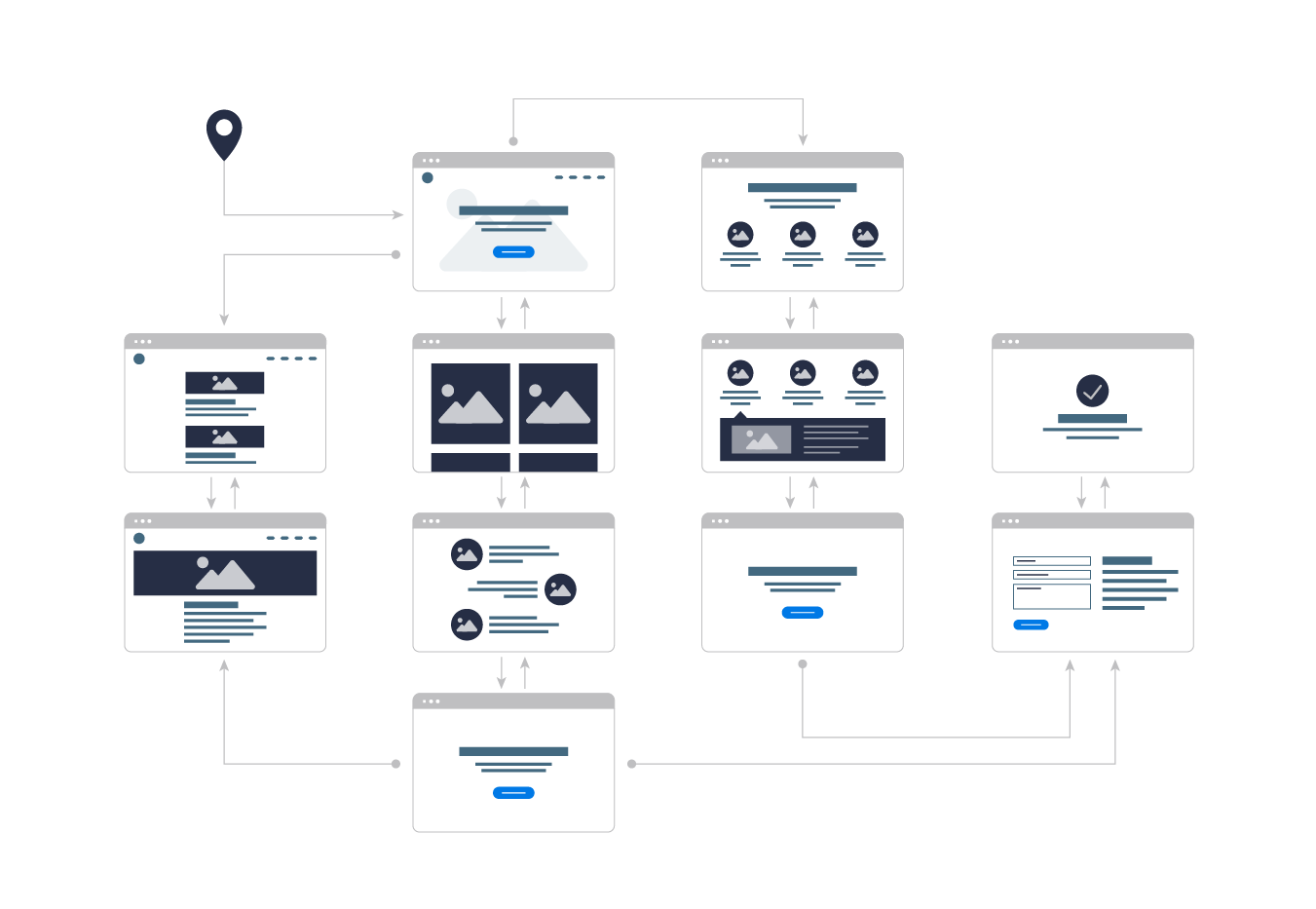
Understanding User Flow Maps: A Visual Representation of User Behavior
A user flow map, often referred to as a user journey map, is a visual representation of the steps a user takes when interacting with a website or application. It illustrates the sequence of actions, decisions, and interactions a user encounters from the initial entry point to the desired outcome.
Key Components of a User Flow Map
A comprehensive user flow map typically includes the following elements:
- Starting Point: This represents the user’s initial entry point into the system, such as a website homepage, a mobile app icon, or an email link.
- User Actions: Each step in the user journey is represented by an action, such as clicking a button, filling out a form, or navigating to a different page.
- Decision Points: These represent points where the user needs to make a choice, such as selecting from a list of options or entering specific information.
- Outcomes: The end goal of the user’s journey is depicted as an outcome, such as completing a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or accessing specific content.
- Pain Points: Potential roadblocks or frustrations encountered by the user are highlighted as pain points, indicating areas needing improvement.
Types of User Flow Maps
User flow maps can be categorized into various types based on their scope and purpose:
- Primary Flow: This map depicts the most common or ideal path users take to achieve their goals.
- Secondary Flow: This map illustrates alternative paths users might take, including those triggered by specific actions or decisions.
- Error Flow: This map focuses on the paths users take when encountering errors or encountering unexpected situations.
- Multi-Device Flow: This map accounts for user journeys across multiple devices, such as a desktop computer, tablet, and smartphone.
Benefits of User Flow Maps: Unveiling the User Experience
User flow maps offer a multitude of benefits for businesses, designers, and developers seeking to enhance the user experience:
- Improved User Understanding: By visualizing user behavior, flow maps provide a clear understanding of how users navigate a website or application.
- Identification of Pain Points: Flow maps highlight areas where users encounter difficulties or frustrations, allowing for targeted improvement efforts.
- Enhanced User Interface Design: The insights gained from user flow maps inform the design of intuitive and user-friendly interfaces that guide users seamlessly towards their goals.
- Optimized User Experience: By identifying and addressing bottlenecks and pain points, user flow maps contribute to a more efficient and enjoyable user experience.
- Increased Conversion Rates: By streamlining the user journey and removing obstacles, flow maps can directly impact conversion rates and business outcomes.
- Improved Communication: Flow maps provide a shared visual language for teams to communicate effectively about user behavior and design decisions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By providing a visual representation of user data, flow maps support data-driven decision-making in product development and design.
Creating Effective User Flow Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a user flow map involves a structured approach, ensuring the map captures essential user behavior and provides actionable insights:
1. Define User Goals: Begin by clearly defining the primary goals users want to achieve through the website or application. This sets the context for the map and guides the identification of key user journeys.
2. Identify User Personas: Develop user personas representing different user segments with distinct needs, motivations, and behaviors. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the user base and their interaction patterns.
3. Map User Journeys: Start with the user’s initial entry point and map out the steps they take to achieve their goals. Include decision points, actions, and potential outcomes.
4. Mark Pain Points: Identify areas where users encounter difficulties, frustrations, or roadblocks. These pain points represent opportunities for improvement and optimization.
5. Create Visual Representation: Utilize diagrams, flowcharts, or other visual tools to represent the user flow map. Clear and concise visual representation enhances communication and understanding.
6. Iterate and Test: Once the initial user flow map is created, test it with real users to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement. Iterate on the map based on user insights and feedback.
FAQs about User Flow Maps
Q: What is the difference between a user flow map and a user journey map?
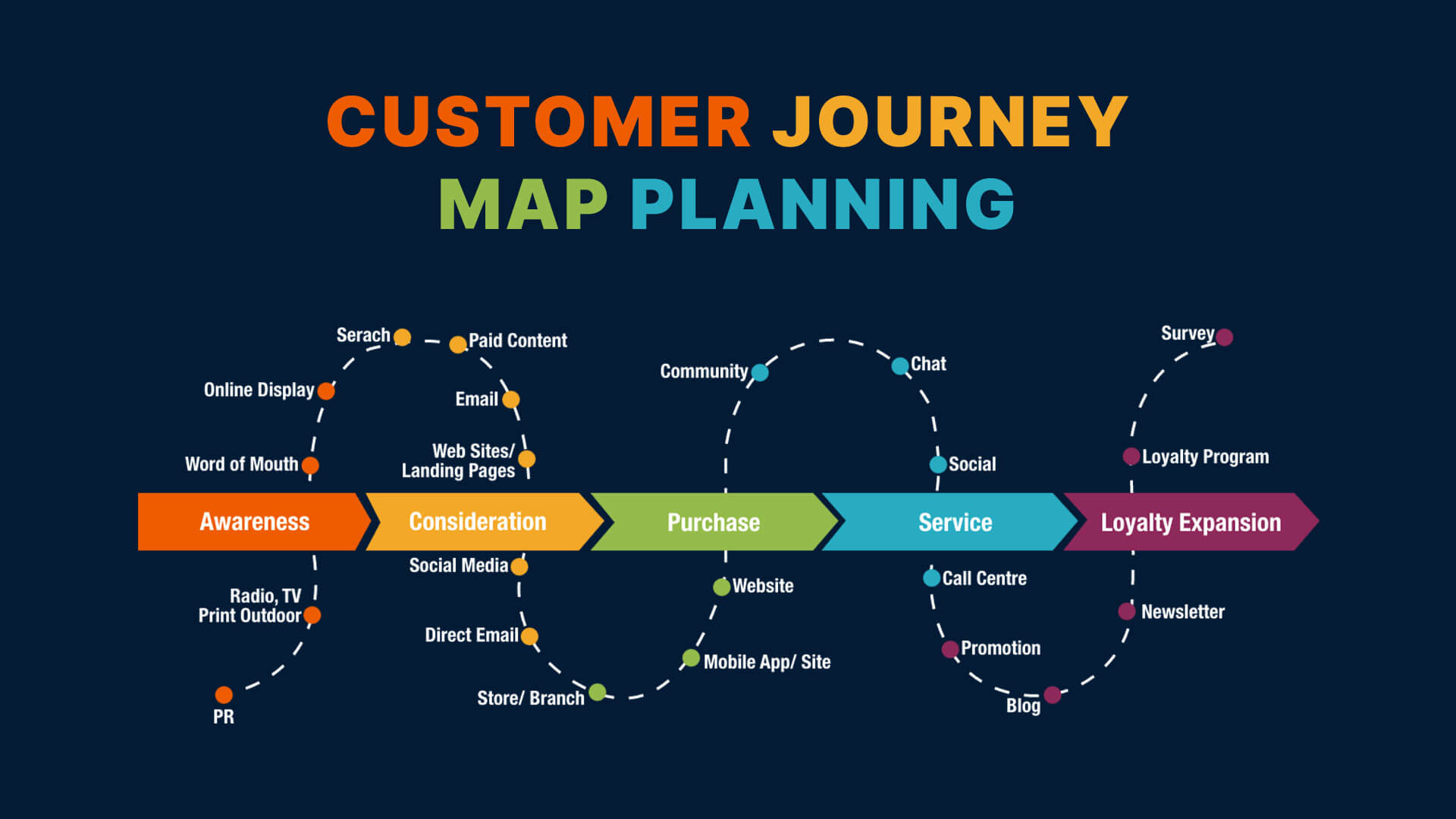
A: While often used interchangeably, user flow maps focus on the specific steps and actions users take within a website or application, while user journey maps provide a broader perspective on the overall user experience, encompassing emotions, motivations, and touchpoints across various channels.
Q: Who should use user flow maps?
A: User flow maps are valuable tools for a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Product Managers: To understand user behavior and guide product development decisions.
- UX Designers: To design intuitive and user-friendly interfaces that facilitate user goals.
- Marketing Teams: To identify opportunities for improving user engagement and conversion rates.
- Developers: To ensure the website or application functions smoothly and addresses user needs.
Q: What are some common tools for creating user flow maps?
A: Numerous tools are available for creating user flow maps, both free and paid:
- Balsamiq: A wireframing and prototyping tool that includes user flow mapping capabilities.
- Lucidchart: A versatile diagramming tool with features for creating user flow maps.
- Miro: A collaborative whiteboard platform that supports user flow mapping and other visual collaboration tasks.
- Google Docs: A simple and accessible option for creating basic user flow maps using text and diagrams.
Tips for Creating Effective User Flow Maps
- Focus on User Goals: Keep the user’s goals at the forefront of map creation, ensuring the map accurately reflects their desired outcomes.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Employ simple and straightforward language to make the map easy to understand for all stakeholders.
- Visualize Decision Points: Clearly depict decision points where users need to make choices, highlighting potential paths they might take.
- Highlight Pain Points: Emphasize areas where users encounter difficulties or frustrations, drawing attention to areas needing improvement.
- Iterate and Test: Regularly review and update the user flow map based on user feedback and data analysis.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders in the map creation process to ensure alignment and shared understanding.
Conclusion: The Power of User Flow Maps in Enhancing User Experience
User flow maps are powerful tools for understanding user behavior, identifying pain points, and optimizing the user experience. By visualizing the user journey, these maps provide valuable insights that inform design decisions, enhance usability, and contribute to a more efficient and enjoyable interaction with digital products and services. By employing a structured approach and leveraging the benefits of user flow maps, businesses can create truly user-centric experiences that drive engagement, conversion, and overall success.

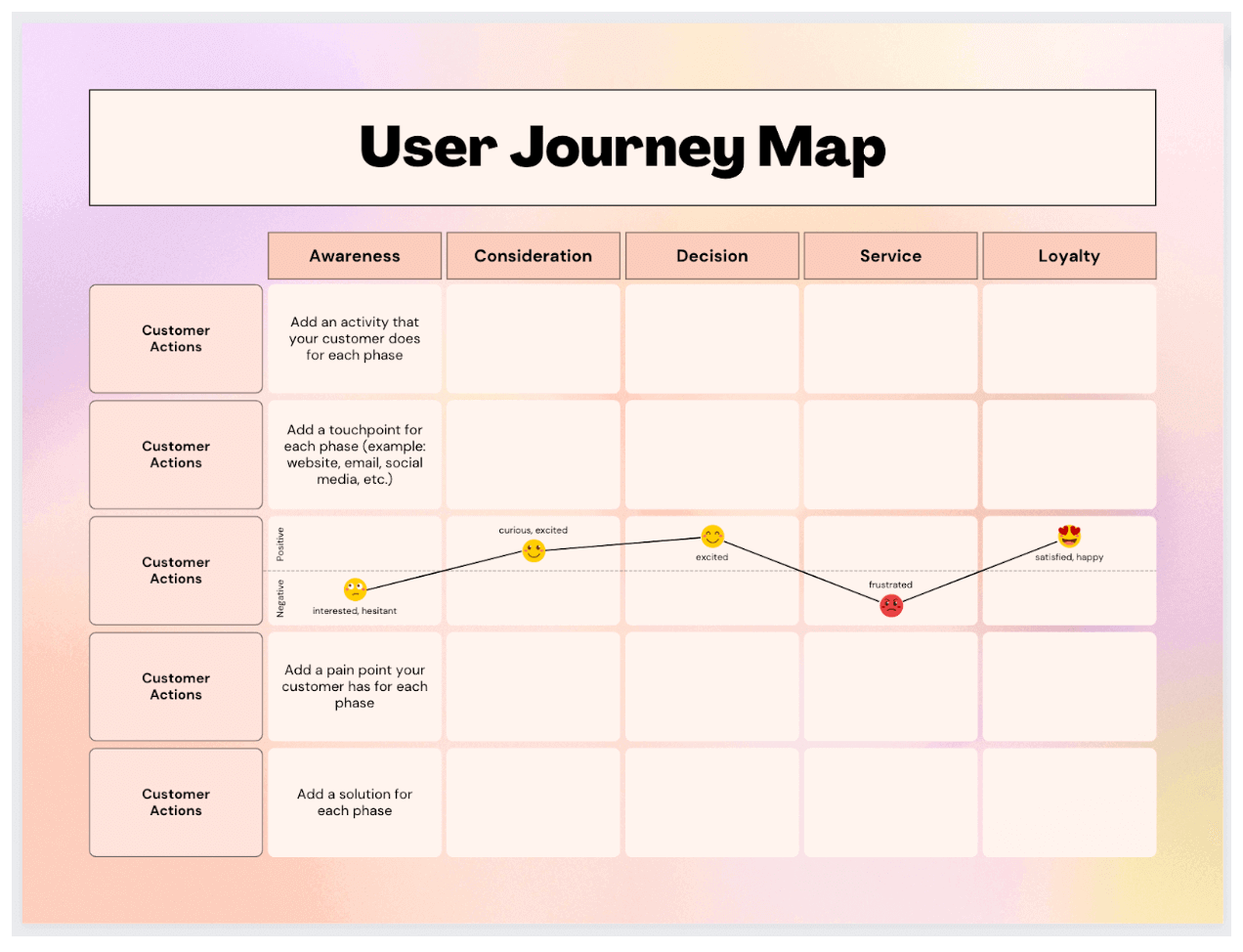
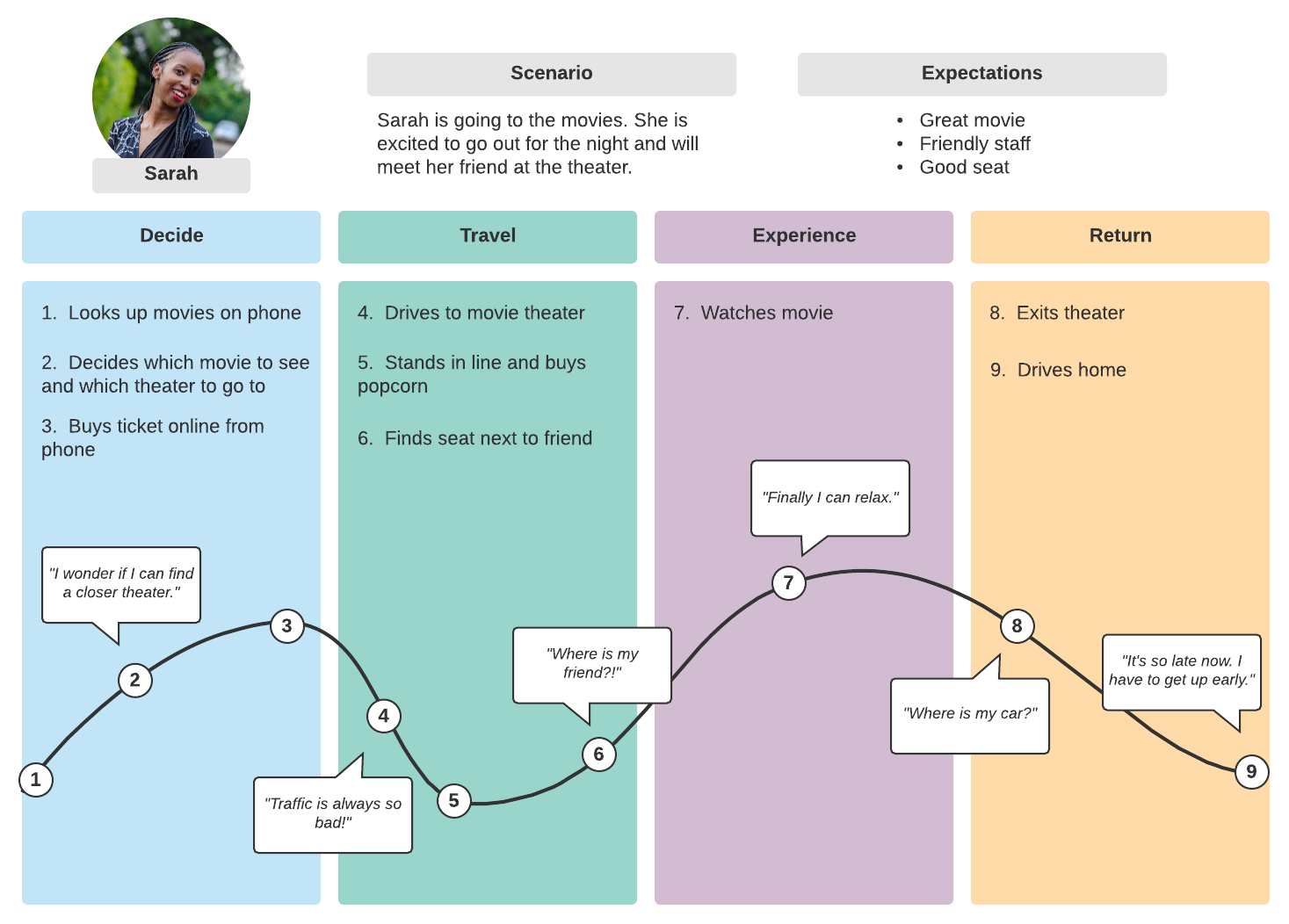

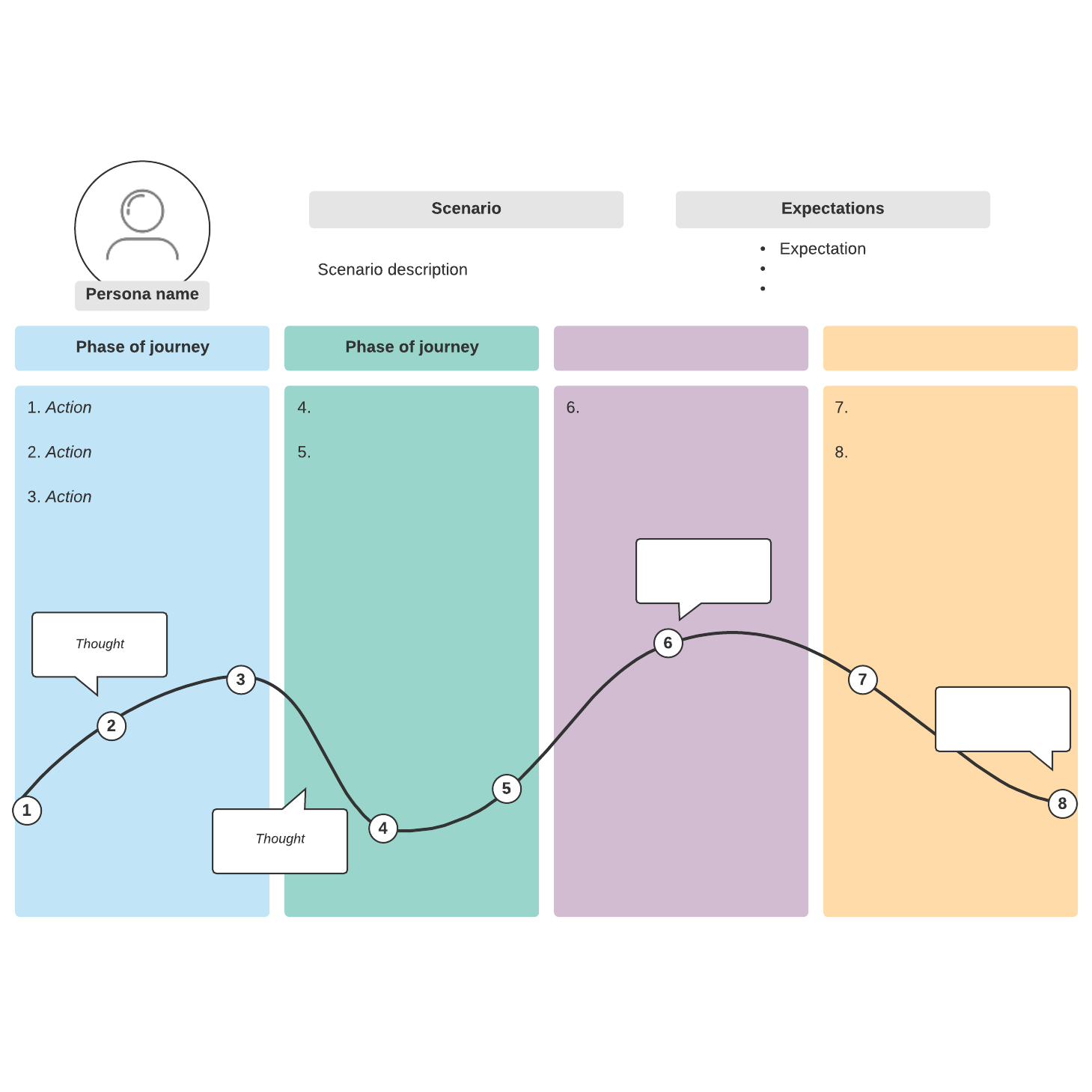

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the User Journey: A Comprehensive Guide to User Flow Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!