The Enduring Stripes: A Global Map of Tiger Habitats
Related Articles: The Enduring Stripes: A Global Map of Tiger Habitats
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Stripes: A Global Map of Tiger Habitats. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Stripes: A Global Map of Tiger Habitats

The tiger, a majestic apex predator, is an iconic symbol of wildness and strength. Yet, its future hangs precariously in the balance. Understanding where tigers live is crucial to their survival, as it informs conservation efforts and highlights the complex challenges they face.
A Shifting Landscape: The Tiger’s Historical and Present Distribution
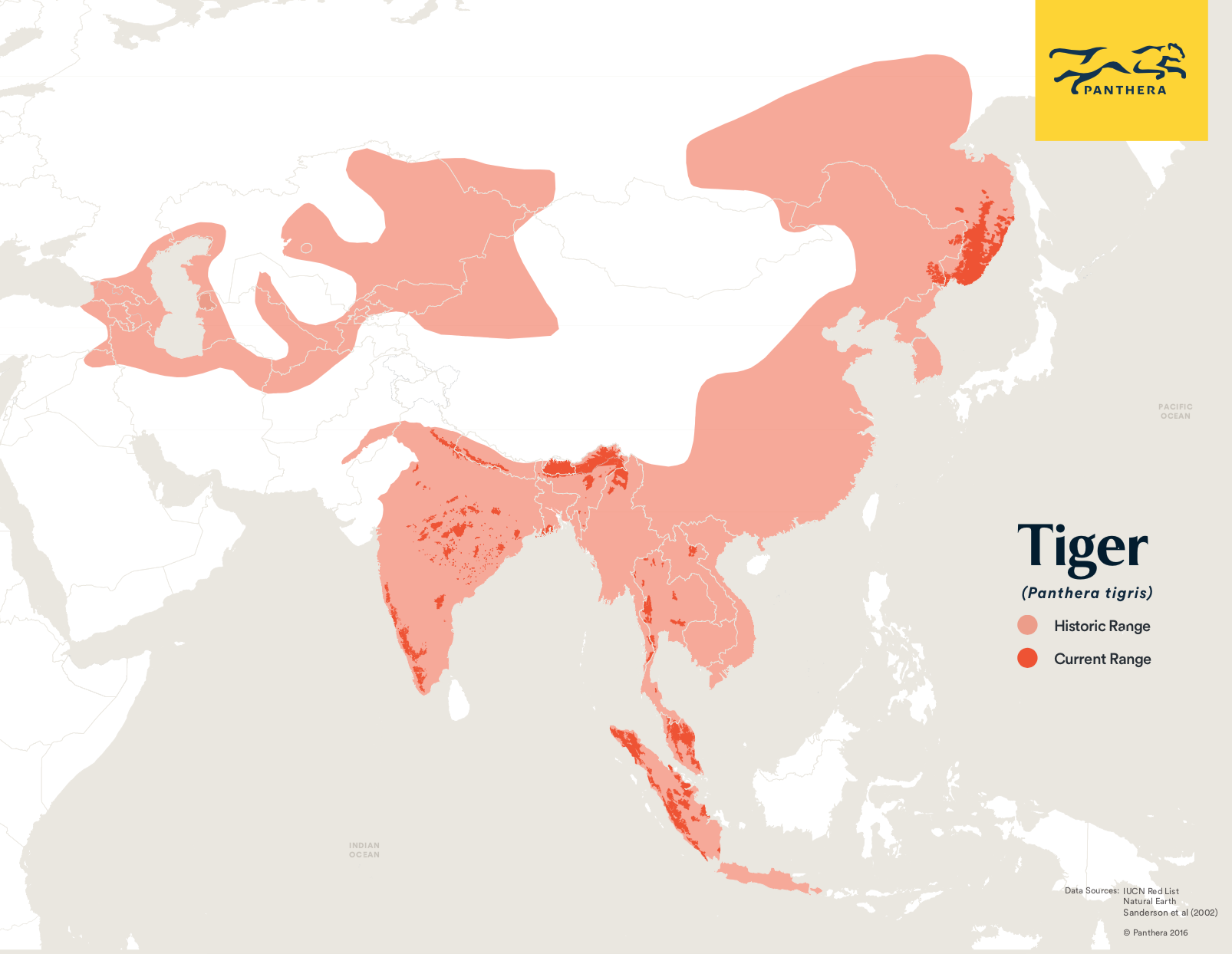
Historically, tigers roamed vast swathes of Asia, from the cold Siberian forests to the humid jungles of Southeast Asia. Their range once spanned across a continuous stretch of territory, encompassing diverse habitats including grasslands, wetlands, and mangrove forests. However, the past century has witnessed a dramatic decline in their numbers and distribution, leading to a fragmented landscape where isolated populations struggle to survive.
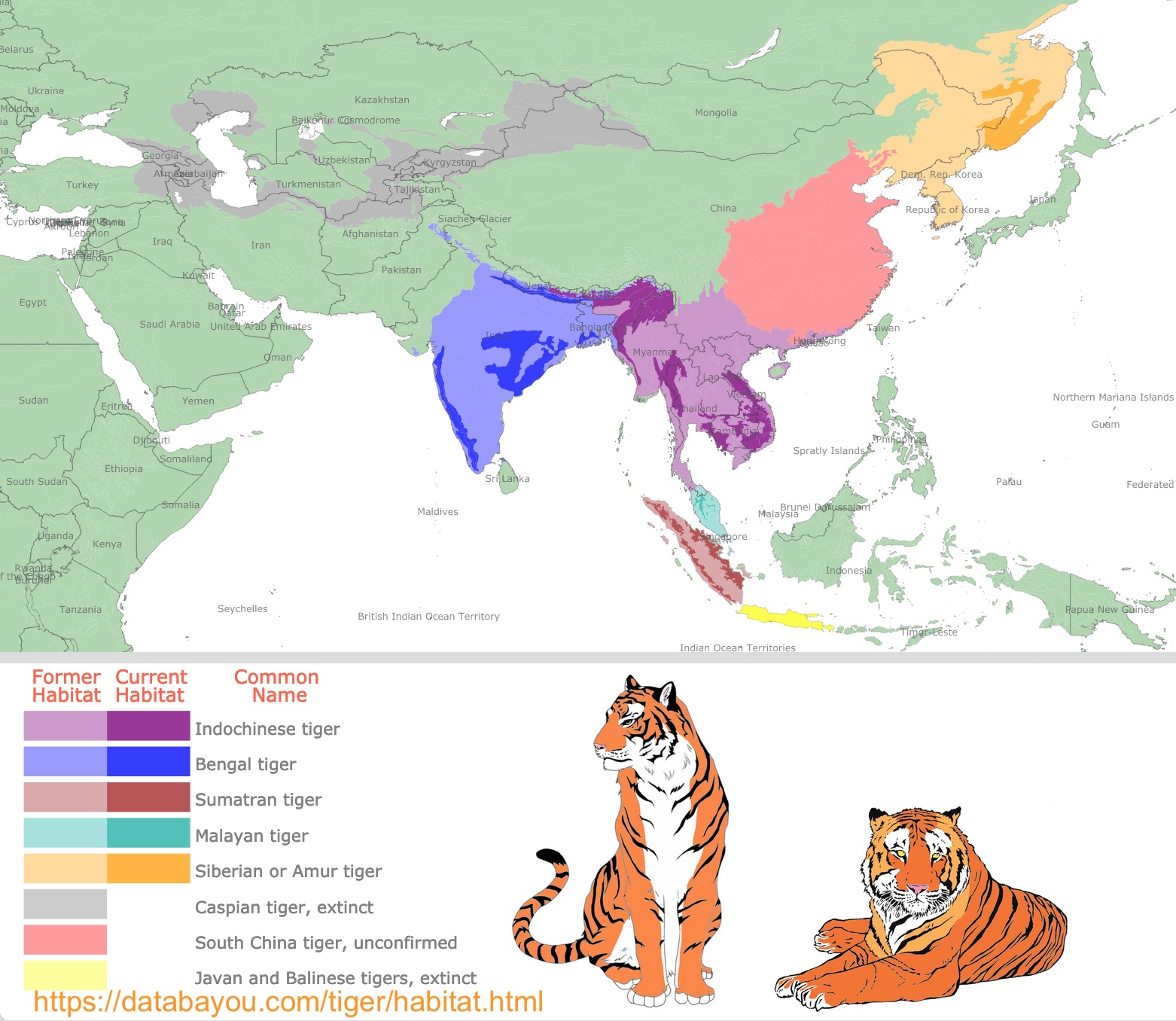
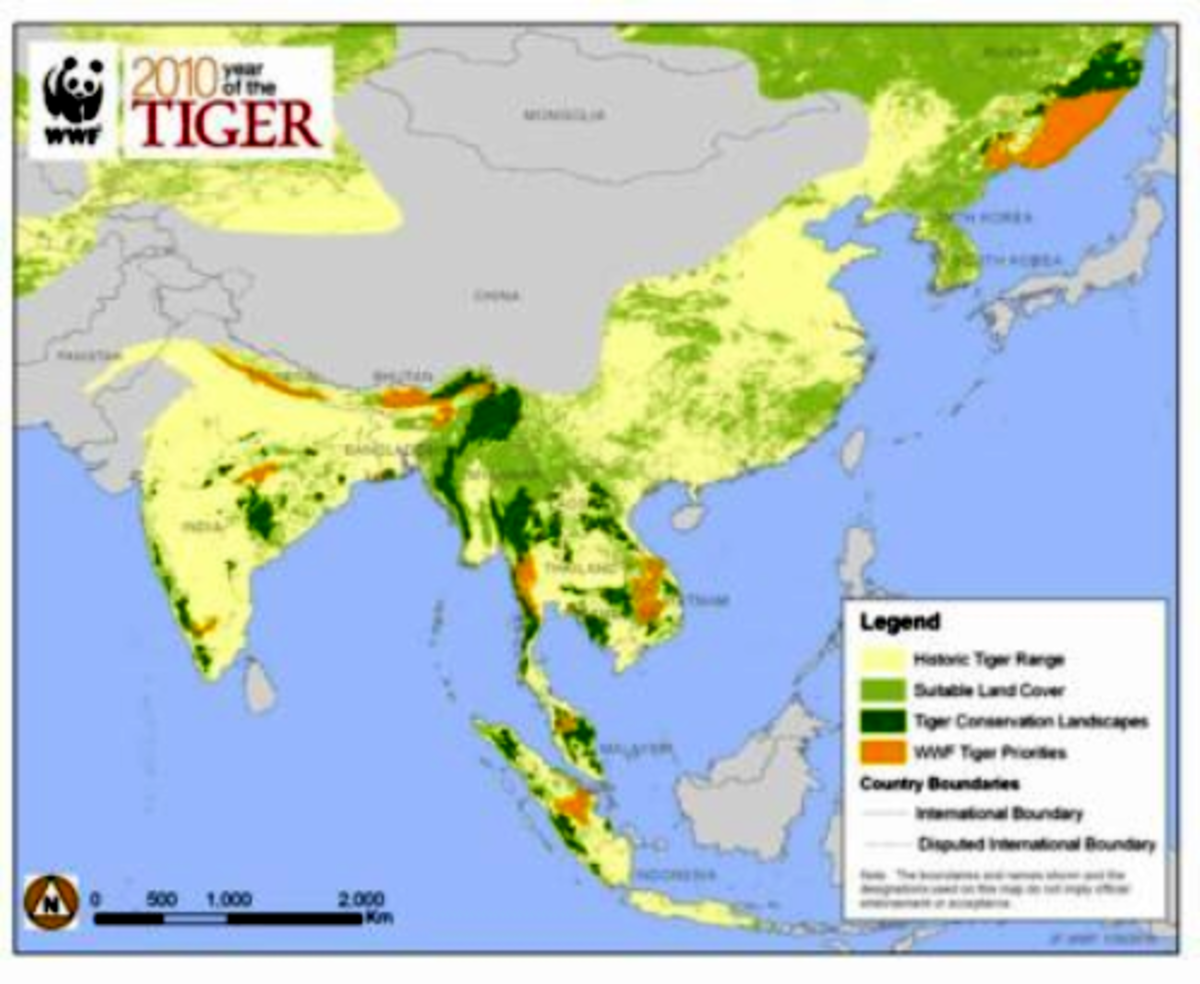
Mapping the Tiger’s Domain: Unveiling the Remaining Strongholds
The map of tiger habitats offers a stark visual representation of this decline. It reveals the current distribution of tiger populations, highlighting the remaining strongholds and the areas where they have vanished. These maps, meticulously compiled through scientific surveys and field studies, are essential tools for conservationists and researchers. They provide insights into the factors influencing tiger populations, such as habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict.
Understanding the Importance of Tiger Habitat Maps:
- Conservation Planning and Prioritization: Maps enable conservationists to identify areas of high tiger density, prioritize conservation efforts, and design effective management strategies. They help focus resources where they are most needed, ensuring the survival of vulnerable populations.
- Identifying Threats and Monitoring Trends: Habitat maps provide a baseline for monitoring changes in tiger populations and habitat quality. They allow researchers to track the impact of conservation initiatives, identify emerging threats, and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Raising Awareness and Public Engagement: Visual representations of tiger distribution can effectively convey the urgency of the situation and inspire public support for conservation efforts. They highlight the importance of protecting not just tigers, but the entire ecosystem they inhabit.
- Supporting Research and Education: Habitat maps serve as valuable resources for scientists, educators, and students, providing a framework for understanding tiger ecology, behavior, and conservation challenges. They foster research and knowledge exchange, contributing to a deeper understanding of these magnificent creatures.
A Geographic Overview of Tiger Habitats:
South Asia:
- India: Home to the largest tiger population in the world, India harbors a diverse range of tiger habitats, including the Sundarbans mangroves, the Western Ghats, and the Terai-Duar savannas.
- Bangladesh: The Sundarbans mangrove forest, shared with India, is a critical habitat for the Bengal tiger.
- Nepal: The Terai-Duar region, known for its rich biodiversity, is a key habitat for the Royal Bengal tiger.
- Bhutan: The Himalayas provide refuge for a small population of tigers, primarily in the Royal Manas National Park.
- Pakistan: The Indus River Valley and the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province support a dwindling tiger population.
Southeast Asia:
- Indonesia: The islands of Sumatra and Borneo are home to distinct subspecies of tigers, facing significant threats from habitat loss and poaching.
- Malaysia: The Malayan tiger, found in the peninsula and on the island of Borneo, is critically endangered.
- Thailand: The western forests of Thailand, including the Khao Sok National Park, are important for tiger conservation.
- Myanmar: The country boasts a diverse range of tiger habitats, but faces challenges from deforestation and poaching.
- Cambodia: The Cardamom Mountains, a stronghold for the Indochinese tiger, are threatened by illegal logging and wildlife trade.
- Vietnam: The Mekong Delta and the central highlands provide refuge for a small number of tigers.
- Laos: The country harbors a dwindling tiger population, facing threats from habitat fragmentation and poaching.
East Asia:
- China: The Siberian tiger, the largest tiger subspecies, finds refuge in the remote forests of northeastern China.
- Russia: The Amur tiger, closely related to the Siberian tiger, is found in the Russian Far East, facing threats from poaching and habitat loss.
Mapping the Future: A Call for Action
The map of tiger habitats is not just a static representation of their current distribution. It is a call to action, a roadmap for safeguarding these magnificent creatures and their vital ecosystems. It highlights the need for collaborative efforts, involving governments, conservation organizations, local communities, and individuals, to address the challenges facing tigers.
FAQs about Tiger Habitats:
Q: What are the biggest threats to tiger habitats?
A: The primary threats to tiger habitats include:
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation: Deforestation, land conversion for agriculture, and infrastructure development are leading to the loss and fragmentation of tiger habitats, isolating populations and reducing their ability to thrive.
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: The demand for tiger parts, used in traditional medicine and for status symbols, fuels poaching, driving tiger populations to the brink of extinction.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: As human populations expand, conflicts with tigers are increasing, leading to retaliatory killings and habitat degradation.
Q: How can we protect tiger habitats?
A: Effective conservation strategies for tiger habitats include:
- Strengthening Protected Area Management: Establishing and effectively managing protected areas is crucial for safeguarding tiger populations and their habitats.
- Combating Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: Enforcing anti-poaching measures, disrupting illegal trade networks, and promoting sustainable alternatives to tiger products are essential for reducing poaching pressure.
- Reducing Human-Wildlife Conflict: Implementing conflict mitigation measures, such as community education programs, livestock protection, and habitat restoration, can minimize conflict between humans and tigers.
- Promoting Sustainable Land Use Practices: Encouraging sustainable agriculture, forestry, and ecotourism practices can help reduce the pressure on tiger habitats and promote coexistence with human communities.
Q: How can I help protect tigers?
A: You can contribute to tiger conservation by:
- Supporting Conservation Organizations: Donate to organizations working to protect tigers and their habitats.
- Raising Awareness: Share information about tiger conservation with friends and family, and advocate for policy changes that support tiger protection.
- Making Sustainable Choices: Choose products that are sourced sustainably and avoid purchasing items made from tiger parts or products that contribute to habitat loss.
- Supporting Ecotourism: When traveling, choose ecotourism operators that promote responsible wildlife viewing and support conservation efforts.
Tips for Understanding Tiger Habitat Maps:
- Pay attention to the scale: Maps can be presented at different scales, so be aware of the area covered.
- Look for key features: Pay attention to features like protected areas, forest cover, and human settlements, as they provide context for tiger distribution.
- Understand the data sources: Maps are often based on different data sources, such as camera trap surveys, interviews with local communities, and satellite imagery.
- Consider the limitations: Maps are a snapshot in time and do not capture the full complexity of tiger populations and their movements.
Conclusion: A Shared Responsibility
The map of tiger habitats serves as a powerful reminder of the challenges facing these magnificent creatures and the urgent need for action. It highlights the interconnectedness of human activities and wildlife conservation, emphasizing the importance of a shared responsibility for protecting tigers and their habitats. By understanding the threats they face and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure that the stripes of the tiger continue to grace the landscapes of Asia for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Stripes: A Global Map of Tiger Habitats. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!