Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 What is a Tick Map?
- 3.2 The Importance of Michigan’s Tick Map
- 3.3 Exploring the Michigan Tick Map: A Detailed Breakdown
- 3.4 Navigating the Michigan Tick Map
- 3.5 FAQs about Michigan’s Tick Map
- 3.6 Tips for Using the Michigan Tick Map Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide

Michigan, with its diverse landscapes and abundant wildlife, is home to a variety of tick species. These tiny arachnids, often carrying potentially harmful diseases, pose a significant health concern for residents and visitors alike. To effectively mitigate the risk of tick-borne illnesses, understanding the distribution of these parasites across the state is crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of Michigan’s tick map, exploring its significance, benefits, and applications.
What is a Tick Map?
A tick map is a visual representation of the geographic distribution of different tick species within a specific region. These maps are compiled by researchers, entomologists, and public health officials using various data sources, including:
- Tick surveillance programs: State and federal agencies conduct regular tick surveillance activities, collecting and identifying ticks from various locations.
- Citizen science initiatives: Public participation programs encourage individuals to report tick encounters, contributing valuable data on tick presence and distribution.
- Disease reporting systems: Reports of tick-borne illnesses, like Lyme disease, provide insights into the geographic areas where infected ticks are prevalent.
The Importance of Michigan’s Tick Map
Understanding the distribution of ticks in Michigan is vital for several reasons:
- Public health awareness: Maps inform the public about areas where certain tick species are common, enabling individuals to take preventive measures and reduce their risk of tick bites.
- Disease surveillance and control: By identifying areas with high tick populations, public health officials can target surveillance efforts and implement appropriate disease control strategies.
- Research and monitoring: Tick maps serve as valuable tools for researchers studying tick ecology, disease transmission, and the effectiveness of control measures.
- Resource management: Land managers can use tick maps to inform decisions regarding habitat management and recreational activities, minimizing the risk of tick encounters.
Exploring the Michigan Tick Map: A Detailed Breakdown
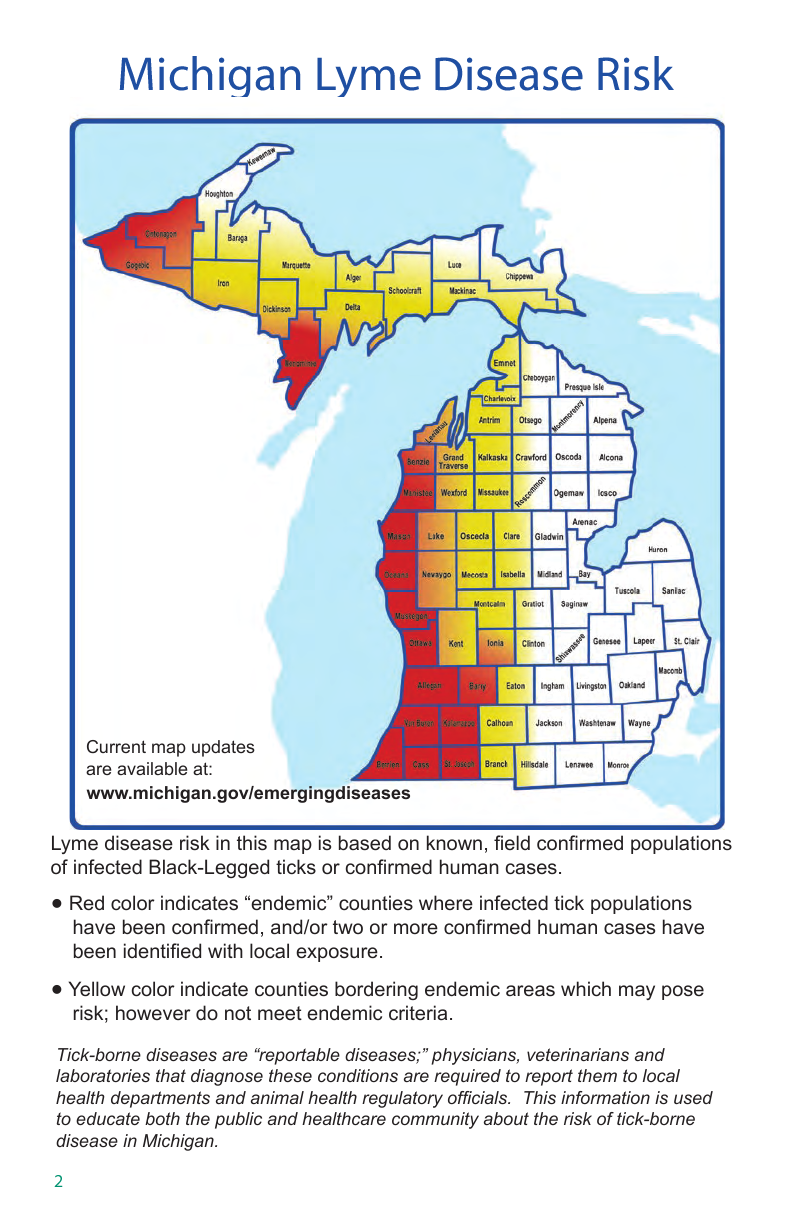
The Michigan tick map, developed by the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services (MDHHS), provides a comprehensive overview of the state’s tick landscape. It showcases the distribution of four primary tick species:
-
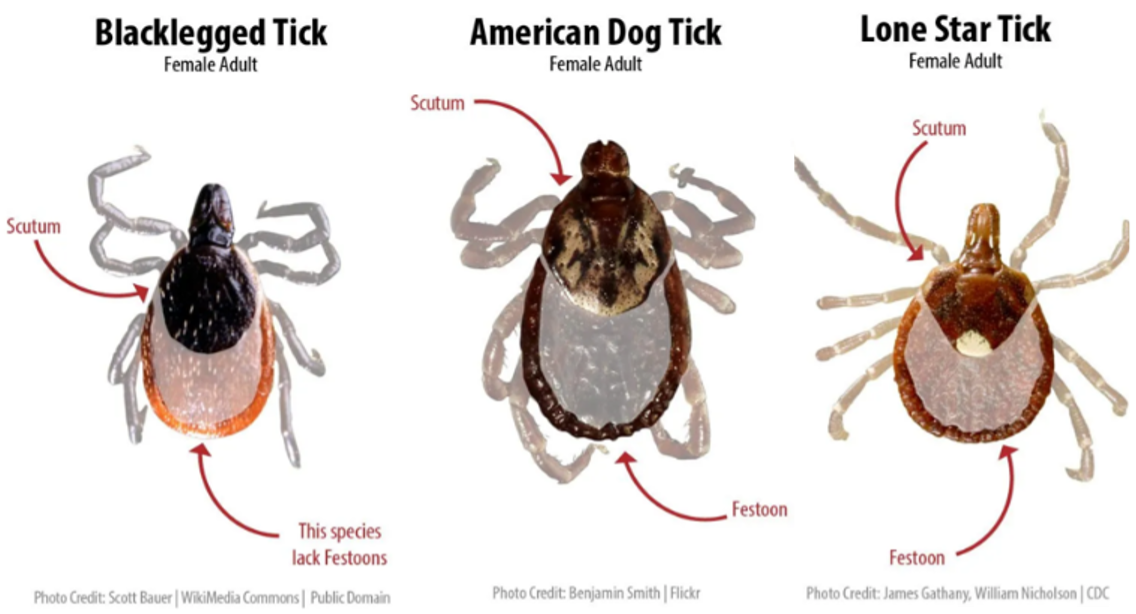
Blacklegged Tick (Ixodes scapularis): This species, commonly known as the deer tick, is the primary vector for Lyme disease, anaplasmosis, and babesiosis. The blacklegged tick is prevalent in the Lower Peninsula, particularly in the eastern and southern regions.
-
American Dog Tick (Dermacentor variabilis): This tick is a common carrier of Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. It is widely distributed throughout the state, with higher concentrations in the southern and eastern Lower Peninsula.
-
Lone Star Tick (Amblyomma americanum): This tick is known to transmit ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis, and the Heartland virus. Its presence in Michigan is increasing, with higher concentrations in the southern Lower Peninsula.
-
Woodchuck Tick (Ixodes cookei): This tick is primarily associated with woodchucks and can transmit Lyme disease. Its distribution is less widespread than other species, with higher concentrations in the eastern and northern Lower Peninsula.
Navigating the Michigan Tick Map
The Michigan tick map is a valuable resource for individuals, healthcare professionals, and researchers. It is accessible online through the MDHHS website and features interactive functionalities allowing users to:
- View the distribution of each tick species: Users can select specific tick species to view their geographic range on the map.
- Identify high-risk areas: The map highlights areas with high tick populations, aiding in risk assessment and preventive measures.
- Access additional information: The map provides links to relevant resources, including information on tick-borne diseases, prevention tips, and reporting procedures.
FAQs about Michigan’s Tick Map
Q: Is the Michigan tick map updated regularly?
A: Yes, the MDHHS continuously updates the tick map based on new data collected from surveillance programs, citizen science initiatives, and disease reporting systems.
Q: How accurate is the Michigan tick map?
A: The map’s accuracy relies on the data collected from various sources. While it provides a comprehensive overview of tick distribution, it’s important to note that local variations and environmental factors can influence tick populations.
Q: Can I report tick encounters on the Michigan tick map?
A: While the map does not offer direct reporting functionality, the MDHHS encourages individuals to report tick encounters to local health departments or the Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development.
Q: Does the Michigan tick map include information on tick-borne diseases?
A: The map provides links to resources with comprehensive information on tick-borne diseases, including symptoms, prevention, and treatment.
Q: How can I use the Michigan tick map to protect myself from ticks?
A: By understanding the distribution of ticks in your area, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk of tick bites, such as avoiding tick-infested areas, wearing protective clothing, and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
Tips for Using the Michigan Tick Map Effectively
- Check the map regularly: Stay informed about the latest updates and changes in tick distribution.
- Consult with healthcare professionals: If you are concerned about tick-borne illnesses, consult with your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional.
- Participate in tick surveillance: Contribute to the accuracy of the map by reporting tick encounters to relevant authorities.
- Share information with others: Educate your community about tick risks and the importance of prevention.
Conclusion
The Michigan tick map serves as a vital tool for understanding the distribution of ticks and mitigating the risk of tick-borne illnesses. By providing comprehensive information on tick populations and geographic locations, the map empowers individuals, healthcare professionals, and researchers to take informed actions to protect public health. By utilizing the map’s resources and implementing preventative measures, we can contribute to a safer and healthier environment for all.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Distribution of Ticks in Michigan: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!