Understanding the Layout of the Tennis Court: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Layout of the Tennis Court: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Layout of the Tennis Court: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Layout of the Tennis Court: A Comprehensive Guide
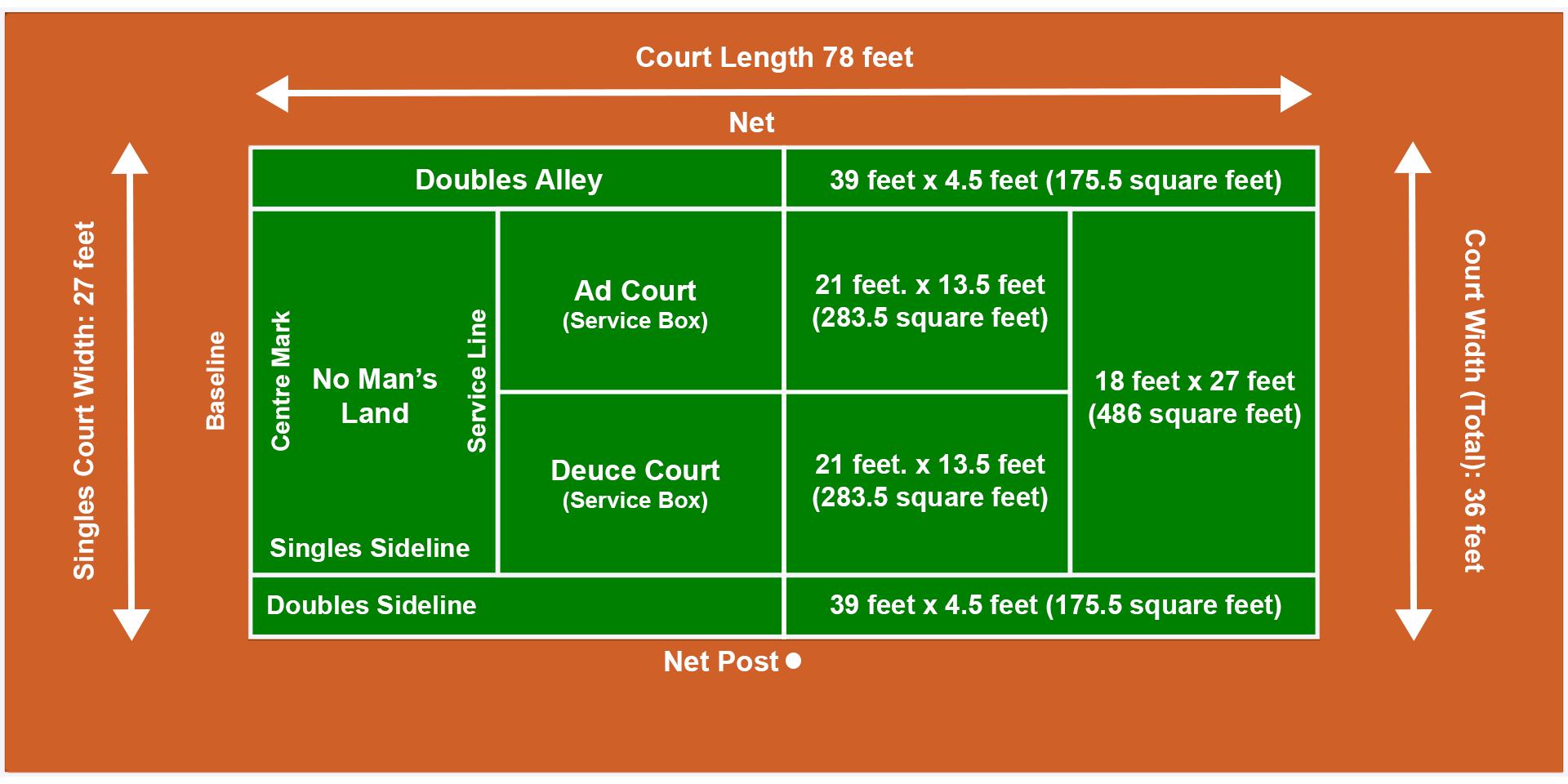
The tennis court, a rectangular expanse of green, holds within its boundaries a world of strategy, athleticism, and competitive spirit. Navigating this playing field effectively requires understanding its unique layout and the various zones it encompasses. This guide delves into the intricacies of the tennis court map, exploring its components and highlighting the strategic implications of each area.
The Essential Elements of a Tennis Court Map
A tennis court map is a visual representation of the court’s dimensions and markings, serving as a blueprint for players and coaches alike. It provides a clear understanding of the court’s boundaries, the service lines, the net, and the various playing zones.
1. Dimensions and Boundaries:
- Length: A standard tennis court measures 78 feet (23.77 meters) in length.
-
Width: The width varies depending on the type of court:
- Singles: 27 feet (8.23 meters)
- Doubles: 36 feet (10.97 meters)
- Baseline: The back line of the court, where players serve from.
- Sidelines: The lines that run parallel to the baseline, marking the lateral boundaries of the court.
2. The Net:
- Height: The net stands 3 feet (0.91 meters) high at the center and 3 feet 6 inches (1.07 meters) high at the posts.
- Length: The net spans the entire width of the court.
3. Service Lines:
- Location: Parallel to the baseline, 21 feet (6.4 meters) from it.
- Purpose: Define the service box, the area where players must serve the ball.
4. Service Boxes:
- Dimensions: 13.5 feet (4.11 meters) long and 21 feet (6.4 meters) wide.
- Location: Located within the service lines, extending from the sidelines to the center of the court.
5. Center Mark:
- Location: Located in the middle of the court, directly opposite the net.
- Purpose: Divides the court into two halves, marking the center of the service box.
6. Doubles Sidelines:
- Location: Located 4.5 feet (1.37 meters) inside the sidelines, parallel to the baseline.
- Purpose: Define the doubles court, which is wider than the singles court.
7. Playing Zones:
- Service Box: The area where players must serve the ball.
- Deuce Court: The half of the court that is right of the center mark for the server.
- Ad Court: The half of the court that is left of the center mark for the server.
- Baseline: The back line of the court, where players must hit the ball to return a serve.
- Net Area: The area directly in front of the net, where players can volley the ball.
Strategic Significance of the Tennis Court Map
The tennis court map is not merely a visual representation; it is a strategic roadmap that guides players’ movements and shot selection. Each zone on the court presents unique opportunities and challenges, demanding specific tactical approaches.
1. The Baseline:
- Strategic Advantage: The baseline offers a solid base from which players can launch powerful groundstrokes and rally with their opponents.
- Strategic Disadvantage: Players at the baseline are vulnerable to drop shots, lobs, and volleys, requiring them to be prepared for a variety of shot types.
2. The Net Area:
- Strategic Advantage: The net area allows players to control the point by forcing their opponents to hit the ball over their heads.
- Strategic Disadvantage: Players at the net are vulnerable to passing shots, requiring them to anticipate their opponent’s movements and react quickly.
3. The Service Box:
- Strategic Advantage: The service box is the only area where players can serve the ball directly into the opponent’s court.
- Strategic Disadvantage: The service box is a small area, making it challenging to hit the ball accurately and consistently.
4. The Deuce Court and Ad Court:
- Strategic Advantage: Players can use the deuce court and ad court to their advantage by positioning themselves to hit cross-court shots or down-the-line shots.
- Strategic Disadvantage: Players must be aware of their position on the court and adjust their shot selection accordingly.
5. The Center Mark:
- Strategic Advantage: The center mark can be used as a reference point to judge the position of the ball and make strategic decisions.
- Strategic Disadvantage: Players must be aware of the center mark and avoid hitting the ball into the net.
Benefits of Understanding the Tennis Court Map
A thorough understanding of the tennis court map offers numerous benefits for both players and coaches:
- Improved Shot Selection: By understanding the different zones on the court, players can make more informed decisions about their shot selection, maximizing their chances of success.
- Enhanced Court Coverage: Knowledge of the court’s layout enables players to move more efficiently, covering the entire court effectively.
- Strategic Planning: Coaches can utilize the court map to develop game plans and strategies based on the strengths and weaknesses of their players and opponents.
- Effective Communication: The court map provides a common language for players and coaches to communicate, ensuring clear understanding of tactical decisions and adjustments.
- Enhanced Visualization: The court map allows players to visualize the court’s layout and anticipate their opponent’s movements, enhancing their overall performance.
FAQs About the Tennis Court Map
1. Why is the tennis court not perfectly square?
The rectangular shape of the tennis court is designed to create a challenging playing surface, forcing players to cover more ground and make more strategic decisions. The slightly longer length and narrower width create a greater distance between the baseline and the net, making it more difficult to hit winning shots.
2. What is the purpose of the service lines?
The service lines define the service box, the area where players must serve the ball. They ensure that the serve is delivered within a specific area, adding an element of precision and strategy to the game.
3. Why is the net higher at the posts?
The net’s higher height at the posts is designed to prevent players from hitting the ball under the net. This rule ensures that the ball must be hit over the net, adding another layer of difficulty to the game.
4. What is the difference between a singles court and a doubles court?
The doubles court is wider than the singles court, as it accommodates two players on each side of the net. The doubles sidelines, located 4.5 feet inside the regular sidelines, define the doubles court area.
5. Why is the center mark important?
The center mark serves as a reference point for players, dividing the court into two halves and marking the center of the service box. It helps players judge the position of the ball and make strategic decisions about their shot selection.
Tips for Utilizing the Tennis Court Map Effectively
- Visualize the Court: Before stepping onto the court, take a moment to visualize its layout, mentally mapping out the different zones and their strategic implications.
- Practice Shot Placement: Dedicate time to practice hitting shots to different areas of the court, developing accuracy and consistency in your shot selection.
- Analyze Your Opponent’s Movements: Pay attention to your opponent’s movements on the court, anticipating their shot selection and adjusting your position accordingly.
- Communicate with Your Coach: Discuss your game plan with your coach, utilizing the court map as a visual aid to communicate strategic decisions and adjustments.
- Review Match Footage: After a match, review the footage and analyze your shot selection, identifying areas where you can improve your court coverage and shot placement.
Conclusion
The tennis court map is an essential tool for players and coaches alike, providing a visual representation of the court’s layout and strategic implications. By understanding the different zones, their advantages and disadvantages, and the strategic significance of each area, players can improve their shot selection, court coverage, and overall performance. The court map serves as a roadmap to success, guiding players towards a deeper understanding of the game and unlocking their full potential.



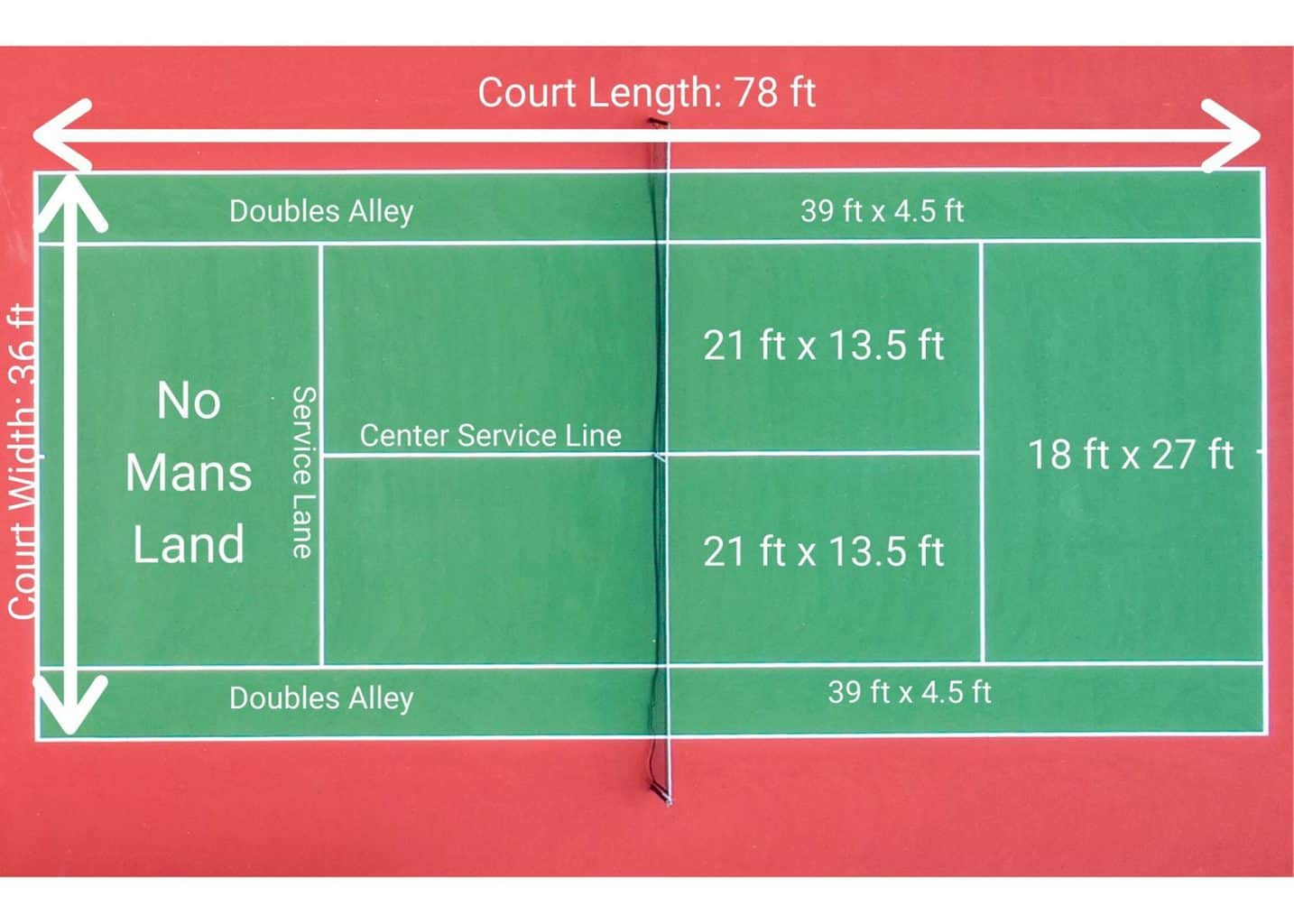



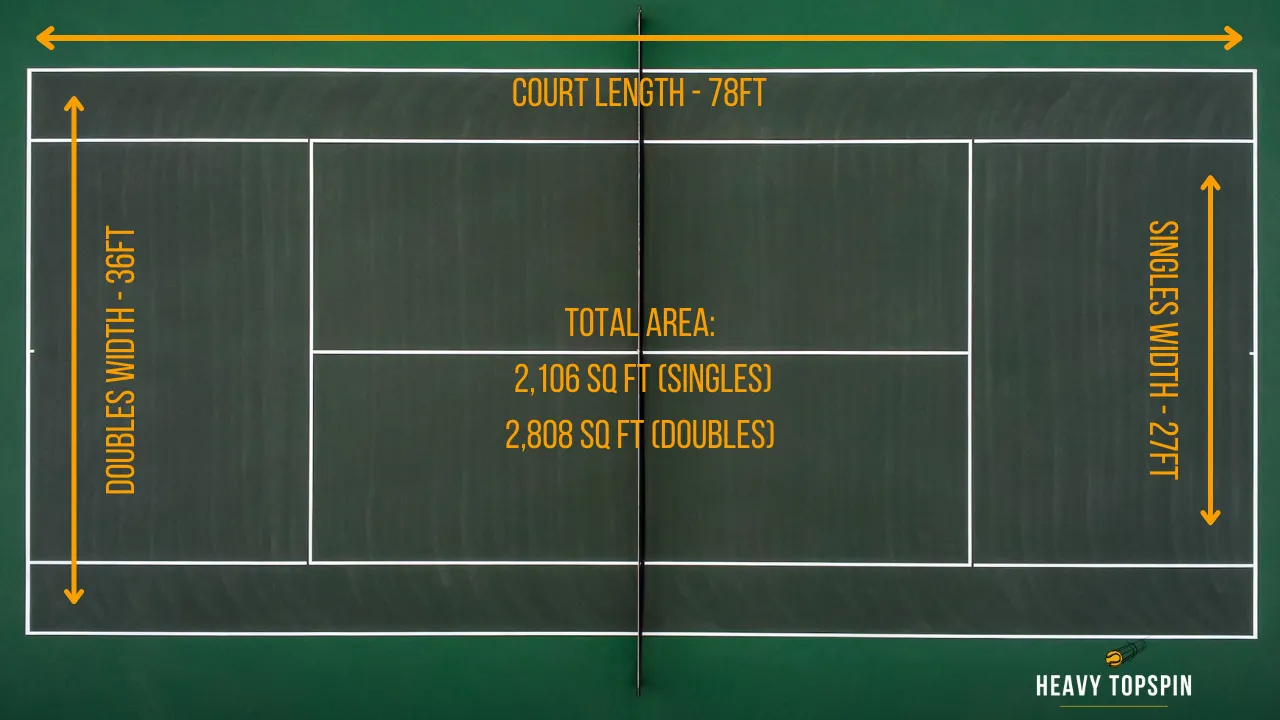
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Layout of the Tennis Court: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!