Unraveling the Secrets of Your Gut: A Comprehensive Guide to GI Map Test Results
Related Articles: Unraveling the Secrets of Your Gut: A Comprehensive Guide to GI Map Test Results
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Secrets of Your Gut: A Comprehensive Guide to GI Map Test Results. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Secrets of Your Gut: A Comprehensive Guide to GI Map Test Results
The human gut, a complex ecosystem teeming with trillions of microorganisms, plays a vital role in overall health and well-being. Understanding the intricate interplay within this microbial community is essential for identifying and addressing imbalances that can manifest as various digestive and systemic issues. The GI Map test, a comprehensive stool analysis, provides a window into the gut’s inner workings, offering valuable insights into its health and functionality.
This in-depth guide aims to demystify the complexities of GI Map test results, offering a clear and informative understanding of the various parameters assessed and their implications for individual health.
Understanding the GI Map Test: A Deeper Dive
The GI Map test, a cutting-edge stool analysis, goes beyond traditional stool tests by examining a wide range of parameters, including:
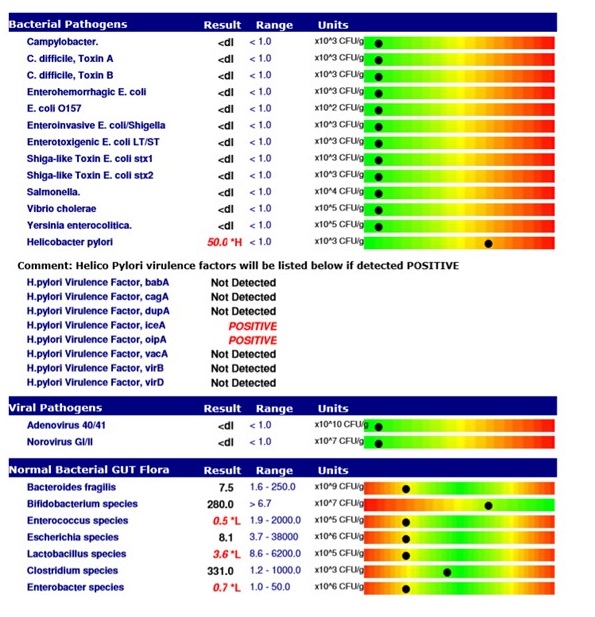
- Microbiome Analysis: This segment analyzes the composition and diversity of gut bacteria, identifying potential imbalances and dysbiosis. It assesses the presence of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, as well as potentially harmful bacteria like Clostridium difficile and E. coli.
- Digestive Enzyme Activity: The test evaluates the activity of digestive enzymes, including pancreatic enzymes (lipase, amylase, protease), which are crucial for breaking down food. Low enzyme activity can indicate maldigestion and nutrient deficiencies.
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO): This section analyzes the presence of excessive bacteria in the small intestine, which can interfere with nutrient absorption and cause digestive symptoms like bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
- Inflammation Markers: The test measures inflammatory markers such as calprotectin, a protein released by white blood cells during inflammation. Elevated levels can indicate gut inflammation or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
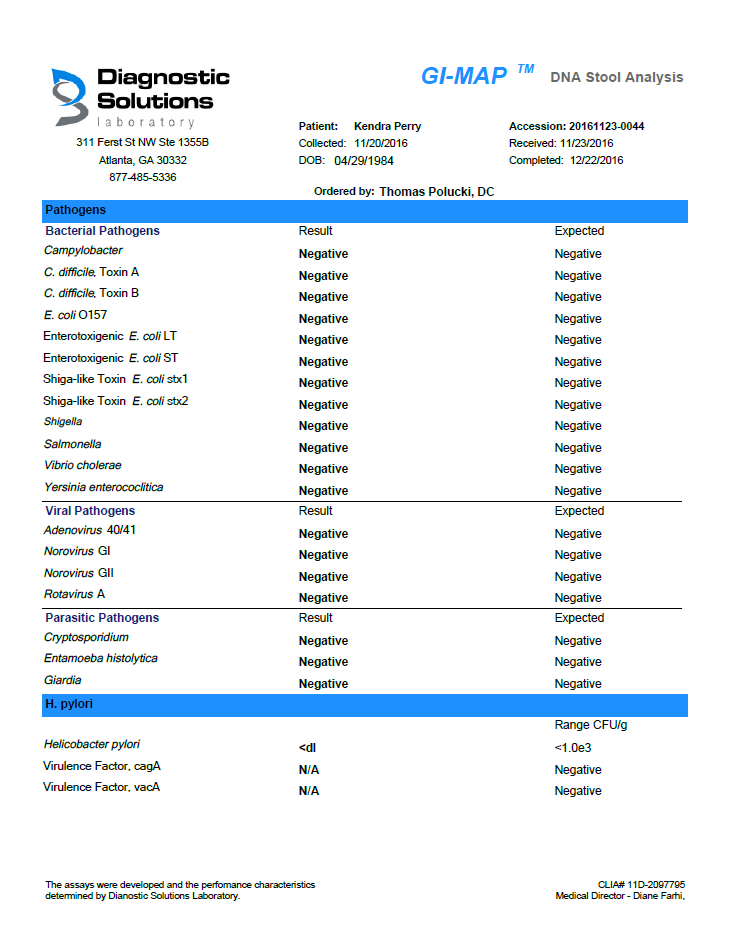
- Parasite Detection: The test screens for the presence of intestinal parasites, which can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss.
- Yeast and Fungal Overgrowth: The test examines the presence of excessive yeast and fungi, which can contribute to digestive issues, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems.
- Gut Permeability: This section assesses the integrity of the intestinal lining, which acts as a barrier against harmful substances. Increased gut permeability, also known as "leaky gut," can contribute to inflammation and autoimmune disorders.
- Digestive Markers: The test analyzes markers of digestive health, such as bile acids, which are essential for fat digestion. Abnormal bile acid levels can indicate liver dysfunction or malabsorption.
- Nutritional Markers: The test assesses markers of nutrient absorption and metabolism, such as vitamin D and folate levels. Deficiencies in these nutrients can have significant health implications.
Decoding the Results: A Comprehensive Guide
The GI Map test report is a detailed document that provides a comprehensive overview of your gut health. Understanding the various parameters and their implications requires a thorough analysis and interpretation, which is best done with the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
Here’s a breakdown of key aspects to consider when analyzing your GI Map test results:
- Microbiome Diversity: A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is crucial for optimal health. The report will highlight the relative abundance of different bacterial groups, identifying potential imbalances and areas for improvement.
- Beneficial Bacteria: The test will identify the presence of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which play a role in digestion, immune function, and overall health. Low levels of these bacteria may indicate dysbiosis and warrant intervention.
- Potentially Harmful Bacteria: The report will also identify the presence of potentially harmful bacteria, such as Clostridium difficile and E. coli. High levels of these bacteria can contribute to gut inflammation, digestive problems, and other health issues.
- Digestive Enzyme Activity: The test will assess the activity of digestive enzymes, including pancreatic enzymes. Low enzyme activity can indicate maldigestion and nutrient deficiencies, requiring dietary modifications or enzyme supplementation.
- SIBO: The test will indicate the presence or absence of SIBO. If SIBO is detected, the report will provide information on the specific types of bacteria involved and the severity of the overgrowth.
- Inflammation Markers: Elevated levels of inflammatory markers like calprotectin can indicate gut inflammation or IBD. The report will provide context for these findings and recommend further investigation if necessary.
- Parasite Detection: The report will identify the presence or absence of intestinal parasites. If parasites are detected, the report will provide information on the specific type of parasite and recommend appropriate treatment options.
- Yeast and Fungal Overgrowth: The test will indicate the presence or absence of excessive yeast and fungi. If overgrowth is detected, the report will provide information on the specific type of yeast or fungus and recommend appropriate treatment options.
- Gut Permeability: The test will assess the integrity of the intestinal lining. Increased gut permeability can be linked to various health issues. The report will provide insights into the extent of gut permeability and recommend strategies to improve gut barrier function.
- Digestive Markers: The report will analyze markers of digestive health, such as bile acids. Abnormal bile acid levels can indicate liver dysfunction or malabsorption.
- Nutritional Markers: The report will assess markers of nutrient absorption and metabolism. Deficiencies in essential nutrients can be identified and addressed through dietary changes or supplementation.
The Importance of Personalized Interpretation
It’s crucial to remember that GI Map test results are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each individual’s gut microbiome is unique, and the interpretation of results should be personalized based on individual symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle factors.
Working with a Healthcare Professional
A qualified healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist, functional medicine practitioner, or naturopathic doctor, can help you interpret your GI Map test results and develop a personalized plan to address any identified imbalances. They can:
- Analyze the results in the context of your individual health history and symptoms.
- Recommend dietary and lifestyle modifications based on the findings.
- Suggest supplements or other therapies, if necessary.
- Monitor your progress and make adjustments to your plan as needed.
FAQs About GI Map Test Results
1. What are the benefits of taking a GI Map test?
The GI Map test offers numerous benefits, including:
- Identifying underlying causes of digestive symptoms.
- Understanding the composition and diversity of your gut microbiome.
- Detecting imbalances in gut bacteria, enzymes, and other markers.
- Assessing the integrity of your gut lining and identifying potential leaks.
- Providing a personalized roadmap for improving gut health.
2. Who should consider taking a GI Map test?
Individuals experiencing persistent digestive symptoms, such as:
- Bloating, gas, and abdominal pain
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Food sensitivities or intolerances
- Fatigue, brain fog, or mood swings
- Skin issues like eczema or acne
- Autoimmune disorders
3. How do I prepare for a GI Map test?
Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions, but generally, it’s recommended to:
- Avoid certain medications or supplements that may interfere with the test results.
- Collect the stool sample according to the instructions provided.
- Store the sample properly and return it to the lab as directed.
4. How long does it take to get the results?
The turnaround time for GI Map test results can vary depending on the laboratory, but it typically takes about 2-3 weeks.
5. What are the limitations of the GI Map test?
The GI Map test is a comprehensive stool analysis, but it’s not a diagnostic test. It can identify potential imbalances and provide insights into gut health, but it cannot definitively diagnose specific conditions. Further testing or consultation with a healthcare professional may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
6. How can I improve my gut health based on my GI Map test results?
The specific recommendations for improving gut health will vary based on your individual results. However, some common strategies include:
- Dietary modifications: Focusing on a balanced diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and prebiotics can promote a healthy gut microbiome.
- Lifestyle changes: Reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly can also support gut health.
- Supplementation: Depending on the specific findings, your healthcare provider may recommend supplements such as probiotics, prebiotics, or digestive enzymes.
- Addressing underlying conditions: If your GI Map test results indicate an underlying condition, such as SIBO or IBD, your healthcare provider will work with you to address these issues.
Tips for Optimizing Gut Health Based on GI Map Test Results
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
- Make gradual changes to your diet and lifestyle.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
- Include fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi in your diet.
- Increase your intake of fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Manage stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Consider probiotics and prebiotic supplements if recommended by your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
The GI Map test provides a powerful tool for understanding the complex ecosystem of the human gut. By analyzing a wide range of parameters, it can identify potential imbalances and provide valuable insights into gut health and functionality. This information can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, working with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for improving gut health and addressing underlying issues. Remember, the key to unlocking the secrets of your gut lies in understanding the intricate workings of this vital organ and taking proactive steps to optimize its health.
![]()





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Secrets of Your Gut: A Comprehensive Guide to GI Map Test Results. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!