Unraveling the Tapestry of the Middle East: A Modern-Day Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of the Middle East: A Modern-Day Geographical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of the Middle East: A Modern-Day Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of the Middle East: A Modern-Day Geographical Perspective
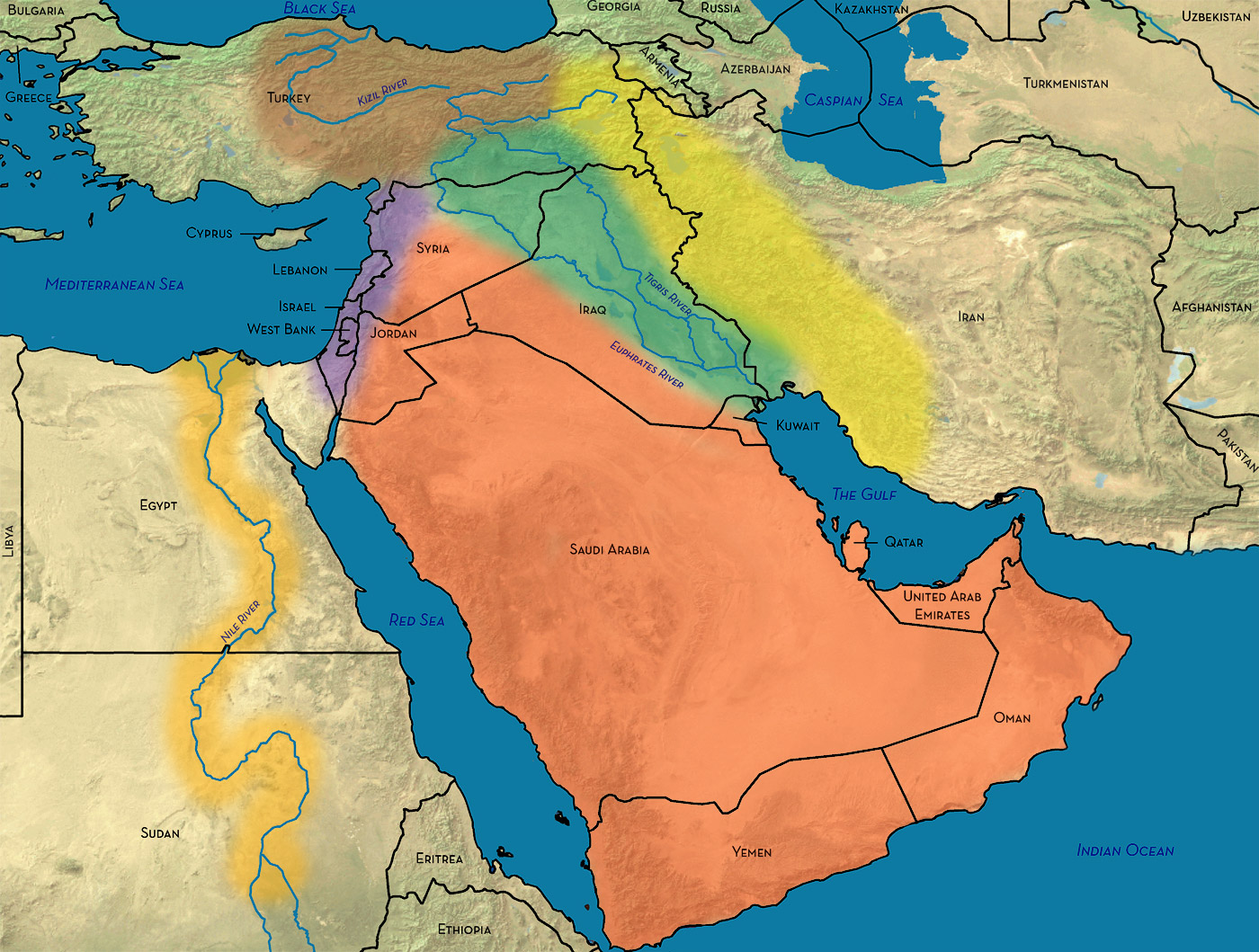
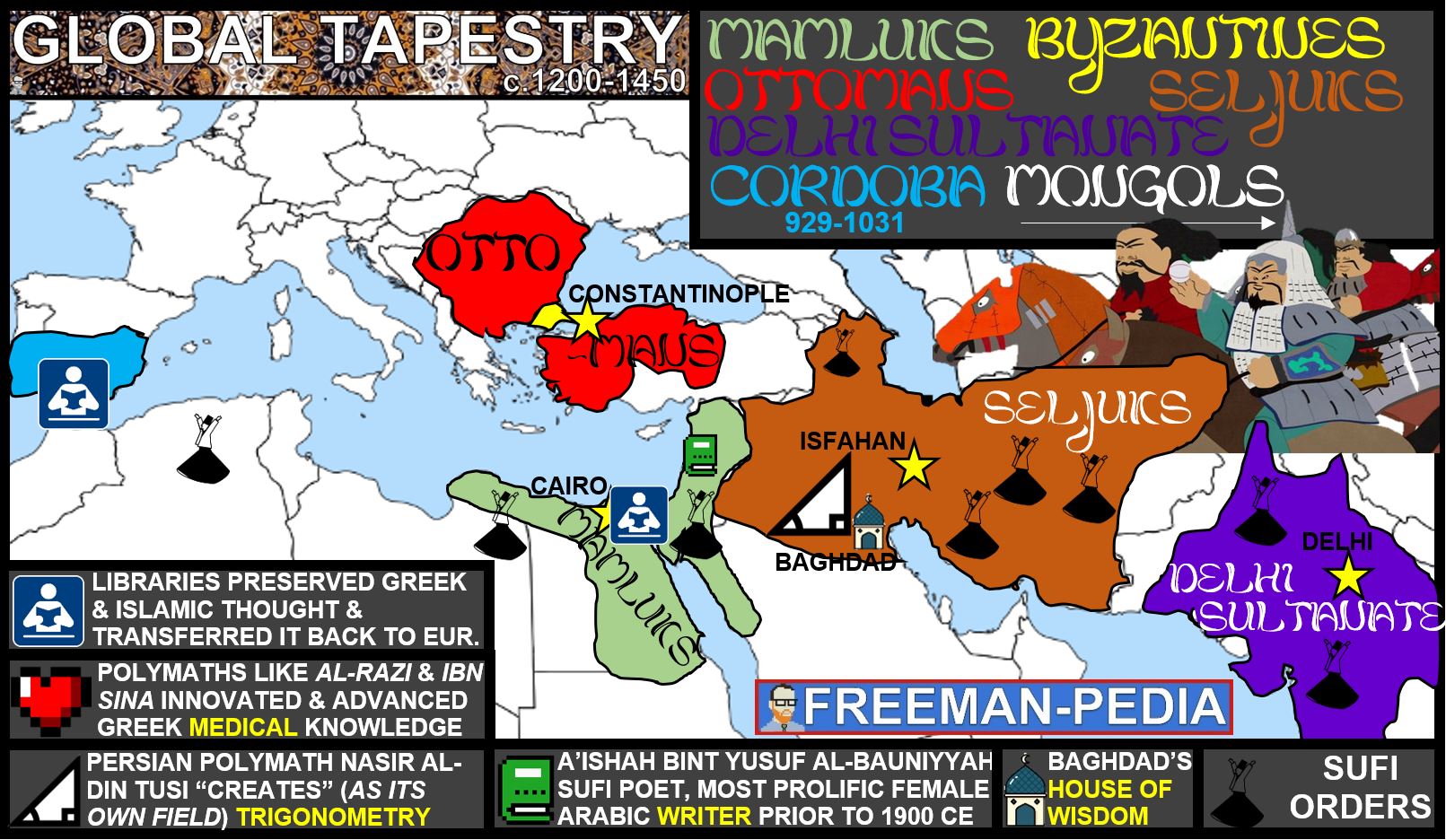
The Middle East, a region steeped in history, culture, and geopolitical significance, continues to be a dynamic and complex area of the world. Understanding its contemporary map is crucial for comprehending its diverse landscapes, intricate political dynamics, and the profound impact it has on global affairs.
Delving into the Geographic Landscape
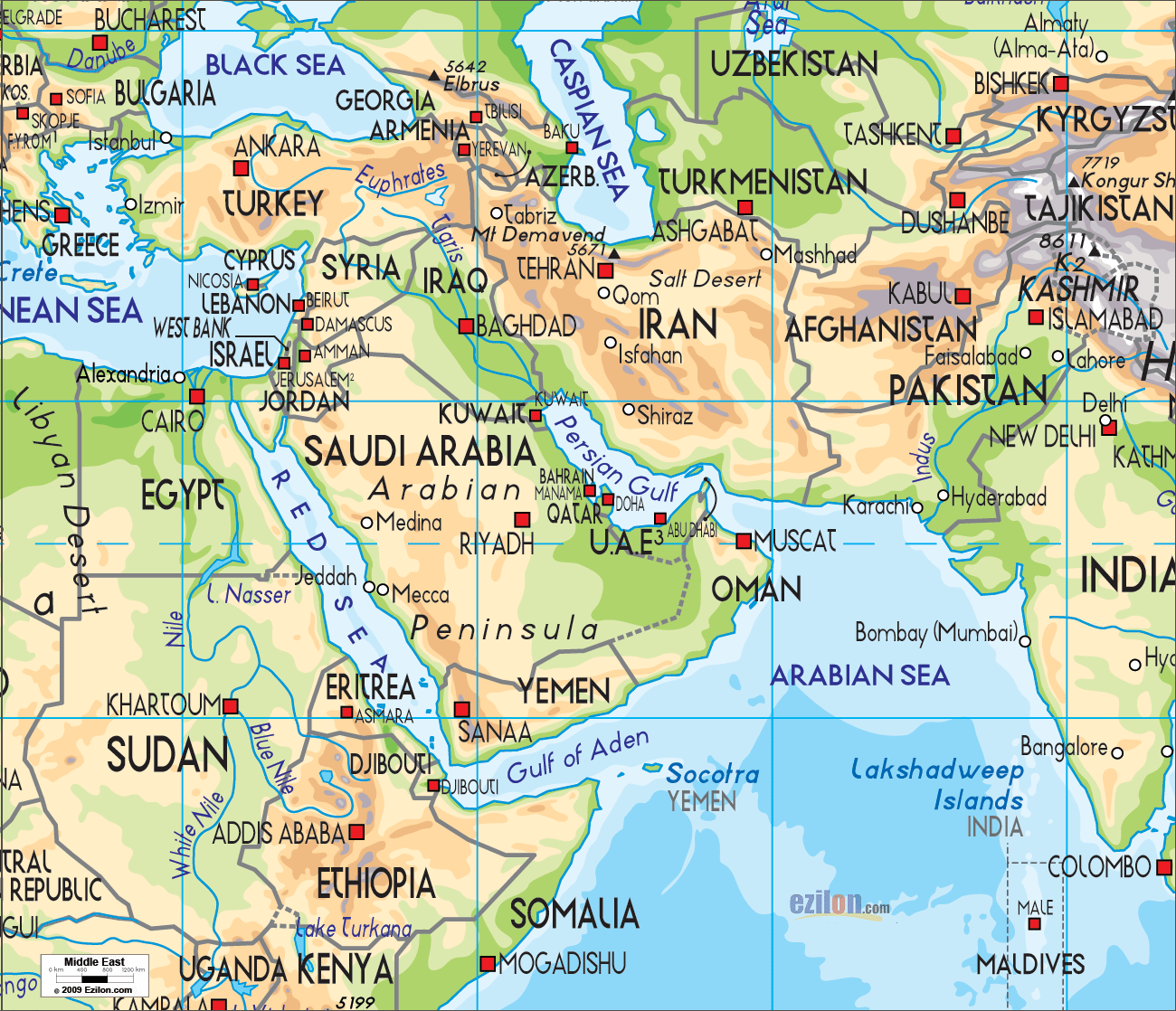
The modern-day Middle East encompasses a vast and diverse region, stretching from the eastern shores of the Mediterranean Sea to the Arabian Sea, and from the Caucasus Mountains in the north to the Horn of Africa in the south. Its geographical boundaries are fluid, with varying interpretations and definitions, but generally include:
- The Arabian Peninsula: Dominated by the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the largest country in the region, it is home to vast deserts, oil reserves, and ancient cultural sites.
- The Levant: This region encompasses the eastern Mediterranean coastline, including countries like Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, and the Palestinian territories. It is characterized by fertile plains, mountainous regions, and a rich history marked by ancient civilizations and contemporary conflicts.
- Mesopotamia: Located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, this historical region encompasses parts of Iraq, Syria, and Turkey. It is renowned for its fertile lands, ancient cities, and the cradle of civilization.
- The Persian Gulf: This strategically vital waterway is home to several oil-rich nations, including Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, and Oman. It is a major hub for global trade and energy production.
- North Africa: While not always considered part of the Middle East, countries like Egypt and Libya share cultural and historical ties with the region. They are geographically connected through the Sinai Peninsula and play a significant role in the region’s dynamics.
Understanding the Political and Cultural Tapestry
The Middle East is a region marked by political and cultural complexities. It is home to a diverse range of ethnicities, religions, and political systems, often leading to intricate and sometimes volatile interactions.
- Political Systems: The region encompasses a variety of political systems, ranging from monarchies to republics, theocracies to democracies. This diversity creates a complex political landscape, with varying levels of political stability and governance.
- Ethnic and Religious Diversity: The Middle East is a melting pot of diverse ethnicities and religions. Arabs, Kurds, Persians, Turks, and other ethnicities coexist, each with their own distinct cultural identities. Islam, Christianity, Judaism, and other faiths have shaped the region’s history and continue to influence its present.
- Geopolitical Challenges: The Middle East is often considered a "hotspot" due to its intricate geopolitical challenges. Conflicts, territorial disputes, and regional rivalries have been defining features of the region’s history.
The Importance of the Middle East in the 21st Century
The Middle East’s importance in the 21st century is undeniable. Its strategic location, vast energy reserves, and cultural significance make it a key player in global affairs.
- Energy Resources: The region holds approximately 60% of the world’s proven oil reserves and significant natural gas reserves. This makes it a crucial player in global energy markets and influences international relations.
- Global Trade: The Middle East is a critical hub for global trade routes, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe. Its strategic location makes it a vital corridor for goods and services.
- Cultural Influence: The Middle East’s rich cultural heritage, encompassing art, literature, music, and cuisine, has influenced global culture and continues to captivate audiences worldwide.
FAQs about the Modern-Day Map of the Middle East
1. What are the major geographical features of the Middle East?
The Middle East is characterized by diverse geographical features, including vast deserts, fertile plains, mountainous regions, and crucial waterways like the Nile River, the Persian Gulf, and the Red Sea.
2. What are the main ethnic groups in the Middle East?
The Middle East is home to a multitude of ethnic groups, including Arabs, Kurds, Persians, Turks, Armenians, and many others, each with their distinct cultural identities.
3. What are the major religions practiced in the Middle East?
Islam, Christianity, and Judaism are the dominant religions in the Middle East, with varying denominations and sects influencing the region’s cultural landscape.
4. What are some of the major geopolitical challenges facing the Middle East?
The Middle East faces numerous geopolitical challenges, including conflicts, territorial disputes, political instability, economic disparities, and the rise of extremist ideologies.
5. How does the Middle East influence global affairs?
The Middle East’s vast energy reserves, strategic location, and cultural significance make it a major player in global affairs, influencing international relations, trade, and security.
Tips for Understanding the Modern-Day Map of the Middle East
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from various sources, including academic journals, news reports, and cultural perspectives, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Focus on historical context: Understand the historical events and developments that have shaped the region’s current landscape.
- Recognize cultural diversity: Appreciate the rich cultural tapestry of the Middle East, encompassing languages, traditions, and artistic expressions.
- Stay informed about current events: Follow news and developments in the region to stay updated on ongoing issues and geopolitical shifts.
- Engage in respectful dialogue: Approach discussions about the Middle East with sensitivity and respect for diverse viewpoints.
Conclusion
The modern-day map of the Middle East is a dynamic and complex tapestry, reflecting a region rich in history, culture, and geopolitical significance. Understanding its geographical features, political dynamics, and cultural diversity is crucial for comprehending its impact on the world stage. As a region with immense energy resources, strategic location, and cultural influence, the Middle East continues to be a focal point of global attention, demanding a nuanced and informed approach to its understanding.
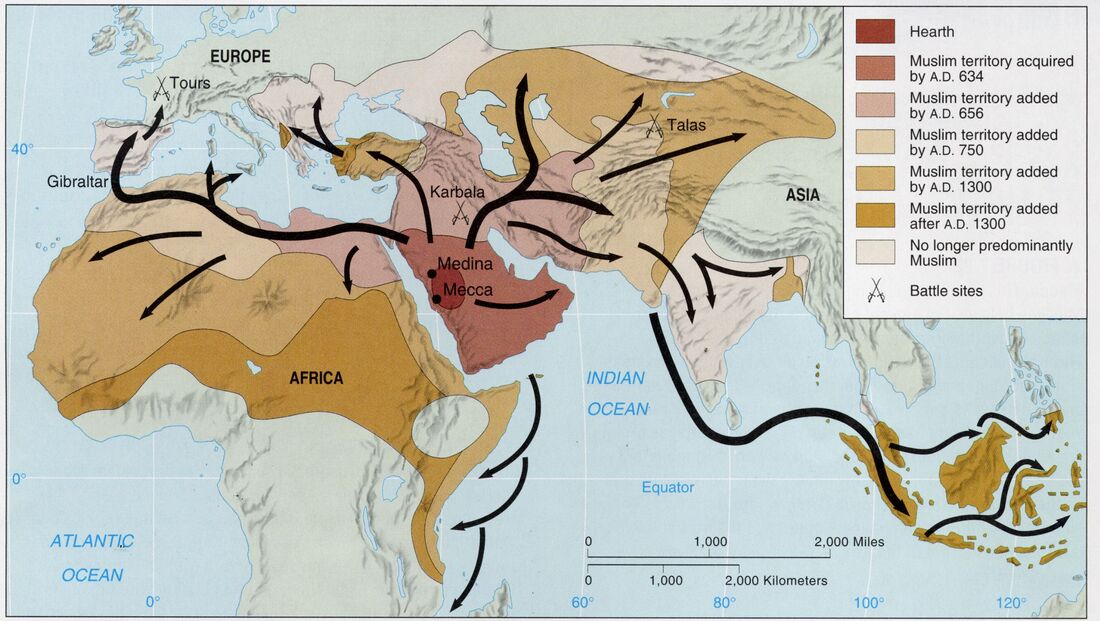

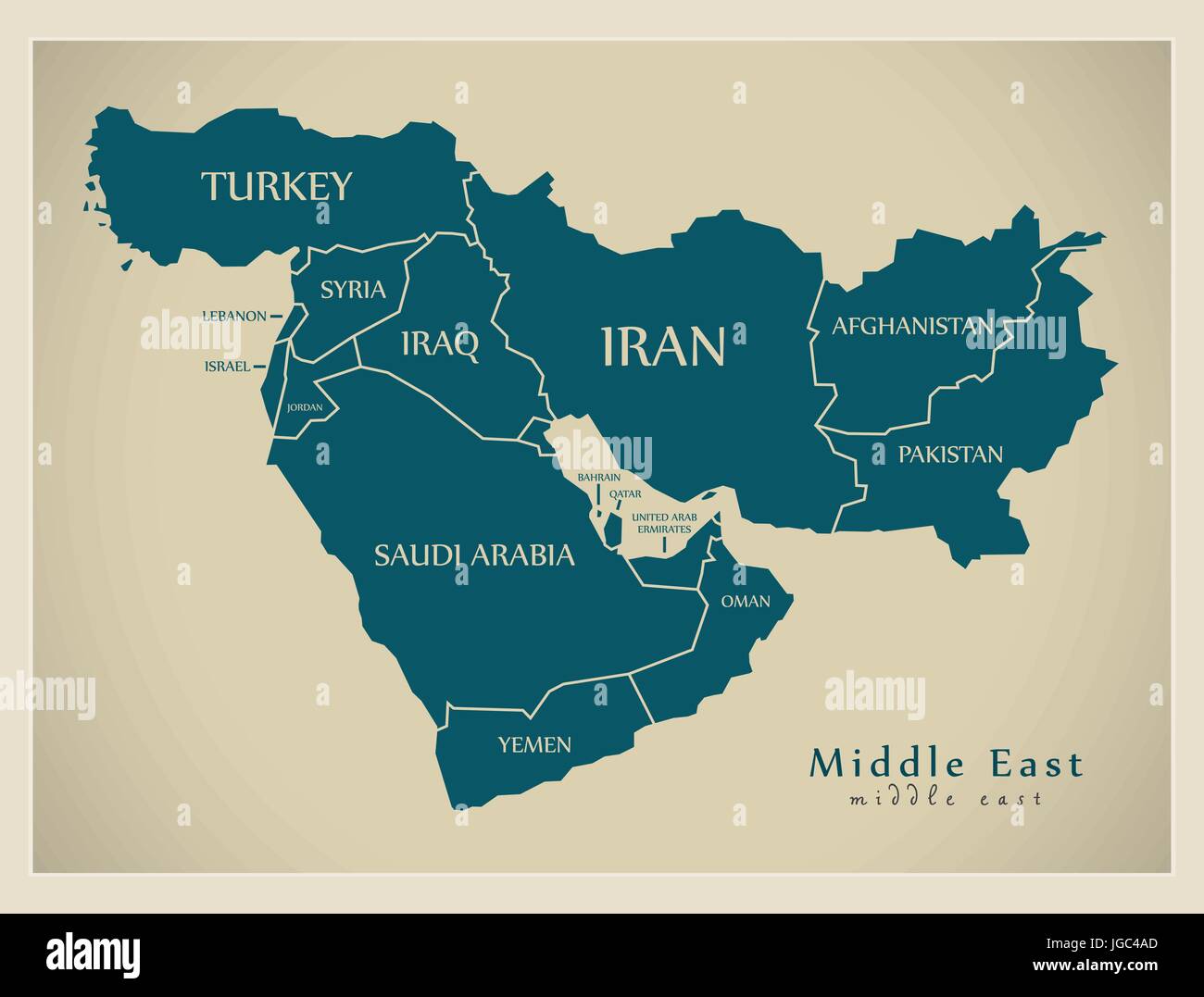
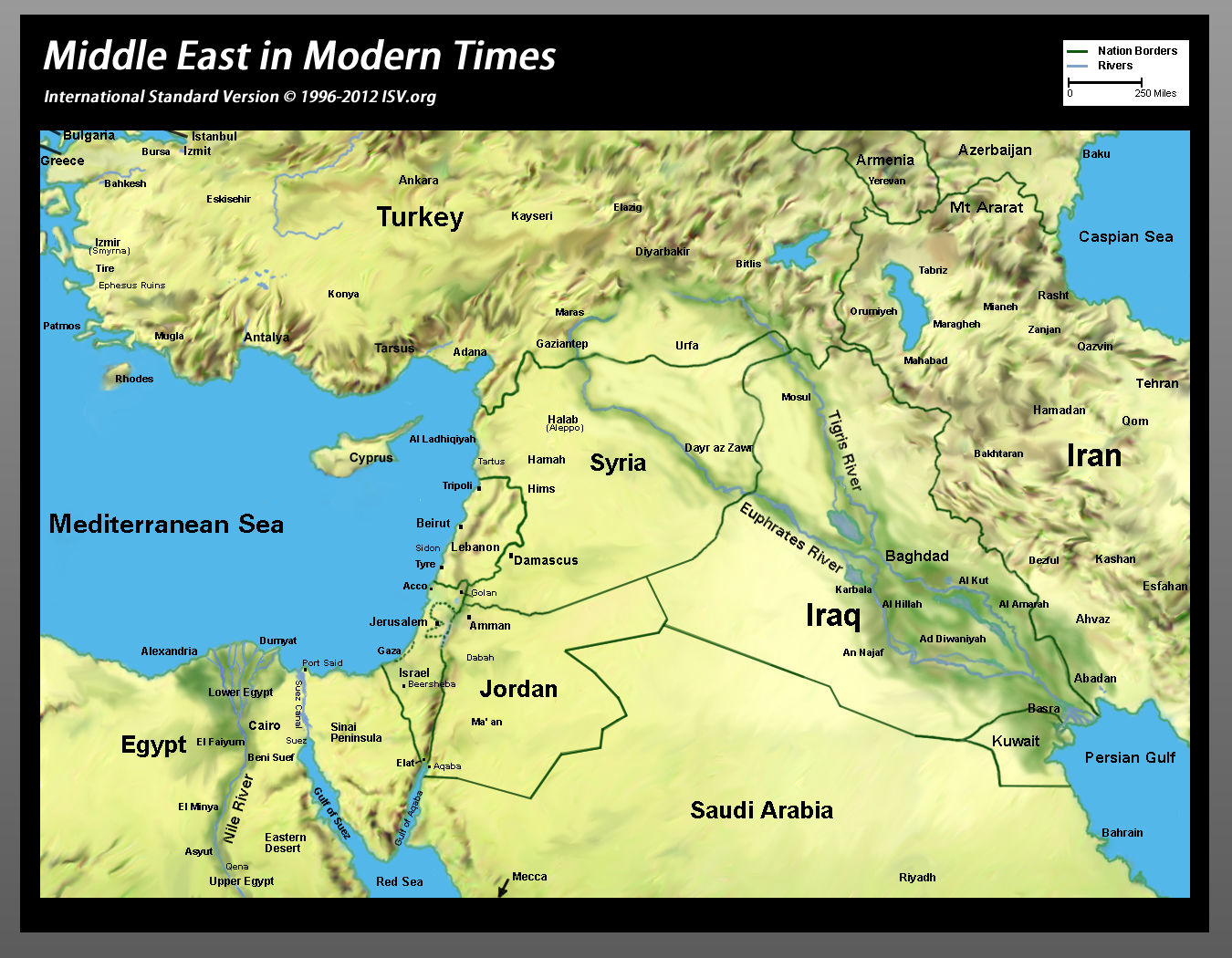


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of the Middle East: A Modern-Day Geographical Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!