Unveiling the Diverse Topography of Africa: A Comprehensive Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Topography of Africa: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Topography of Africa: A Comprehensive Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Topography of Africa: A Comprehensive Exploration

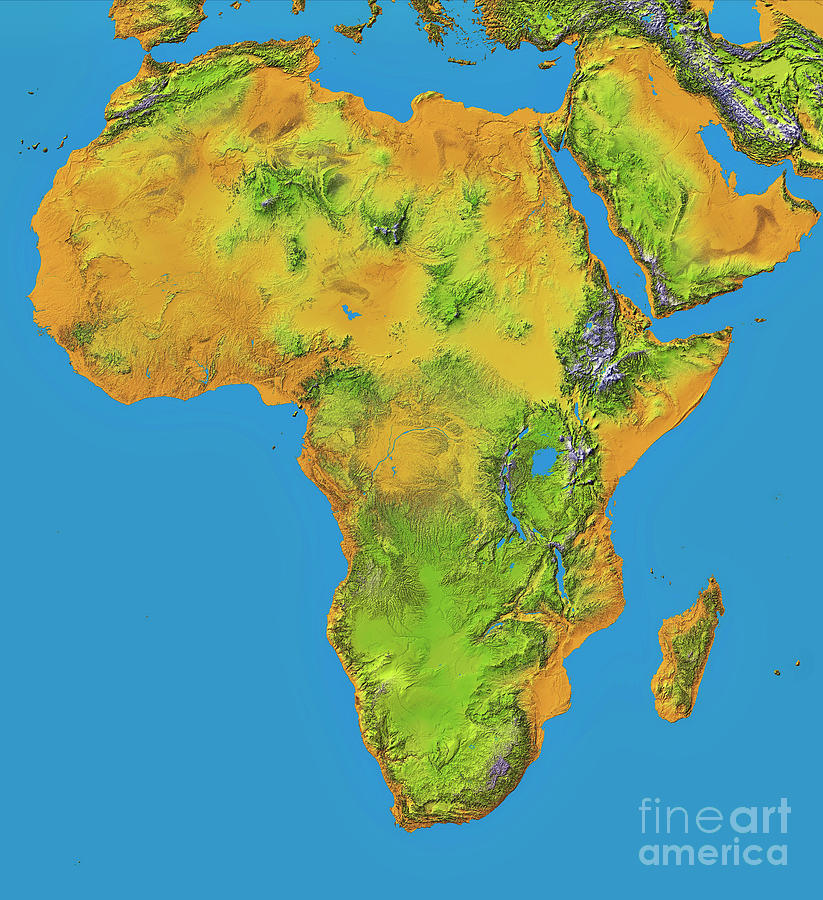
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes, each shaped by unique geological forces and environmental influences. From the towering peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, the African terrain showcases an incredible range of geographical features that have profoundly impacted the continent’s history, culture, and development. This exploration delves into the intricate details of Africa’s terrain, highlighting its key characteristics and the factors that have contributed to its remarkable diversity.
A Continent of Contrasts: Understanding the Terrain
Africa’s terrain can be broadly categorized into several distinct geographical regions, each with its own unique characteristics:
1. The Great Escarpment: A defining feature of Africa’s landscape, the Great Escarpment is a series of cliffs and plateaus that runs along the eastern and southern edges of the continent. This geological formation is a result of tectonic uplift and erosion, forming a dramatic barrier between the interior highlands and the coastal plains. The escarpment plays a vital role in shaping rainfall patterns, influencing biodiversity, and creating distinct microclimates across Africa.
2. The Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, the Sahara Desert dominates North Africa, covering an area of over 9 million square kilometers. Its arid climate, characterized by extreme temperatures, sparse vegetation, and limited rainfall, is a result of its location within the Hadley Cell circulation pattern. The Sahara’s harsh environment has shaped the lives of its inhabitants, forcing them to adapt to its challenges and develop unique survival strategies.
3. The Sahel: A semi-arid region bordering the Sahara Desert, the Sahel experiences a transition zone between the desert’s harsh conditions and the more humid savannas to the south. It is characterized by a fragile ecosystem, vulnerable to desertification, and prone to frequent droughts. The Sahel’s ecological challenges have become increasingly prominent in recent years, highlighting the impact of climate change on the region’s environment and livelihoods.
4. The Savannas: Stretching across vast areas of central and southern Africa, the savannas are characterized by grasslands interspersed with scattered trees. This region is home to a rich biodiversity, including iconic animals like lions, elephants, and giraffes. The savannas are influenced by seasonal rainfall patterns, resulting in distinct wet and dry seasons that impact the vegetation and animal populations.
5. The Congo Basin: This region encompasses the Congo River and its surrounding rainforest, the second-largest rainforest in the world. The Congo Basin is known for its dense vegetation, high humidity, and rich biodiversity, supporting a wide range of plant and animal life. The basin’s immense rainforest plays a vital role in regulating global climate, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen.
6. The Mountains: Africa is home to several mountain ranges, including the Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Ethiopian Highlands, and the Drakensberg Mountains in South Africa. These mountain ranges are characterized by their elevation, rugged terrain, and diverse microclimates. They play a significant role in influencing rainfall patterns, supporting unique ecosystems, and providing resources for local communities.
The Impact of Terrain on Africa’s Development
Africa’s diverse terrain has played a crucial role in shaping the continent’s history, culture, and development. The following points highlight some of the key impacts:
-
Agriculture and Food Security: Africa’s terrain influences agricultural practices and food security. The fertile soils of the savannas and river valleys support a wide range of crops, while the mountainous regions provide opportunities for livestock grazing. However, challenges like desertification in the Sahel and soil erosion in other areas pose threats to agricultural productivity and food security.
-
Water Resources and Hydropower: Africa’s terrain plays a significant role in shaping its water resources and hydropower potential. The Great Escarpment, for example, creates waterfalls and rapids, providing opportunities for hydroelectric power generation. However, the continent also faces challenges related to water scarcity, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions, requiring sustainable management strategies.
-
Biodiversity and Conservation: Africa’s diverse terrain is home to a remarkable array of biodiversity, including a vast array of plant and animal species. The continent’s rich ecosystems, from rainforests to savannas, are vital for global biodiversity and require careful conservation efforts to protect them from threats like habitat loss and climate change.
-
Transportation and Infrastructure: Africa’s terrain poses challenges to transportation and infrastructure development. Mountainous regions can be difficult to access, while vast deserts and dense rainforests present obstacles to road and rail construction. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for promoting economic development and connecting communities across the continent.
-
Cultural Diversity and Identity: Africa’s terrain has influenced the development of distinct cultures and identities across the continent. The unique adaptations and traditions of communities living in different landscapes, from the nomadic tribes of the Sahara to the fishing communities of the coastal regions, reflect the influence of their environment.
FAQs about Africa’s Terrain
1. What are the highest and lowest points in Africa?
The highest point in Africa is Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania, reaching an elevation of 5,885 meters (19,308 feet). The lowest point is Lake Assal in Djibouti, which lies 155 meters (509 feet) below sea level.
2. What are the major rivers in Africa?
Africa is home to several major rivers, including the Nile, the Congo, the Niger, and the Zambezi. These rivers play a vital role in the continent’s water resources, transportation, and agriculture.
3. What are the main geological formations in Africa?
Africa’s terrain is characterized by a variety of geological formations, including the Great Escarpment, the Sahara Desert, the Rift Valley, and the Atlas Mountains. These formations have shaped the continent’s landscape and influenced its environmental and cultural diversity.
4. How does climate change affect Africa’s terrain?
Climate change is having a significant impact on Africa’s terrain, leading to increased desertification, rising sea levels, and more frequent droughts. These changes pose threats to the continent’s ecosystems, agriculture, and water resources.
5. What are some of the challenges and opportunities related to Africa’s terrain?
Africa’s diverse terrain presents both challenges and opportunities. Challenges include the difficulty of accessing remote areas, the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change, and the need for sustainable resource management. Opportunities include the potential for hydropower generation, the rich biodiversity, and the potential for tourism and ecotourism.
Tips for Understanding Africa’s Terrain
-
Utilize Maps and Satellite Imagery: Explore detailed maps and satellite imagery to visualize Africa’s diverse terrain and understand the distribution of its key geographical features.
-
Read Books and Articles: Engage with academic literature, travelogues, and other resources to gain deeper insights into the history, geography, and culture of Africa’s different regions.
-
Watch Documentaries and Films: Immerse yourself in documentaries and films that explore the continent’s diverse landscapes and the challenges and opportunities they present.
-
Travel and Experience: If possible, embark on a journey to Africa and experience its diverse terrain firsthand. Witnessing the beauty and complexity of its landscapes will enhance your understanding and appreciation.
Conclusion
Africa’s terrain is a testament to the power of geological forces and the diversity of life on Earth. From the towering peaks of its mountains to the vast expanse of its deserts, the continent’s landscapes have shaped its history, culture, and development. Understanding the intricacies of Africa’s terrain is crucial for appreciating its unique characteristics, addressing its challenges, and harnessing its potential for sustainable development. By engaging with the diverse facets of this remarkable continent, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the importance of protecting its natural wonders.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Topography of Africa: A Comprehensive Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!