Unveiling the Geography of Greece: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unveiling the Geography of Greece: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Geography of Greece: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Geography of Greece: A Comprehensive Guide

Greece, a nation steeped in history and renowned for its stunning landscapes, is a captivating destination that draws travelers from around the globe. Understanding its geography is key to appreciating the country’s diverse offerings, from ancient ruins to pristine beaches. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Greece’s geographical features, exploring its unique topography, regional distinctions, and the significance of its location.
A Land Shaped by Time and Tectonics:
Greece’s geography is a testament to its dynamic geological history. The country is located at the crossroads of three continents – Europe, Asia, and Africa – and sits atop the complex tectonic plates that have shaped its landscape over millennia. This dynamic interplay of tectonic forces has resulted in a land characterized by:
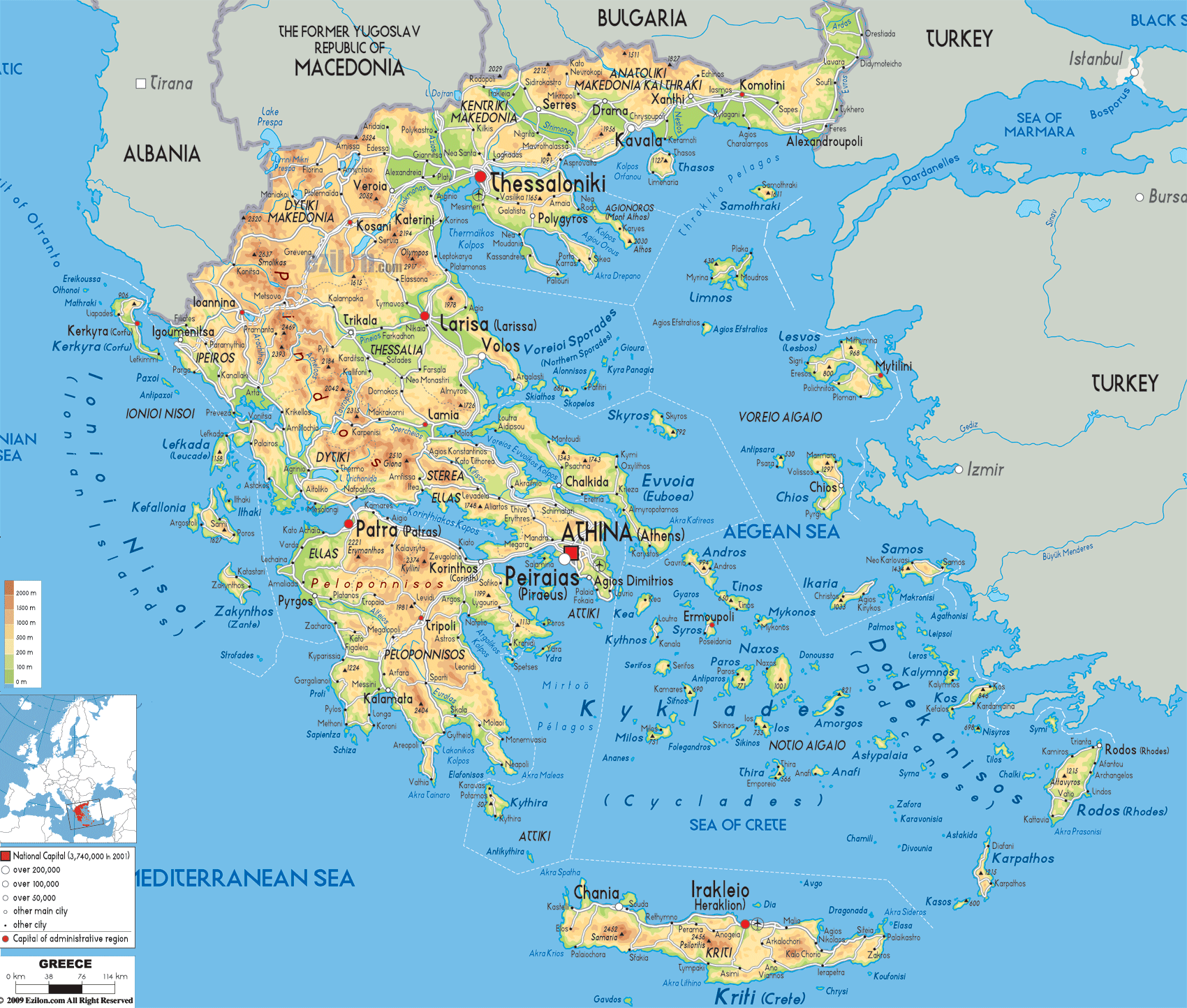
- Mountainous Terrain: The Greek mainland is dominated by a series of mountain ranges, including the Pindus Mountains, the Rhodope Mountains, and the Peloponnese Mountains. These towering peaks, reaching elevations of over 2,900 meters, create a dramatic and varied landscape.
- Island Archipelago: Greece is home to thousands of islands, with over 200 inhabited. These islands are scattered across the Aegean, Ionian, and Mediterranean Seas, offering a diverse range of experiences, from bustling ports to secluded coves.
- Coastal Landscapes: The extensive coastline of Greece stretches over 13,676 kilometers, providing a wealth of opportunities for exploring hidden beaches, quaint fishing villages, and vibrant coastal cities.
- Rich Biodiversity: The diverse geography of Greece supports a rich tapestry of plant and animal life. From the iconic olive groves and vineyards to the diverse ecosystems of its islands, Greece boasts a remarkable biodiversity.
Exploring Regional Distinctions:
Greece is divided into 13 administrative regions, each with its own distinct character and attractions:
- Attica: Home to the capital city of Athens, Attica is a region of ancient history, bustling urban life, and scenic landscapes.
- Central Greece: This region encompasses the Pindus Mountains, Delphi, and the iconic Meteora monasteries, offering a blend of natural beauty and historical significance.
- Peloponnese: The southern peninsula of Greece, the Peloponnese is known for its ancient sites, charming villages, and picturesque coastline.
- Thessaly: This region is home to the fertile plains of Thessaly, ancient cities, and the legendary Mount Olympus.
- Epirus: Nestled in the northwest, Epirus is a region of rugged mountains, picturesque villages, and ancient ruins.
- Western Greece: This region encompasses the Ionian Islands, known for their stunning beaches, Venetian architecture, and verdant landscapes.
- Central Macedonia: This region is home to the city of Thessaloniki, a vibrant cultural hub, and the historic Pella, the ancient capital of Macedon.
- Eastern Macedonia and Thrace: This region borders Turkey and Bulgaria and is known for its rich history, diverse landscapes, and ancient sites.
- Thessaloniki: This region comprises the city of Thessaloniki, a vibrant cultural center with a rich history and diverse population.
- Crete: The largest of the Greek islands, Crete is a destination of myth and legend, boasting ancient ruins, stunning beaches, and a rich cultural heritage.
- South Aegean: This region encompasses the Cyclades and Dodecanese islands, known for their white-washed villages, stunning beaches, and vibrant nightlife.
- North Aegean: This region is home to the islands of Lesbos, Samos, and Chios, known for their unique landscapes, historical sites, and rich cultural traditions.
- Ionian Islands: This region encompasses the islands of Corfu, Zakynthos, Kefalonia, and Lefkada, renowned for their stunning beaches, Venetian architecture, and verdant landscapes.
The Significance of Greece’s Location:
Greece’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa has played a pivotal role in its history and development. This strategic position has:
- Facilitated Trade and Cultural Exchange: Greece has served as a bridge between different cultures and civilizations, fostering trade and cultural exchange throughout history.
- Shaped Political and Military History: Greece’s location has made it a key player in regional and international conflicts, shaping its political and military history.
- Influenced Art and Architecture: Greece’s unique location and diverse cultural influences have contributed to its rich artistic and architectural heritage.
Understanding the Benefits of Exploring Greece’s Geography:
A deeper understanding of Greece’s geography unlocks a wealth of benefits for travelers and scholars alike:
- Enhanced Travel Experiences: Knowing the geographical features of Greece allows travelers to plan itineraries that maximize their experiences, from exploring ancient ruins to hiking through mountainous landscapes.
- Greater Appreciation for History and Culture: Understanding the geographical context of Greece’s history and culture provides a richer understanding of its ancient civilizations, myths, and traditions.
- Informed Decision Making: Knowledge of Greece’s geography enables informed decision-making regarding travel, accommodation, and activities, ensuring a more fulfilling and enjoyable experience.
FAQs about the Geography of Greece:
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Greece?
A: The major mountain ranges in Greece include the Pindus Mountains, the Rhodope Mountains, the Peloponnese Mountains, and Mount Olympus.
Q: How many islands are there in Greece?
A: Greece has over 6,000 islands, with over 200 inhabited.
Q: What are the main geographical regions of Greece?
A: Greece is divided into 13 administrative regions, each with its own distinct character and attractions. These regions include Attica, Central Greece, Peloponnese, Thessaly, Epirus, Western Greece, Central Macedonia, Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, Thessaloniki, Crete, South Aegean, North Aegean, and Ionian Islands.
Q: What is the significance of Greece’s location?
A: Greece’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa has played a pivotal role in its history and development. This location has facilitated trade and cultural exchange, shaped political and military history, and influenced art and architecture.
Tips for Exploring Greece’s Geography:
- Embrace the Islands: Take advantage of the diverse island archipelago, exploring each island’s unique character and attractions.
- Explore the Mainland: Venture beyond the islands and discover the beauty and history of the Greek mainland, including its mountains, plains, and ancient sites.
- Use Maps and Guides: Utilize maps and travel guides to plan itineraries and understand the geographical context of your destinations.
- Engage with Local Experts: Seek out local guides and experts to gain deeper insights into the geography, history, and culture of the regions you visit.
Conclusion:
The geography of Greece is a tapestry woven from millennia of geological forces, cultural influences, and historical events. Understanding its diverse landscapes, regional distinctions, and strategic location enriches the travel experience, providing a deeper appreciation for the country’s rich history, vibrant culture, and natural beauty. By embracing the geographical context, travelers can unlock the secrets of this captivating nation, forging unforgettable memories and gaining a profound appreciation for its unique charm.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Geography of Greece: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
.PNG)