Unveiling the Power of Business Process Maps: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Business Process Maps: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Business Process Maps: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Business Process Maps: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
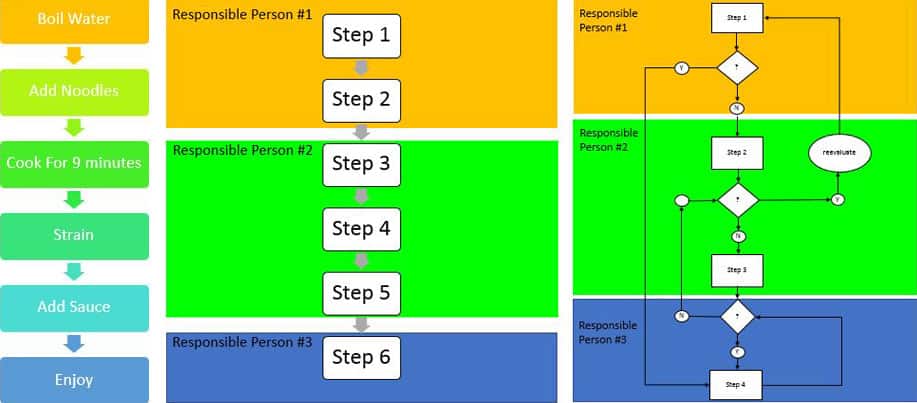
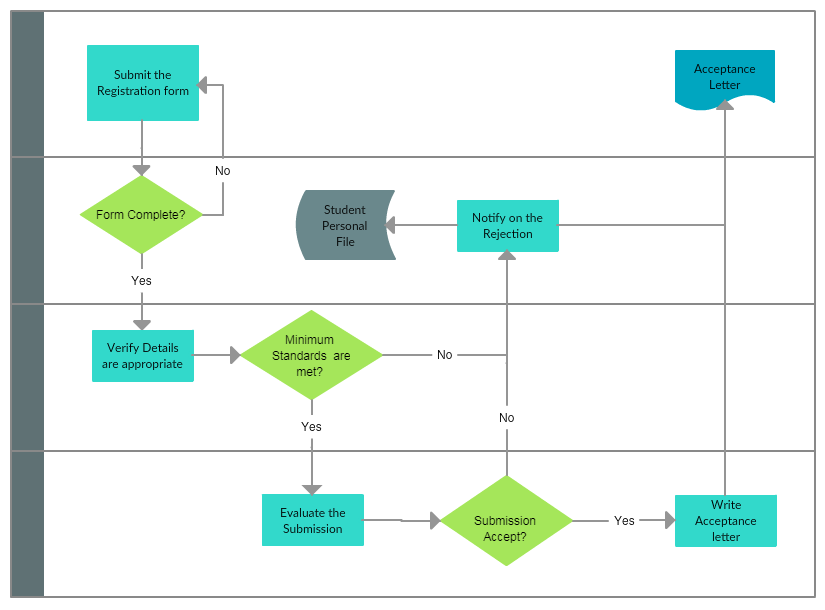
In the intricate tapestry of modern business, efficiency and clarity are paramount. Business process maps, often referred to as process flowcharts, serve as the visual blueprints that illuminate the intricate pathways of operations, offering a clear understanding of how tasks flow from start to finish. These maps are not mere diagrams; they are powerful tools that empower businesses to streamline processes, identify bottlenecks, and foster continuous improvement. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of business process maps, exploring their significance, diverse applications, and practical examples.
Understanding the Essence of Business Process Maps
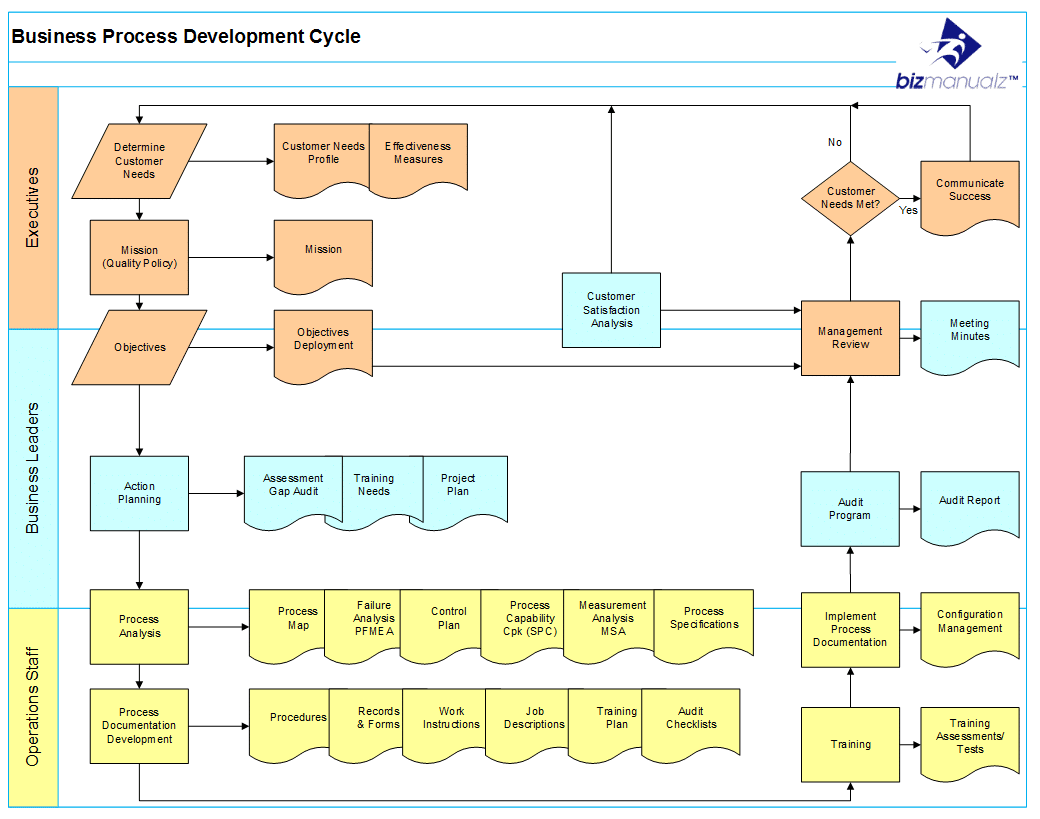
A business process map is a graphical representation of a sequence of activities or tasks, showcasing their logical order and interdependencies. They provide a visual narrative of how work gets done within an organization, highlighting key steps, decision points, and the individuals or departments involved.
The Multifaceted Benefits of Business Process Maps
The value of business process maps extends far beyond mere visualization. They serve as catalysts for significant improvements across various aspects of an organization:
- Enhanced Visibility and Understanding: Maps offer a clear, concise overview of how processes function, promoting transparency and fostering a shared understanding among team members.
- Improved Efficiency and Streamlining: By identifying redundant steps, unnecessary delays, and areas prone to errors, process maps facilitate streamlining, leading to increased efficiency and reduced wasted effort.
- Effective Communication and Collaboration: Visual representations simplify complex processes, enabling seamless communication and collaboration between departments and teams.
- Enhanced Process Control and Standardization: Maps establish clear guidelines for performing tasks, ensuring consistency and adherence to established procedures, minimizing variations and improving overall quality.
- Identification of Bottlenecks and Areas for Improvement: By pinpointing areas where processes slow down or encounter difficulties, maps provide valuable insights for optimization and improvement.
- Facilitating Automation and Digital Transformation: Process maps serve as a foundation for automating repetitive tasks and integrating technology, accelerating digital transformation efforts.
- Compliance and Regulatory Adherence: Maps ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards by clearly outlining procedures and accountability.
Exploring Diverse Business Process Map Examples
To illustrate the versatility and practical application of business process maps, let’s explore examples across various industries:
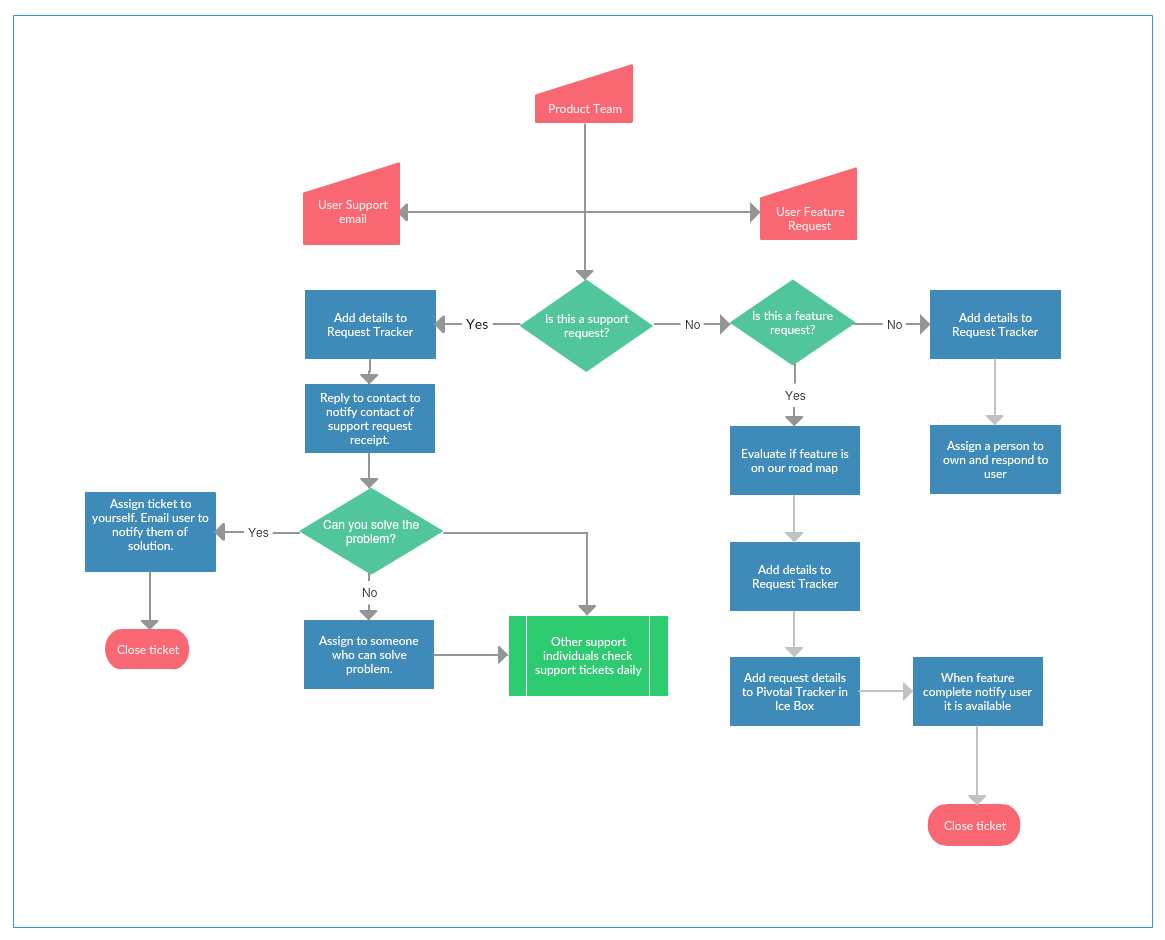
1. Customer Service Process Map:
- Objective: Streamline customer interactions and ensure a positive experience.
- Process: Depicts the flow of a customer’s request, from initial contact to resolution, including steps like inquiry submission, ticket assignment, communication with the customer, resolution, and satisfaction feedback.
- Benefits: Reduces resolution time, enhances customer satisfaction, and standardizes customer service procedures.
2. Product Development Process Map:
- Objective: Ensure efficient product development and timely market launch.
- Process: Outlines the stages from ideation to product launch, including market research, product design, prototyping, testing, manufacturing, and marketing.
- Benefits: Improves collaboration between departments, optimizes resource allocation, and reduces time-to-market.
3. Order Fulfillment Process Map:
- Objective: Ensure accurate and timely order fulfillment.
- Process: Depicts the journey of an order, from placement to delivery, including steps like order processing, inventory management, packaging, shipping, and tracking.
- Benefits: Reduces errors, minimizes delays, and enhances customer satisfaction through efficient order handling.
4. Employee Onboarding Process Map:
- Objective: Facilitate a smooth and effective onboarding experience for new employees.
- Process: Outlines the steps involved in welcoming new hires, including paperwork completion, orientation, training, and performance evaluation.
- Benefits: Improves employee retention, enhances productivity, and fosters a positive work environment.
5. Financial Reporting Process Map:
- Objective: Ensure accurate and timely financial reporting.
- Process: Depicts the steps involved in generating financial statements, including data collection, analysis, reconciliation, and reporting.
- Benefits: Improves transparency, enhances financial accountability, and facilitates informed decision-making.
6. Marketing Campaign Process Map:
- Objective: Ensure a successful and impactful marketing campaign.
- Process: Outlines the stages of a marketing campaign, including planning, execution, monitoring, and evaluation.
- Benefits: Optimizes campaign effectiveness, maximizes return on investment, and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
7. Project Management Process Map:
- Objective: Ensure successful project completion within defined timelines and budgets.
- Process: Depicts the project lifecycle, including initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
- Benefits: Improves project visibility, enhances resource allocation, and facilitates effective project management.
8. Software Development Process Map:
- Objective: Ensure efficient and quality software development.
- Process: Outlines the stages of software development, including requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
- Benefits: Improves collaboration between developers, enhances code quality, and accelerates software development cycles.
9. Supply Chain Management Process Map:
- Objective: Optimize the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers.
- Process: Depicts the entire supply chain, including sourcing, procurement, production, distribution, and delivery.
- Benefits: Reduces costs, minimizes delays, and enhances supply chain visibility and responsiveness.
10. Human Resources Process Map:
- Objective: Streamline HR processes and ensure effective talent management.
- Process: Outlines HR functions, including recruitment, onboarding, performance management, compensation, and employee relations.
- Benefits: Optimizes HR operations, enhances employee engagement, and improves overall workforce productivity.
FAQs about Business Process Maps
1. What are the different types of business process maps?
Business process maps can be categorized based on their level of detail and purpose:
- High-Level Process Maps: Provide a broad overview of the process, showcasing major steps and decision points.
- Detailed Process Maps: Offer a granular view of the process, including specific tasks, inputs, outputs, and responsibilities.
- Swimlane Process Maps: Depict the process flow by dividing activities into lanes representing different departments or roles.
- Cross-Functional Process Maps: Illustrate how different departments or teams interact within a process.
- Value Stream Maps: Focus on identifying value-adding activities and eliminating waste.
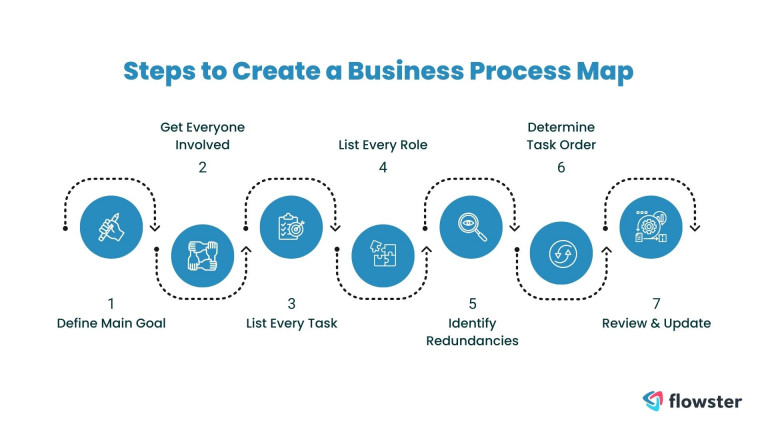
2. How do I create a business process map?
Creating a business process map involves several steps:
- Define the Scope: Identify the specific process you want to map.
- Gather Information: Collect data on the process, including tasks, inputs, outputs, and involved parties.
- Choose a Mapping Method: Select a suitable mapping method, such as flowcharting, BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation), or SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers).
- Map the Process: Create a visual representation of the process, including steps, decision points, and responsibilities.
- Review and Validate: Ensure accuracy and completeness, seeking feedback from stakeholders.
- Document and Maintain: Store the map in a readily accessible format and update it as needed.
3. What software tools can I use for creating business process maps?
Numerous software tools facilitate business process mapping, offering features like drag-and-drop functionality, collaboration tools, and integration with other business systems:
- Lucidchart: A cloud-based diagramming tool with extensive templates and collaboration features.
- Visio: A Microsoft software offering a wide range of diagramming capabilities, including process mapping.
- Draw.io: A free, open-source diagramming tool with a user-friendly interface.
- Creately: A web-based diagramming tool with a focus on collaboration and real-time editing.
- ProcessOn: A collaborative diagramming tool offering a variety of templates and integrations.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating business process maps?
- Overcomplicating the map: Avoid including unnecessary details or jargon that may confuse stakeholders.
- Ignoring feedback: Seek input from stakeholders to ensure the map accurately reflects the process.
- Failing to update the map: Regularly review and update the map to reflect changes in the process.
- Not using the map to drive improvement: Leverage the map as a tool for identifying areas for improvement and implementing changes.
Tips for Effective Business Process Mapping
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the map and the specific process you want to analyze.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve relevant individuals and departments in the mapping process to ensure accuracy and buy-in.
- Use a standardized notation: Adopt a consistent mapping method to ensure clarity and understanding.
- Keep it simple and clear: Avoid clutter and excessive details, focusing on conveying the essential information.
- Use clear and concise language: Employ easily understandable terminology and avoid technical jargon.
- Test and refine: Validate the map with stakeholders and make adjustments as needed.
- Maintain and update: Regularly review and update the map to reflect changes in the process.
Conclusion
Business process maps are indispensable tools for organizations seeking to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and foster continuous improvement. By providing a clear and concise visual representation of how work gets done, these maps empower businesses to streamline processes, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions. By embracing the power of process mapping, organizations can unlock their full potential, driving innovation, growth, and sustained success.
.png#keepProtocol)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Business Process Maps: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!