Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Georgia
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Georgia
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Georgia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Georgia
The state of Georgia, with its diverse landscape, bustling cities, and rich history, presents a complex tapestry of information. To effectively manage and understand this intricate web of data, Georgia has embraced the power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS, a technology that integrates location data with other types of information, provides a powerful lens through which to analyze and visualize the state’s unique characteristics.
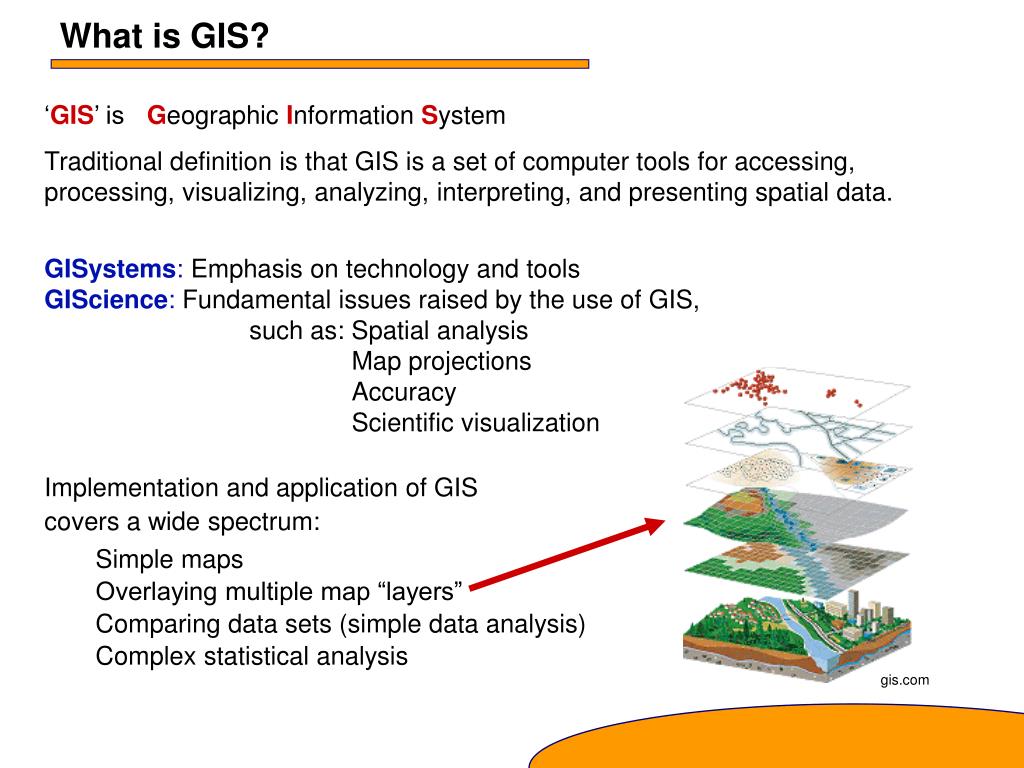
Understanding the Foundation: What is GIS?
At its core, GIS is a system for capturing, storing, analyzing, managing, and displaying geographically referenced data. It combines the principles of cartography, database management, and computer science to create dynamic maps that reveal intricate patterns and relationships within spatial data. This data can encompass a wide range of elements, including:
- Physical features: Land cover, elevation, rivers, lakes, and forests.
- Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, pipelines, power lines, and communication networks.
- Social and economic factors: Population density, demographics, income levels, and business locations.
- Environmental data: Air and water quality, soil conditions, and wildlife habitats.
The Advantages of GIS in Georgia:
The application of GIS in Georgia is far-reaching, impacting numerous sectors and contributing to informed decision-making across various disciplines. Some key benefits include:
1. Planning and Development:
- Land Use Planning: GIS enables efficient land use planning by analyzing land suitability for different purposes, minimizing conflict between development and environmental protection.
- Infrastructure Development: GIS assists in planning and managing infrastructure projects, optimizing routes, minimizing environmental impact, and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
- Urban Planning: GIS facilitates the development of sustainable urban environments by analyzing population density, transportation patterns, and resource availability.
2. Emergency Management and Disaster Response:
- Real-time Situational Awareness: GIS provides real-time data on disaster events, enabling authorities to assess the situation, allocate resources effectively, and coordinate response efforts.
- Evacuation Planning: GIS supports the development of evacuation plans, identifying safe routes and shelters, and ensuring the timely and efficient movement of populations.
- Damage Assessment: GIS aids in assessing the extent of damage caused by natural disasters, helping to prioritize recovery efforts and allocate resources effectively.
3. Environmental Management:
- Resource Management: GIS helps track and manage natural resources like water, forests, and wildlife, ensuring their sustainable utilization and conservation.
- Environmental Monitoring: GIS facilitates the monitoring of environmental conditions, detecting pollution, identifying areas at risk, and enabling timely intervention.
- Climate Change Adaptation: GIS assists in understanding the impacts of climate change, identifying vulnerable areas, and developing adaptation strategies.
4. Public Safety and Law Enforcement:
- Crime Mapping: GIS allows law enforcement agencies to analyze crime patterns, identify hot spots, and deploy resources effectively.
- Emergency Response: GIS supports rapid response to emergencies, optimizing route planning, locating victims, and coordinating rescue efforts.
- Resource Allocation: GIS helps allocate resources, including personnel and equipment, based on crime statistics and population density.
5. Transportation and Logistics:
- Route Optimization: GIS optimizes transportation routes, minimizing travel time, fuel consumption, and costs.
- Traffic Management: GIS helps analyze traffic patterns, identify congestion points, and implement strategies to improve traffic flow.
- Logistics and Delivery: GIS facilitates efficient logistics operations by optimizing delivery routes and tracking shipments in real-time.
The Power of Data Visualization:
GIS excels in presenting complex spatial data in a clear and intuitive way. Through interactive maps, charts, and graphs, GIS empowers users to:
- Identify trends and patterns: Analyze data to reveal spatial relationships and understand how different factors interact.
- Communicate insights effectively: Share findings with stakeholders, making complex data accessible and understandable.
- Make informed decisions: Use data-driven insights to guide decision-making and optimize resource allocation.
Examples of GIS in Action in Georgia:
- Georgia Department of Transportation (GDOT): Uses GIS to manage road networks, plan construction projects, and analyze traffic patterns.
- Georgia Environmental Protection Division (EPD): Employs GIS to monitor air and water quality, manage environmental resources, and assess the impact of pollution.
- Georgia Emergency Management Agency (GEMA): Utilizes GIS for disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
- City of Atlanta: Leverages GIS for urban planning, infrastructure management, and public safety initiatives.
FAQs about GIS in Georgia:
1. What are the key data sources used in GIS in Georgia?
GIS in Georgia relies on a diverse range of data sources, including:
- Government data: Data collected by agencies like GDOT, EPD, and GEMA.
- Satellite imagery: Provides aerial views of the state, enabling analysis of land cover, infrastructure, and environmental conditions.
- Aerial photography: Provides detailed images of specific areas, facilitating land use planning and infrastructure management.
- LiDAR data: Provides precise elevation measurements, crucial for modeling terrain and understanding flood risks.
- Census data: Provides demographic and socio-economic information, essential for urban planning and resource allocation.
- Private sector data: Data collected by businesses and organizations, such as utility companies, real estate developers, and environmental consultants.
2. How can I access and utilize GIS data in Georgia?
Several resources provide access to GIS data in Georgia:
- Georgia Geographic Information Office (GGIO): Provides a central repository for state-level GIS data, including maps, datasets, and metadata.
- Georgia Spatial Data Infrastructure (GSDI): A collaborative effort to develop and maintain a comprehensive GIS framework for the state.
- Local government websites: Many cities and counties in Georgia provide access to their GIS data and mapping tools.
- Commercial GIS platforms: Companies like Esri and Google offer GIS software and data services.
3. What are some examples of how GIS is used in specific industries in Georgia?
GIS finds applications in various industries, including:
- Agriculture: GIS supports precision agriculture, optimizing crop yields, managing irrigation systems, and minimizing environmental impact.
- Healthcare: GIS facilitates the analysis of disease outbreaks, identifying vulnerable populations, and optimizing healthcare resource allocation.
- Tourism: GIS helps develop tourism itineraries, identify attractions, and create interactive maps for visitors.
- Education: GIS is used in classrooms to teach geography, environmental science, and other subjects, fostering spatial thinking and data analysis skills.
Tips for Utilizing GIS Effectively:
- Clearly define your goals: Identify the specific questions you want to answer or problems you want to solve.
- Choose the right data: Select data relevant to your goals, ensuring its quality and accuracy.
- Use appropriate tools and techniques: Select GIS software and analytical methods suitable for your needs.
- Collaborate with experts: Work with GIS professionals to ensure the effective utilization of the technology.
- Communicate your findings clearly: Present your results in a concise and understandable manner, using maps, charts, and graphs.
Conclusion:
GIS technology is transforming the way Georgia understands and manages its diverse landscape and resources. By integrating location data with other information, GIS provides a powerful tool for planning, development, emergency response, environmental management, and countless other applications. As the state continues to embrace the potential of GIS, its impact on decision-making and resource management will only grow, ensuring a more informed and sustainable future for Georgia.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Georgia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!