Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples
- 3.1 Understanding the Significance of Tableau Maps
- 3.2 Exploring a Spectrum of Tableau Map Examples
- 3.3 Exploring the Power of Tableau Map Interactivity
- 3.4 Unlocking the Benefits of Tableau Maps
- 3.5 Addressing Common Questions About Tableau Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Creating Effective Tableau Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: Elevating Data Analysis through Visual Storytelling
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples
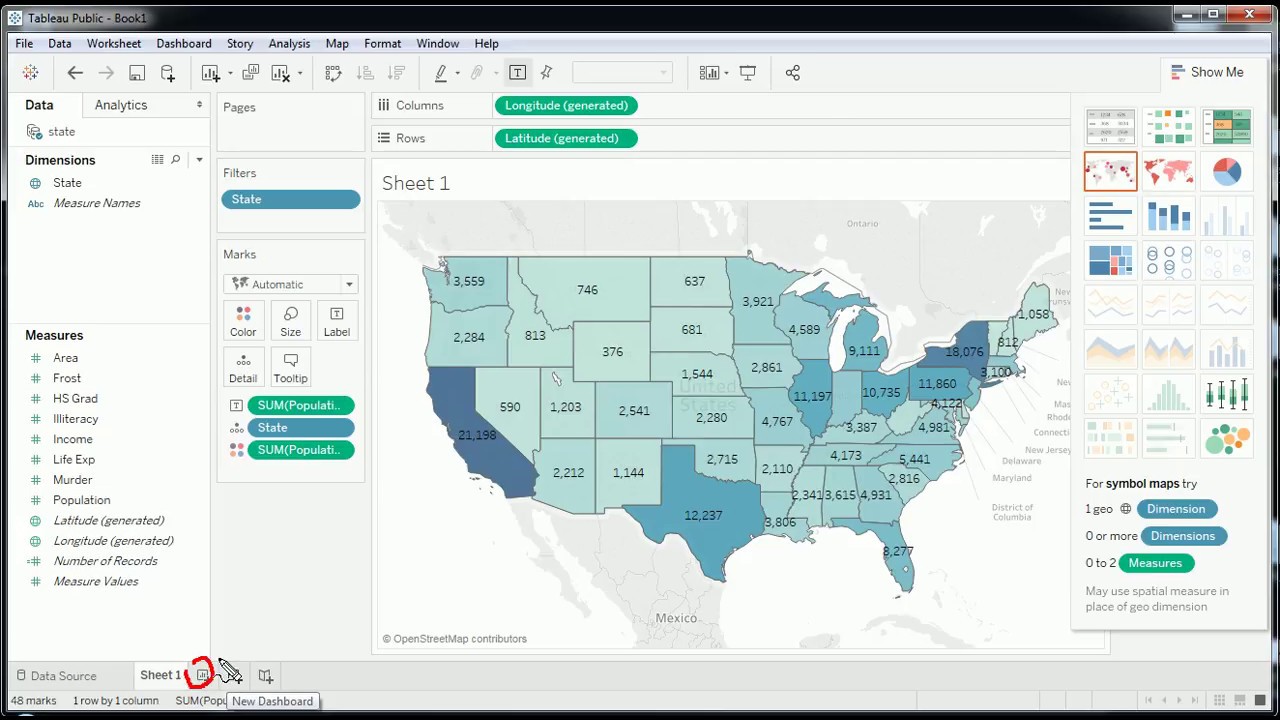
In the realm of data analysis, visualization reigns supreme. It transforms raw data into captivating narratives, revealing hidden patterns and insights that might otherwise remain obscured. Among the powerful tools available for data visualization, Tableau stands out as a user-friendly and versatile platform, particularly when it comes to creating compelling maps. This guide delves into the world of Tableau map examples, showcasing their potential to illuminate geographical trends and unlock valuable business intelligence.
Understanding the Significance of Tableau Maps
Tableau maps are not merely static representations of geographical data. They are dynamic, interactive visualizations that empower users to explore data in a geographical context, uncovering trends, anomalies, and relationships that might be missed in traditional tabular formats. This ability to visualize data spatially unlocks a wealth of possibilities for:
- Identifying geographical patterns: Uncovering regional variations in sales performance, customer demographics, disease prevalence, or environmental factors.
- Analyzing spatial relationships: Exploring how different data points interact within a geographical context, such as the correlation between population density and crime rates or the impact of proximity to a certain facility on customer behavior.
- Making informed decisions: Leveraging visual insights to guide strategic planning, resource allocation, and targeted marketing campaigns.
Exploring a Spectrum of Tableau Map Examples
The versatility of Tableau maps extends beyond simple location markers. Let’s dive into various examples, showcasing the diverse applications of this powerful visualization tool:
1. Sales Performance by Region:
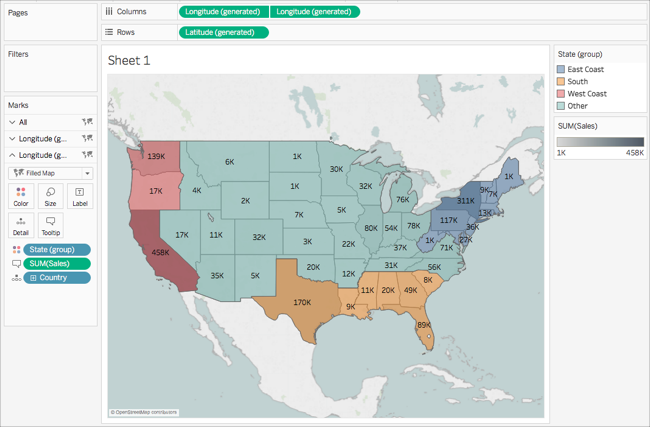
Imagine a business with a nationwide presence. A Tableau map can visually depict sales performance across different regions, highlighting areas with high sales, low sales, or potential growth opportunities. Color-coding regions based on sales volume or percentage change over time allows for quick identification of key trends. Users can further interact with the map, drilling down to individual states, counties, or even specific zip codes to gain a more granular understanding of sales patterns.
2. Customer Distribution and Segmentation:
Understanding customer demographics and their geographical distribution is crucial for targeted marketing campaigns. A Tableau map can visually represent customer concentration areas, highlighting regions with high customer density. By layering additional data, such as customer age, income, or purchase history, businesses can segment customers based on their geographical location and tailor their marketing messages accordingly.
3. Disease Prevalence and Hotspot Identification:
In the healthcare sector, visualizing disease prevalence across geographic regions is vital for public health initiatives. A Tableau map can effectively display the distribution of various diseases, highlighting regions with high incidence rates. By overlaying data on population density, healthcare infrastructure, and environmental factors, public health officials can identify hotspots and prioritize resource allocation for disease prevention and control efforts.
4. Real Estate Market Analysis:
Real estate professionals rely heavily on geographical data to understand market trends and make informed investment decisions. A Tableau map can visualize property prices across different regions, highlighting areas with high demand, low supply, or potential for appreciation. By incorporating additional factors like property type, amenities, and proximity to key attractions, real estate analysts can gain a comprehensive understanding of the local market and identify profitable investment opportunities.
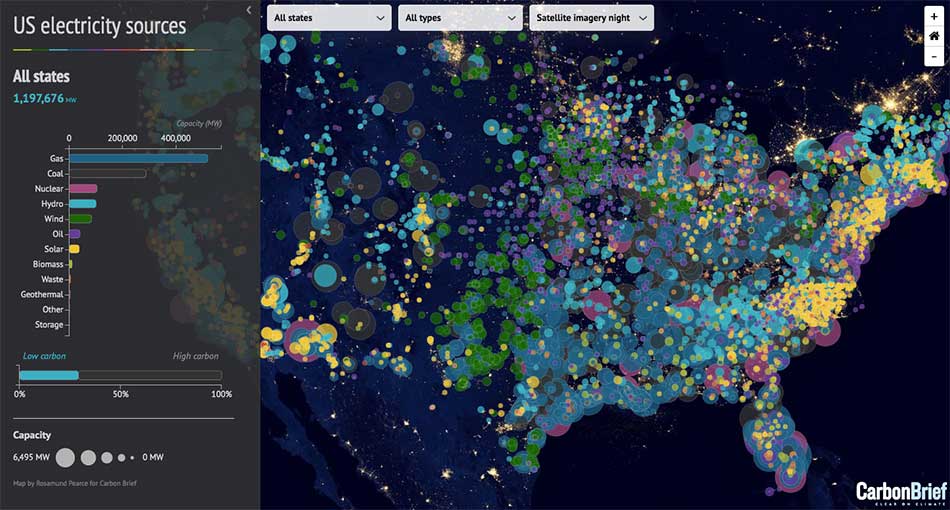
5. Environmental Monitoring and Impact Assessment:
Monitoring environmental factors like air quality, water pollution, and deforestation requires accurate visualization of data across geographical areas. A Tableau map can display pollution levels, deforestation rates, or water quality indicators, allowing environmental agencies to identify areas of concern, track changes over time, and implement targeted conservation measures.
6. Supply Chain Optimization:
Efficient supply chain management relies on understanding the geographical distribution of suppliers, warehouses, and distribution centers. A Tableau map can visualize the entire supply chain network, highlighting potential bottlenecks, transportation routes, and areas for optimization. By incorporating data on transportation costs, delivery times, and inventory levels, businesses can optimize their supply chain operations and minimize logistical challenges.
7. Election Results and Voter Demographics:
During elections, visualizing election results and voter demographics across different regions is crucial for understanding political trends and identifying key constituencies. A Tableau map can effectively display election results, highlighting areas where a particular candidate won or lost. By layering data on voter demographics, political analysts can identify key voting blocs, understand voter preferences, and develop targeted campaign strategies.
8. Crime Mapping and Incident Analysis:
Law enforcement agencies utilize Tableau maps for crime mapping and incident analysis, visualizing the spatial distribution of criminal activity. By plotting crime incidents on a map, police departments can identify crime hotspots, track trends over time, and allocate resources effectively to combat crime. Additionally, maps can be used to analyze the relationship between crime and socioeconomic factors, providing valuable insights for crime prevention strategies.
9. Natural Disaster Response and Relief Efforts:
In the aftermath of natural disasters, understanding the geographical impact and coordinating relief efforts is critical. A Tableau map can visualize the affected areas, highlighting areas with the most damage, population density, and access to resources. By incorporating data on infrastructure damage, evacuation routes, and available resources, relief organizations can prioritize their response efforts and ensure efficient distribution of aid.
10. Travel and Tourism Analysis:
For travel and tourism businesses, understanding the geographical distribution of attractions, accommodation options, and tourist hotspots is essential. A Tableau map can visualize tourist destinations, highlighting popular attractions, hotel locations, and transport routes. By incorporating data on visitor demographics, travel patterns, and customer reviews, tourism companies can optimize their marketing strategies, improve visitor experiences, and enhance tourism development initiatives.
Exploring the Power of Tableau Map Interactivity
The real magic of Tableau maps lies in their interactivity. Users can go beyond static visualizations and engage with the data in dynamic ways, uncovering deeper insights and drawing more informed conclusions. Some key interactive features of Tableau maps include:
- Zooming and Panning: Explore different geographical areas with ease, zooming in on specific regions of interest or panning across vast landscapes.
- Filtering and Selection: Isolate data based on specific criteria, highlighting particular regions, demographics, or time periods.
- Tooltips and Pop-ups: Gain detailed information about individual data points by hovering over them, revealing relevant metrics and additional context.
- Drill-down Functionality: Explore data at multiple levels of granularity, starting with a high-level overview and gradually drilling down to more specific details.
- Dynamic Coloring and Symbol Sizing: Visually represent data variations through color gradients, symbol sizes, or other visual cues, allowing for quick identification of trends and anomalies.
- Time-Based Animations: Track data changes over time through animated maps, revealing trends, patterns, and the evolution of geographical phenomena.
Unlocking the Benefits of Tableau Maps
Beyond their visual appeal, Tableau maps offer a multitude of benefits that enhance data analysis and decision-making:
- Improved Communication: Visualizing data geographically makes it easier to communicate complex information to stakeholders, regardless of their technical expertise.
- Enhanced Insight Discovery: By exploring data in a spatial context, users can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and relationships that might be missed in traditional data analysis methods.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Visual insights derived from Tableau maps provide a solid foundation for making informed decisions about resource allocation, marketing campaigns, operational efficiency, and strategic planning.
- Faster Problem Solving: By quickly identifying areas of concern, trends, and anomalies, Tableau maps enable faster problem solving and intervention.
- Increased Collaboration: Interactive Tableau maps facilitate collaboration among team members, allowing them to explore data together, share insights, and make collective decisions.
Addressing Common Questions About Tableau Maps
FAQs:
1. What are the prerequisites for creating Tableau maps?
To create Tableau maps, you need a Tableau Desktop license and access to geographical data. The data can be in various formats, including CSV, Excel, and shapefiles.
2. How can I import geographical data into Tableau?
Tableau offers various options for importing geographical data. You can directly connect to data sources like Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, or shapefiles. Alternatively, you can use Tableau’s built-in mapping features to create maps based on latitude and longitude coordinates.
3. What are the different types of maps available in Tableau?
Tableau offers a variety of map types, including:
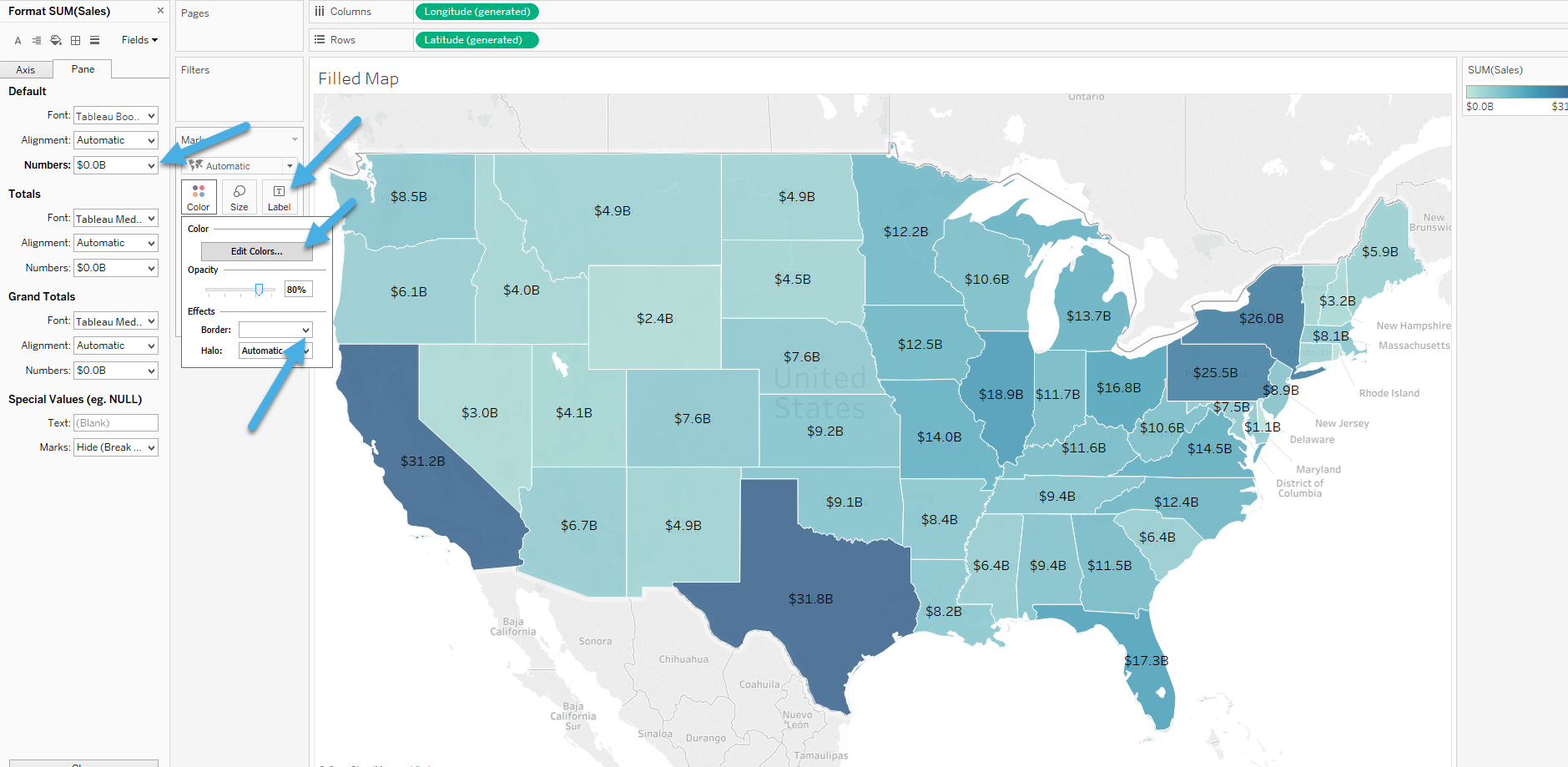
- Choropleth Maps: Color-coded maps that display data variations across geographical regions.
- Symbol Maps: Maps that use symbols to represent data points, with symbol size or color representing data values.
- Heat Maps: Maps that use color gradients to represent data density, highlighting areas with high or low concentrations.
- Cluster Maps: Maps that group similar data points together, revealing clusters of activity or trends.
- Flow Maps: Maps that visualize movement or flow between different locations, representing migration patterns, transportation routes, or supply chains.
4. Can I customize Tableau maps to meet specific needs?
Yes, Tableau offers extensive customization options for maps, allowing you to:
- Choose different map backgrounds and basemaps: Select from various map providers like Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, or Tableau’s built-in basemaps.
- Adjust map projections: Select the most appropriate projection for your data and geographical context.
- Customize map colors, symbols, and labels: Choose colors, symbols, and labels that align with your brand or data visualization goals.
- Add interactive elements: Incorporate tooltips, pop-ups, filters, and other interactive features to enhance data exploration.
5. How can I share Tableau maps with others?
You can share Tableau maps in various ways:
- Tableau Public: Publish maps online and share them with a wider audience.
- Tableau Server or Tableau Online: Publish maps to a secure server or online platform for internal use or sharing with specific stakeholders.
- Static Images or PDFs: Export maps as images or PDFs for inclusion in presentations or reports.
Tips for Creating Effective Tableau Maps
Tips:
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific insights you want to convey with your map and select the appropriate map type and data visualization techniques accordingly.
- Choose the right map projection: Select a projection that accurately represents the geographical area you are visualizing and minimizes distortion.
- Use color effectively: Choose colors that are visually appealing, contrast well, and convey the desired message.
- Keep it simple and clear: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information or complex visualizations. Focus on highlighting the key insights and trends.
- Use labels and annotations: Add clear labels and annotations to provide context and identify important data points.
- Consider interactivity: Incorporate interactive features like tooltips, filters, and drill-down functionality to enhance user engagement and data exploration.
- Test and refine: Iterate on your map design, testing different visualization techniques and refining your approach to achieve the most effective communication of your insights.
Conclusion: Elevating Data Analysis through Visual Storytelling
Tableau maps are more than just geographical representations; they are powerful tools for data visualization and storytelling. By leveraging the versatility of Tableau maps, users can transform raw data into captivating narratives, revealing hidden patterns, trends, and relationships that drive informed decision-making. From sales performance analysis to environmental monitoring, public health initiatives to real estate market analysis, the applications of Tableau maps are vast and continue to expand as businesses leverage the power of spatial data visualization to unlock new insights and navigate a data-driven world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Visualization: A Comprehensive Guide to Tableau Map Examples. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!