Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Gaul: A Journey Through Maps and History
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Gaul: A Journey Through Maps and History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Gaul: A Journey Through Maps and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Gaul: A Journey Through Maps and History
.jpg)
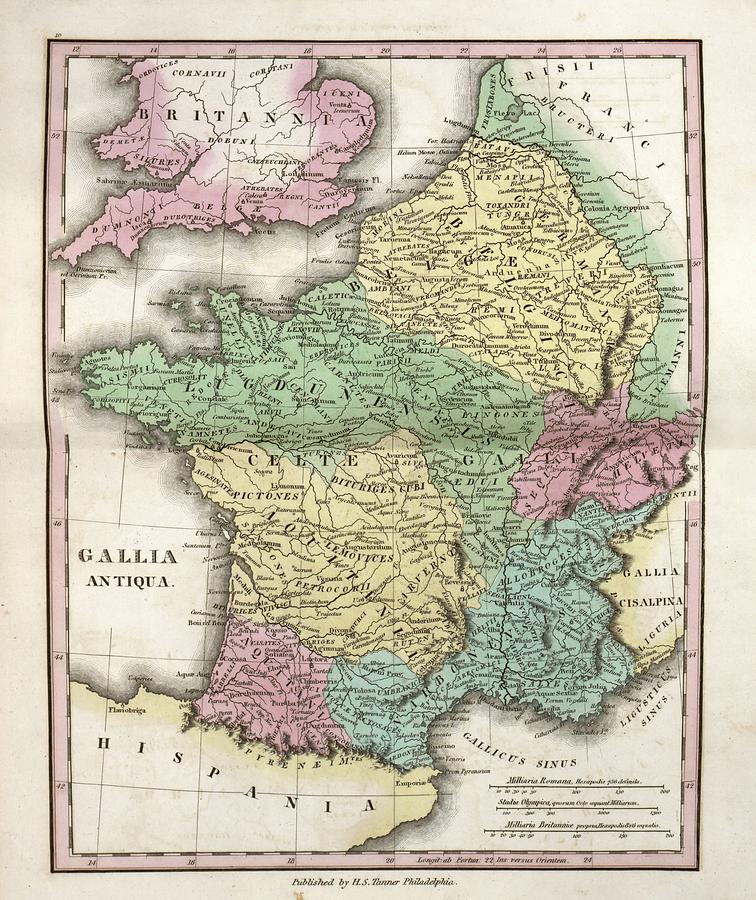
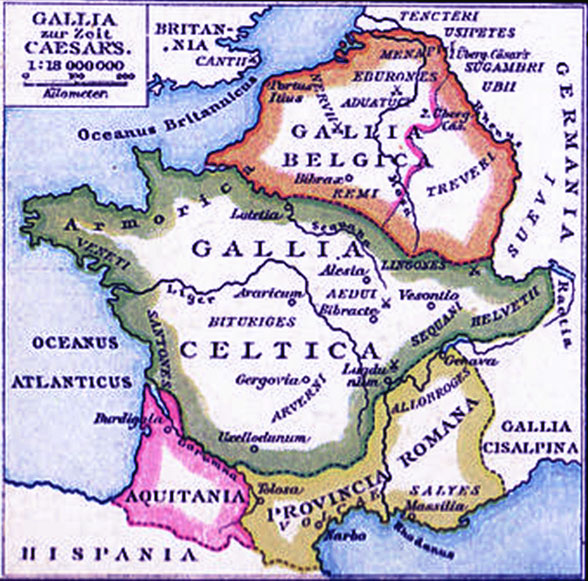
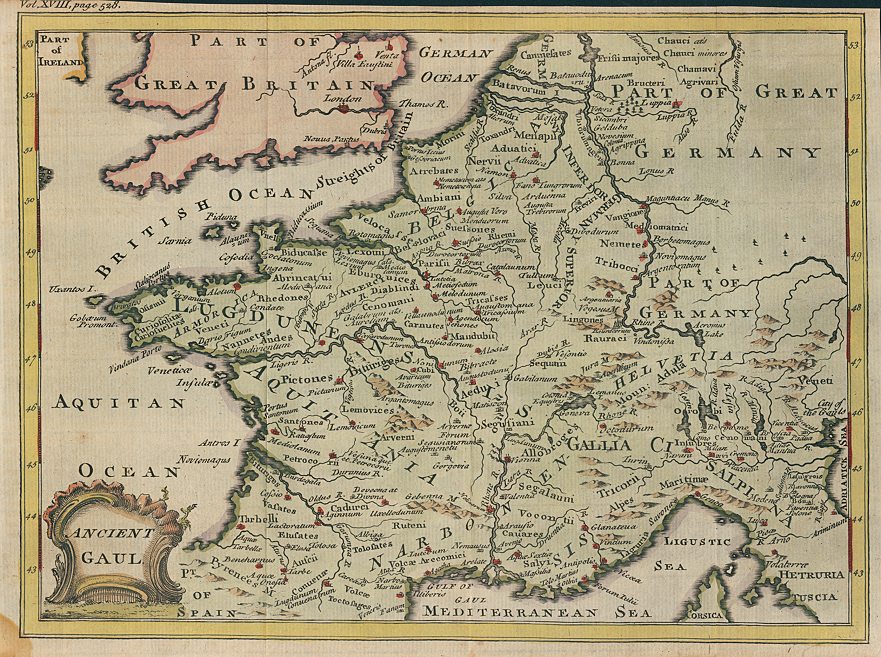
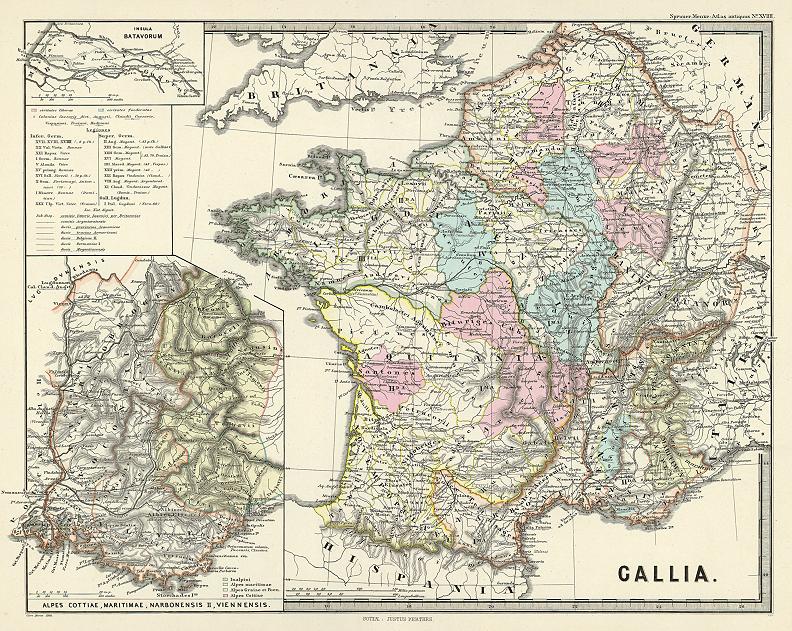
The land of Gaul, now encompassing much of modern-day France, Belgium, Switzerland, and parts of Italy and Germany, holds a rich tapestry of history woven into its very fabric. To understand the complexities of this ancient region, a journey through its cartographic representations is essential. Ancient Gaul maps, though limited in their detail compared to modern cartography, offer invaluable insights into the political, social, and cultural landscape of the region during antiquity.
The Significance of Ancient Gaul Maps
Ancient Gaul maps serve as vital historical records, providing a window into the past and illuminating several key aspects of the region’s development:
- Political Boundaries and Tribal Structures: Maps offer a visual representation of the intricate network of Celtic tribes that inhabited Gaul. They reveal the territorial divisions and alliances that shaped the region’s political landscape. Studying these maps allows historians to trace the rise and fall of various tribes, their interactions, and the complex power dynamics that played out across Gaul.
- Roman Conquest and Administration: The Roman conquest of Gaul, spanning centuries, is vividly documented in ancient maps. These maps illustrate the strategic routes of Roman armies, the locations of key battles, and the gradual expansion of Roman control over the region. They also depict the establishment of Roman cities, roads, and administrative structures, demonstrating the Romanization of Gaul.
- Economic and Trade Routes: Maps reveal the vital trade networks that crisscrossed Gaul, connecting it to other parts of the Roman Empire. These networks facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences, shaping the economic and social development of the region.
- Cultural and Religious Landscapes: Ancient maps often incorporate information about religious sites, sacred groves, and other places of cultural significance. This information helps historians reconstruct the religious beliefs and practices of the Gauls, revealing their complex relationship with the natural world and their deities.
- Geographical Understanding: Ancient maps, despite their limitations, offered a valuable understanding of the geography of Gaul. They helped navigate the region, identify key geographical features, and understand the natural resources available. This knowledge was crucial for military campaigns, trade, and settlement planning.
Types of Ancient Gaul Maps
Ancient maps of Gaul come in various forms, each offering unique insights into the region:
- Military Maps: These maps were primarily used by the Roman military for planning campaigns, logistics, and troop movements. They often focused on strategic locations, roads, and terrain features.
- Road Maps: These maps documented the network of Roman roads that connected various cities and regions of Gaul. They were used for transportation, communication, and trade.
- Regional Maps: These maps focused on specific regions of Gaul, highlighting key cities, towns, and landmarks. They were used for administrative purposes, trade, and cultural understanding.
- Itinerary Maps: These maps provided detailed descriptions of routes and distances between various locations, serving as travel guides for merchants, travelers, and pilgrims.
Challenges in Interpreting Ancient Gaul Maps
While invaluable, ancient Gaul maps present several challenges for modern interpretation:
- Limited Detail: Ancient maps were often limited in detail, focusing on key features rather than providing a comprehensive representation of the region.
- Lack of Standardization: Ancient cartography lacked standardized symbols and conventions, making it difficult to interpret the meaning of various markings.
- Historical Bias: Ancient maps were often created for specific purposes and may reflect the biases of their creators. For example, Roman maps may have emphasized Roman achievements and control over the region.
- Fragmentation and Loss: Many ancient maps have been lost or damaged over time, limiting our understanding of the region.
Famous Ancient Gaul Maps
Several ancient maps of Gaul have survived to this day and offer valuable insights into the region:
- The Tabula Peutingeriana: This 12th-century copy of a 4th-century Roman map depicts the road network of the Roman Empire, including a detailed representation of Gaul.
- The Ravenna Cosmography: This 7th-century manuscript contains a map of the world, including a depiction of Gaul, highlighting key cities and geographical features.
- The Peutinger Table: This 13th-century copy of a 4th-century Roman map provides a detailed representation of the Roman road network, including roads connecting key cities in Gaul.
Modern Uses of Ancient Gaul Maps
Ancient Gaul maps continue to hold relevance in the 21st century, offering several uses:
- Historical Research: Historians use ancient maps to study the political, social, and cultural landscape of ancient Gaul, reconstructing its past and understanding its evolution.
- Archaeological Exploration: Maps can guide archaeological investigations, helping locate ancient sites, roads, and settlements.
- Tourism and Heritage Preservation: Ancient maps contribute to understanding and preserving the historical and cultural heritage of Gaul, promoting tourism and cultural awareness.
FAQs about Ancient Gaul Maps
Q: What is the oldest known map of Gaul?
A: The oldest known map of Gaul is the Tabula Peutingeriana, a 12th-century copy of a 4th-century Roman map.
Q: What are the main differences between ancient Gaul maps and modern maps?
A: Ancient maps were often less detailed, lacking standardized symbols and conventions. They were created for specific purposes, such as military campaigns or road travel, and often reflected the biases of their creators. Modern maps are more standardized, detailed, and accurate, incorporating advancements in cartography and technology.
Q: How did ancient Gauls create maps?
A: The methods used by ancient Gauls to create maps are not fully understood. They likely relied on observations of the landscape, oral traditions, and perhaps rudimentary surveying techniques.
Q: What can we learn about the Gauls from their maps?
A: Ancient Gaul maps provide valuable insights into the political, social, cultural, and economic landscape of the region. They reveal the territorial divisions of Celtic tribes, the expansion of Roman control, the importance of trade routes, and the religious beliefs of the Gauls.
Tips for Studying Ancient Gaul Maps
- Context is Key: Understanding the historical context of a map is crucial for accurate interpretation. Consider the time period, the purpose of the map, and the biases of its creator.
- Look for Patterns: Examine the map for recurring symbols, patterns, and geographical features. These patterns can reveal important information about the region and its inhabitants.
- Compare with Other Sources: Compare the map with other historical sources, such as written accounts, archaeological evidence, and other maps. This comparison can help clarify ambiguities and provide a more comprehensive understanding.
- Use Modern Tools: Utilize modern technology, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), to analyze and visualize ancient maps. This can help create more accurate and detailed representations of the region.
Conclusion
Ancient Gaul maps are not merely static representations of a bygone era; they are dynamic windows into a complex and fascinating past. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the political, social, cultural, and economic forces that shaped the region of Gaul, paving the way for the rich history and vibrant culture of modern-day France and its surrounding regions. These maps serve as a reminder that the past is not merely a collection of facts but a living story, waiting to be deciphered and understood through the lens of cartographic evidence.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Roman_Gaul_-_AD_400-56aaca365f9b58b7d008f778.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/antique-map-of-gaul-157743111-5b75d192c9e77c0025628ca4.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Gaul: A Journey Through Maps and History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!