Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence
- 3.1 The Core Tenets of Confucianism: Building Blocks of a Moral Order
- 3.2 The Path to Self-Cultivation: Cultivating Virtue for a Harmonious Society
- 3.3 The Role of Education: Nurturing the Next Generation of Virtuous Citizens
- 3.4 The Significance of Rituals and Ceremonies: Maintaining Social Order and Harmony
- 3.5 Confucianism in the Modern World: Adapting to Changing Times
- 3.6 The Confucian Map: A Guide for Navigating the Modern World
- 3.7 FAQs about the Confucian Map
- 3.8 Tips for Applying the Confucian Map in Daily Life
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence

Confucianism, a philosophy and social system originating in ancient China, has profoundly shaped East Asian societies for centuries. Its enduring influence stems from its focus on ethical and moral principles, emphasizing social harmony, good governance, and individual self-cultivation. Understanding the "Confucian map," a metaphorical framework encompassing its core tenets and their interconnectedness, provides a valuable lens through which to analyze its impact and relevance in the modern world.
The Core Tenets of Confucianism: Building Blocks of a Moral Order
The Confucian map can be visualized as a network of interconnected principles, each contributing to a harmonious and ethical society. These principles, often referred to as the "Five Constant Relationships," form the foundation of Confucian thought:
1. Ruler and Minister: This relationship emphasizes the ruler’s responsibility to govern justly and the minister’s duty to serve loyally and with wisdom. It underscores the importance of mutual respect and accountability in leadership and governance.
2. Father and Son: This relationship emphasizes the father’s role as a guide and protector, while the son is expected to show filial piety and respect. It highlights the importance of family bonds and intergenerational transmission of values.
3. Husband and Wife: This relationship emphasizes mutual respect and cooperation, with the husband as the head of the household and the wife responsible for domestic duties. It underscores the importance of gender roles and the complementary nature of relationships.
4. Elder Brother and Younger Brother: This relationship emphasizes the elder brother’s responsibility to guide and protect the younger brother, while the younger brother is expected to show deference and respect. It highlights the importance of sibling bonds and the hierarchical structure within families.
5. Friend and Friend: This relationship emphasizes mutual respect, trust, and loyalty. It underscores the importance of friendship and the value of supportive relationships.
These relationships are not static but rather fluid and dynamic, requiring constant effort and adaptation. They are not merely about obedience or hierarchy but about mutual respect, responsibility, and the pursuit of virtue.
The Path to Self-Cultivation: Cultivating Virtue for a Harmonious Society
Confucianism emphasizes the importance of individual self-cultivation as the cornerstone of a harmonious society. The ultimate goal is to achieve "ren" (仁), often translated as benevolence, humaneness, or goodness. This involves cultivating virtues such as:
1. Li (礼): This refers to proper etiquette, rituals, and social norms. It emphasizes the importance of behaving appropriately in different social contexts, promoting order and harmony.
2. Yi (义): This refers to righteousness, justice, and doing what is right. It emphasizes the importance of ethical decision-making and acting in accordance with principles.
3. Xin (信): This refers to trustworthiness and sincerity. It emphasizes the importance of being honest and reliable in relationships and interactions.
4. Zhi (智): This refers to wisdom, knowledge, and understanding. It emphasizes the importance of intellectual development and seeking knowledge to navigate complex situations.
5. Yong (勇): This refers to courage, determination, and perseverance. It emphasizes the importance of standing up for what is right and pursuing one’s goals with conviction.
By cultivating these virtues, individuals can contribute to a harmonious society, fostering a virtuous cycle of ethical behavior and social responsibility.
The Role of Education: Nurturing the Next Generation of Virtuous Citizens
Confucianism places immense value on education as a means of fostering virtue and promoting social harmony. Education is not merely about acquiring knowledge but about developing character, cultivating moral values, and promoting ethical conduct. The Confucian classics, including the Analects, Mencius, and the Doctrine of the Mean, serve as a guide for ethical conduct and personal development.
Education in Confucianism is a lifelong pursuit, involving learning from elders, engaging in self-reflection, and striving for continuous improvement. It emphasizes the importance of respecting teachers and valuing knowledge, fostering a culture of learning and intellectual growth.
The Significance of Rituals and Ceremonies: Maintaining Social Order and Harmony
Confucianism places great importance on rituals and ceremonies, seeing them as essential for maintaining social order and promoting harmony. These rituals, ranging from ancestor worship to formal greetings, serve as a reminder of social norms and ethical principles. They provide a framework for social interaction, reinforcing the importance of respect, deference, and community.
Rituals and ceremonies also play a role in fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity, promoting social cohesion and strengthening community bonds. They provide opportunities for individuals to express their respect for others and contribute to the well-being of the community.
Confucianism in the Modern World: Adapting to Changing Times
While Confucianism originated in ancient China, its influence continues to resonate in the modern world. Its core principles of ethics, social harmony, and individual self-cultivation remain relevant in a globalized and interconnected world.
However, Confucianism is not static but rather a dynamic system that has evolved over time, adapting to changing social and cultural contexts. In the modern world, Confucianism is being reinterpreted and applied in various ways, addressing contemporary challenges such as globalization, technological advancements, and social inequality.
The Confucian Map: A Guide for Navigating the Modern World
Understanding the Confucian map, with its emphasis on ethics, social harmony, and individual self-cultivation, offers valuable insights for navigating the complexities of the modern world. Its principles provide a framework for ethical decision-making, fostering responsible leadership, promoting social justice, and cultivating a sense of community.
By embracing the core tenets of Confucianism, individuals can contribute to a more just, equitable, and harmonious society. This involves embracing the values of respect, responsibility, and self-cultivation, striving to live a virtuous life and contribute to the well-being of others.
FAQs about the Confucian Map
1. Is Confucianism a religion?
Confucianism is often described as a philosophy or a system of social ethics, rather than a religion. It does not have a deity or focus on supernatural beliefs. However, Confucianism emphasizes rituals and ceremonies, and its teachings have been deeply intertwined with religious practices in East Asian societies.
2. How does Confucianism differ from other philosophies?
Confucianism distinguishes itself from other philosophies through its emphasis on practical ethics and social harmony. While other philosophies may focus on abstract concepts or individual enlightenment, Confucianism prioritizes the well-being of society and the cultivation of virtuous individuals.
3. What is the role of the "Five Constant Relationships" in Confucianism?
The "Five Constant Relationships" form the foundation of Confucian social ethics, outlining the proper conduct and responsibilities within different social roles. They provide a framework for harmonious interactions and foster a sense of order and stability within society.
4. What is the significance of "ren" in Confucianism?
"Ren" is the ultimate goal of self-cultivation in Confucianism, representing the highest form of humaneness and virtue. It involves cultivating compassion, empathy, and a deep understanding of human nature, enabling individuals to contribute to a just and harmonious society.
5. How can Confucianism be applied in the modern world?
Confucianism’s principles of ethical decision-making, social responsibility, and individual self-cultivation remain relevant in the modern world. Its teachings can inform ethical leadership, promote social justice, and foster a sense of community in a globalized and interconnected society.
Tips for Applying the Confucian Map in Daily Life
1. Practice Respect and Deference: Treat others with respect, regardless of their social status or position. Show deference to elders and those in authority, recognizing the importance of hierarchical structures in society.
2. Cultivate Self-Discipline and Ethical Conduct: Strive to live a virtuous life, adhering to ethical principles and behaving in accordance with Confucian values. Practice self-reflection and seek continuous improvement in your character and conduct.
3. Engage in Meaningful Relationships: Foster strong and supportive relationships with family, friends, and colleagues. Value loyalty, trust, and mutual respect in all your interactions.
4. Seek Knowledge and Wisdom: Continuously strive to learn and expand your understanding of the world. Value education and engage in meaningful intellectual pursuits.
5. Contribute to the Well-being of Others: Seek opportunities to make a positive impact on your community and the world. Act with compassion and empathy, striving to create a more just and harmonious society.
Conclusion
The Confucian map provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the philosophy and social system of Confucianism. Its emphasis on ethical conduct, social harmony, and individual self-cultivation continues to resonate in the modern world, offering valuable insights for navigating the complexities of contemporary life. By embracing its core tenets and applying them in daily life, individuals can contribute to a more just, equitable, and harmonious society, fostering a virtuous cycle of ethical behavior and social responsibility.
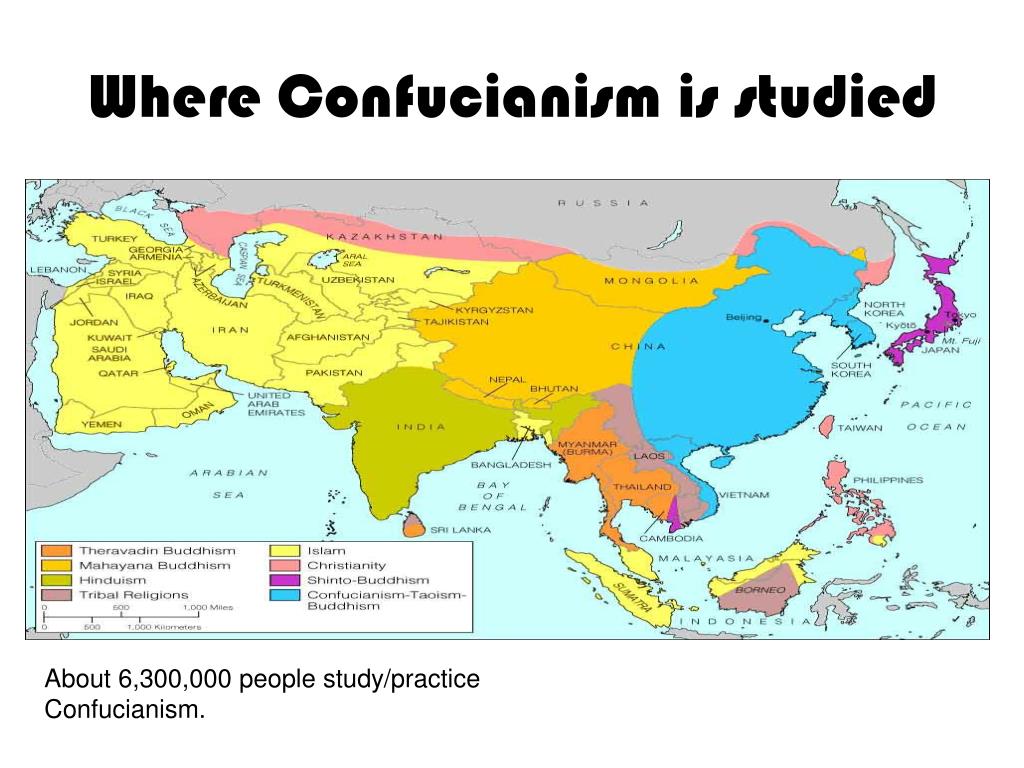
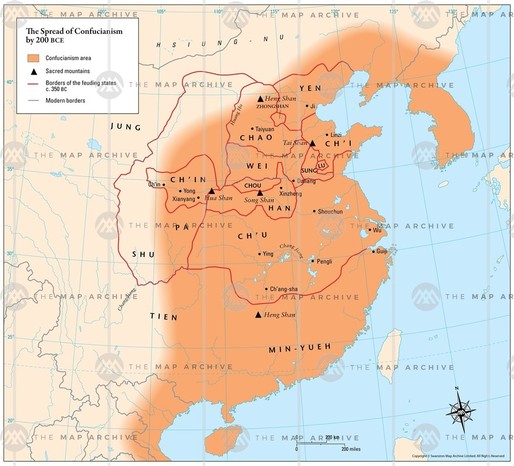


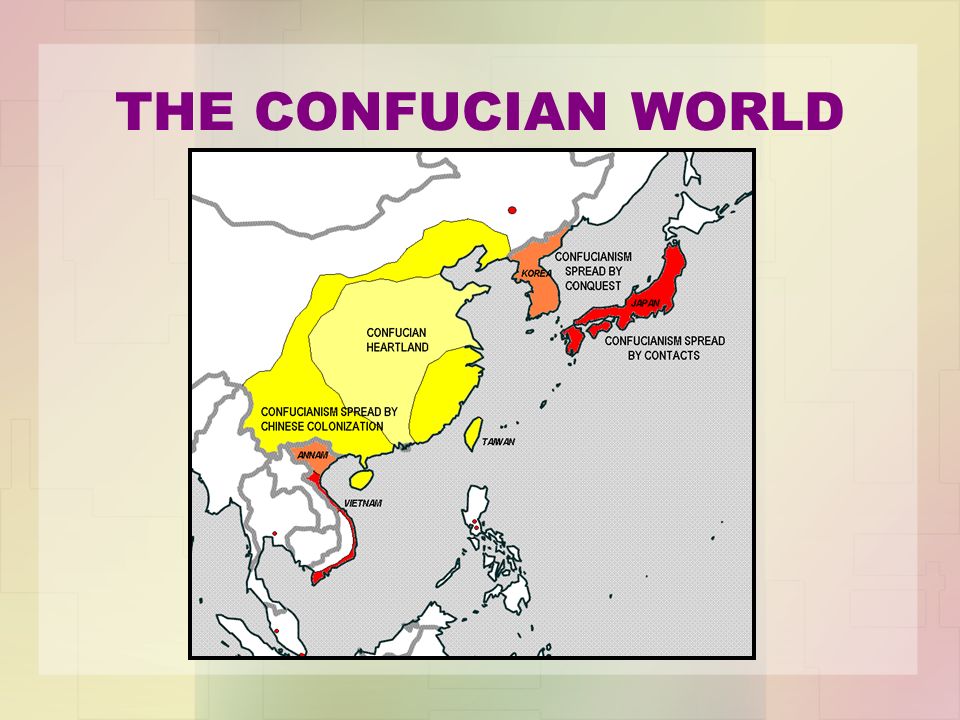

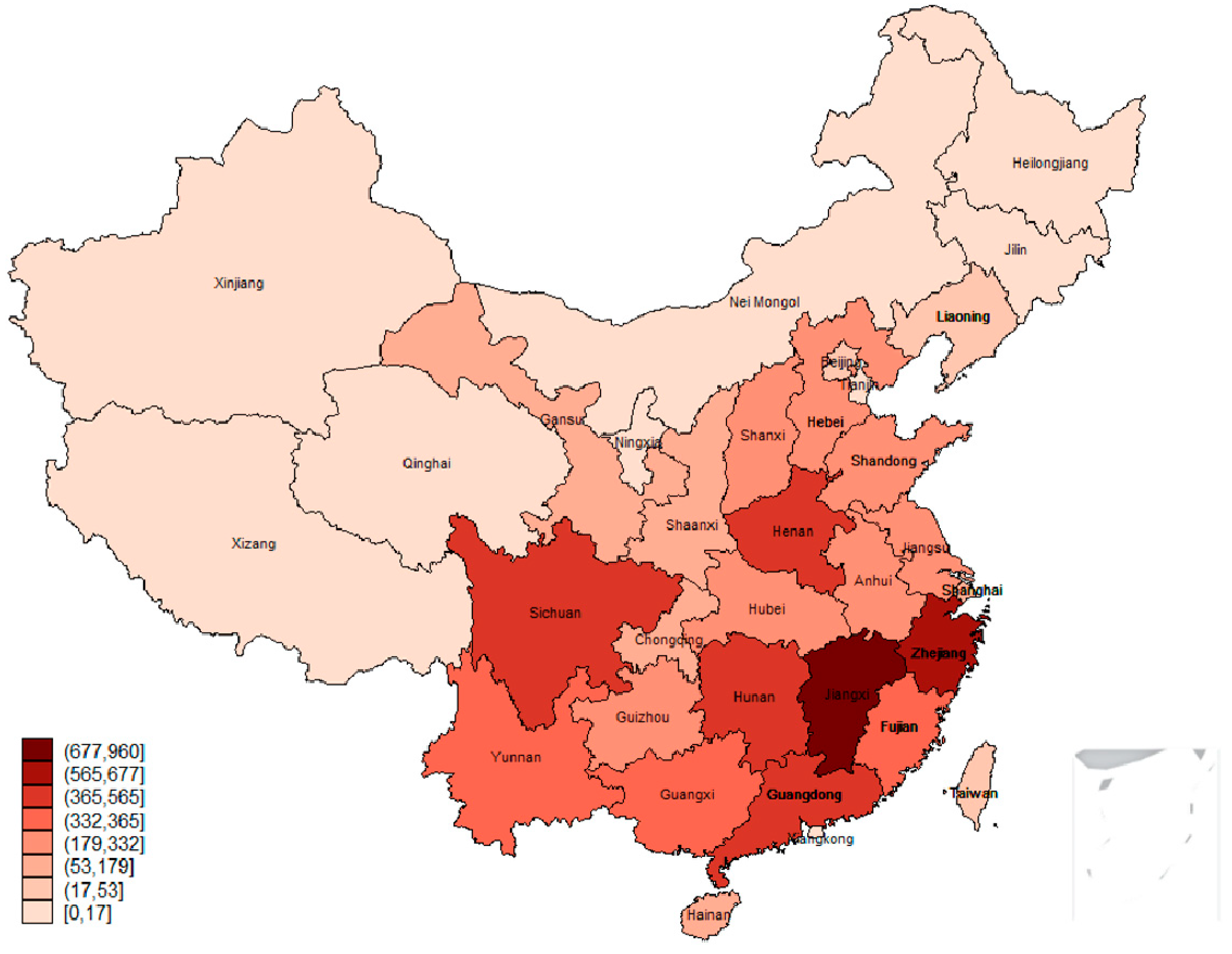

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Confucianism: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Map and Influence. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!