Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
- 3.1 Understanding DNR Wetland Maps: A Key to Conservation
- 3.2 Navigating the Benefits of DNR Wetland Maps: A Comprehensive Overview
- 3.3 Unlocking the Potential of DNR Wetland Maps: A Practical Guide
- 3.4 Addressing Common Queries: A Comprehensive FAQ Guide
- 3.5 Conclusion: A Call to Action for Wetland Conservation
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps
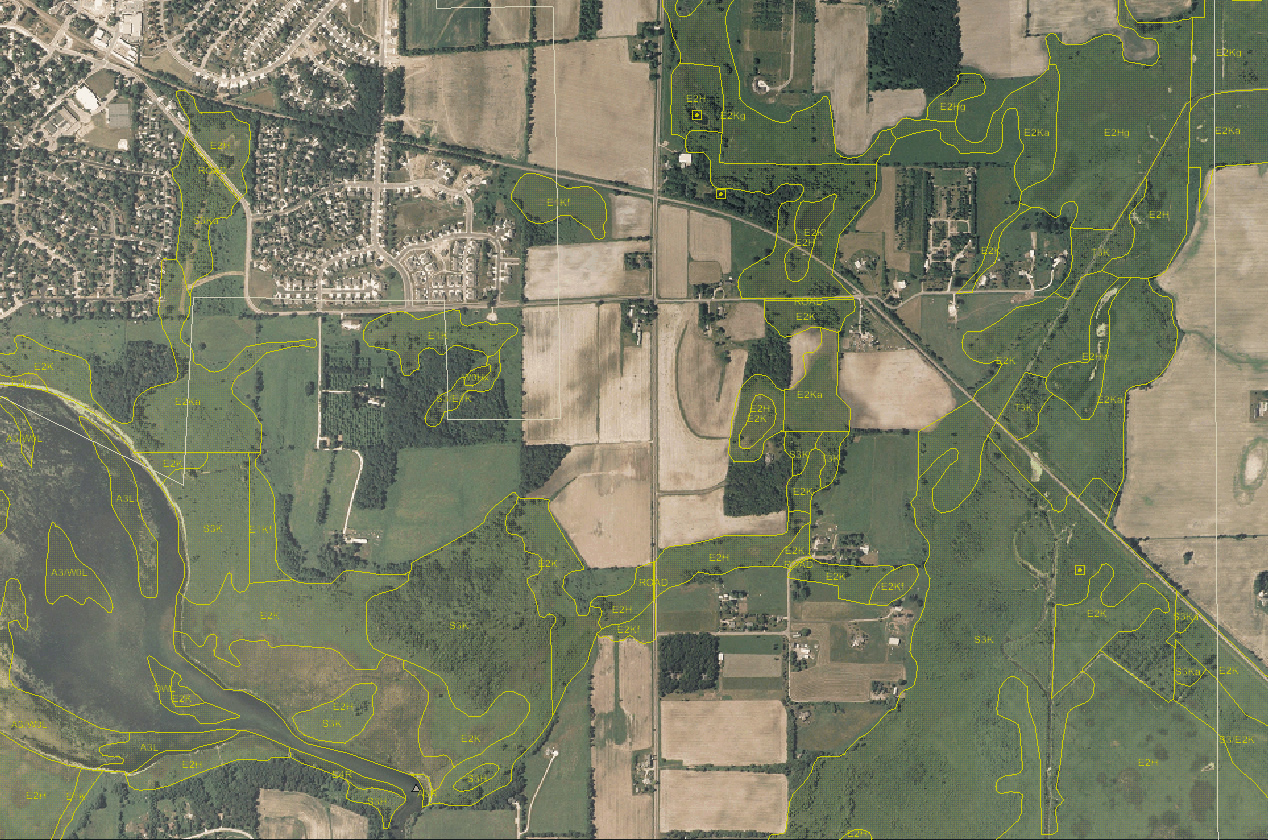
Wetlands, often referred to as "nature’s kidneys," are crucial ecosystems that play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of our environment. They serve as natural filters, flood control mechanisms, and vital habitats for a diverse array of plant and animal life. Recognizing their significance, government agencies like the Department of Natural Resources (DNR) have developed comprehensive wetland maps to provide a clear understanding of these valuable resources.
Understanding DNR Wetland Maps: A Key to Conservation
DNR wetland maps are invaluable tools that serve as a blueprint for understanding the distribution, characteristics, and ecological importance of wetlands within a specific region. These maps are meticulously crafted using aerial imagery, field surveys, and advanced Geographic Information System (GIS) technology.
The core elements of a DNR wetland map typically include:
- Wetland Boundaries: Precisely delineating the extent of each wetland area, allowing for accurate identification and monitoring.
- Wetland Types: Categorizing wetlands based on their vegetation, hydrology, and soil characteristics, providing insights into their unique ecological functions.
- Wetland Status: Indicating the current condition of wetlands, such as pristine, degraded, or restored, highlighting areas requiring conservation efforts.
- Adjacent Land Uses: Mapping surrounding land uses, such as agriculture, urban development, or forestry, to understand potential threats and pressures on wetlands.
- Water Bodies: Representing rivers, streams, lakes, and other water bodies, showcasing the interconnectedness of wetlands within a larger hydrological system.
Navigating the Benefits of DNR Wetland Maps: A Comprehensive Overview
DNR wetland maps are not merely static representations of wetlands; they are dynamic tools that offer a multitude of benefits, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding wetland conservation and management.
Key benefits of utilizing DNR wetland maps include:
1. Informed Land Use Planning and Development:
- Preventing Wetland Loss: The maps provide a clear visual representation of wetland locations, allowing planners and developers to avoid encroaching on these valuable ecosystems.
- Minimizing Environmental Impacts: By understanding the extent and characteristics of wetlands, developers can design projects that minimize disruption to sensitive habitats and water quality.
- Promoting Sustainable Development: The maps guide the implementation of sustainable development practices, ensuring that new infrastructure and development projects coexist harmoniously with wetland ecosystems.
2. Effective Wetland Management and Restoration:
- Targeted Conservation Efforts: The maps pinpoint areas of high ecological value, allowing agencies to focus conservation resources on the most critical wetlands.
- Monitoring Wetland Health: By comparing maps over time, changes in wetland boundaries, vegetation, and water quality can be tracked, enabling early detection of threats and facilitating timely intervention.
- Prioritizing Restoration Projects: The maps identify degraded or impacted wetlands, providing valuable data for prioritizing restoration efforts and ensuring efficient allocation of resources.
3. Enhancing Public Awareness and Education:
- Visualizing the Value of Wetlands: The maps serve as powerful visual aids, effectively communicating the importance and vulnerability of wetlands to the general public.
- Promoting Environmental Stewardship: By showcasing the interconnectedness of wetlands with the broader ecosystem, the maps encourage responsible land use practices and foster a deeper appreciation for wetland conservation.
- Engaging Local Communities: The maps can be used to educate local communities about wetland values and encourage their participation in conservation and restoration initiatives.
4. Supporting Scientific Research and Monitoring:
- Long-Term Data Collection: DNR wetland maps provide a baseline for long-term monitoring of wetland conditions, facilitating scientific research and understanding of ecological trends.
- Analyzing Wetland Dynamics: The maps can be used to study how wetlands respond to climate change, human activities, and other environmental pressures.
- Evaluating the Effectiveness of Conservation Efforts: By comparing data from different time periods, scientists and managers can assess the effectiveness of wetland conservation programs and adjust strategies as needed.
Unlocking the Potential of DNR Wetland Maps: A Practical Guide
DNR wetland maps are readily accessible to the public through various online platforms and resources. Understanding how to navigate these maps and utilize their information effectively is crucial for maximizing their potential.
Practical tips for using DNR wetland maps:
- Explore Online Resources: Visit the DNR website or other relevant online platforms to access interactive maps, data layers, and accompanying documentation.
- Understand Map Symbols and Legends: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and legends used on the maps to interpret the information accurately.
- Utilize Zoom and Pan Features: Zoom in on specific areas of interest and pan across the map to explore different regions and identify key features.
- Combine Data Layers: Overlay various data layers, such as land use, elevation, and soil type, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of wetland characteristics and surrounding environments.
- Consult with DNR Experts: For more specific questions or assistance in interpreting the maps, contact the DNR directly for expert guidance and support.
Addressing Common Queries: A Comprehensive FAQ Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about DNR Wetland Maps:
Q: What is the purpose of DNR wetland maps?
A: DNR wetland maps serve as essential tools for understanding the distribution, characteristics, and ecological importance of wetlands within a region. They are used for informed land use planning, effective wetland management, enhancing public awareness, and supporting scientific research.
Q: How are DNR wetland maps created?
A: DNR wetland maps are created using a combination of aerial imagery, field surveys, and advanced Geographic Information System (GIS) technology. Aerial imagery provides a bird’s-eye view of the landscape, while field surveys verify and refine the data. GIS software then integrates and analyzes this information to produce detailed maps.
Q: How can I access DNR wetland maps?
A: DNR wetland maps are typically available online through the DNR website or other relevant platforms. Some maps may be downloadable in various formats, such as PDF or shapefiles.
Q: How can I use DNR wetland maps to make informed decisions about land use?
A: DNR wetland maps help identify wetland locations, boundaries, and characteristics, allowing for informed planning to avoid impacting these valuable ecosystems. They can be used to determine appropriate setbacks, buffer zones, and mitigation measures to minimize environmental impacts.
Q: How can I use DNR wetland maps to support wetland restoration efforts?
A: DNR wetland maps can help prioritize restoration projects by identifying degraded or impacted wetlands. They can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of restoration activities and track changes in wetland conditions over time.
Q: How can I contribute to wetland conservation through the use of DNR wetland maps?
A: By understanding the importance and vulnerability of wetlands, you can advocate for responsible land use practices, support wetland restoration efforts, and educate others about the value of these crucial ecosystems.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for Wetland Conservation
DNR wetland maps serve as invaluable tools for promoting responsible land use, managing wetland resources effectively, and fostering a deeper appreciation for the ecological significance of these vital ecosystems. By utilizing these maps, stakeholders can make informed decisions that protect and restore wetlands, ensuring their continued contribution to the health and well-being of our environment for generations to come.
The future of wetlands hinges on our collective commitment to conservation and sustainable management. Let us leverage the power of DNR wetland maps to guide our actions, ensuring that these precious ecosystems remain a vital part of our natural heritage.

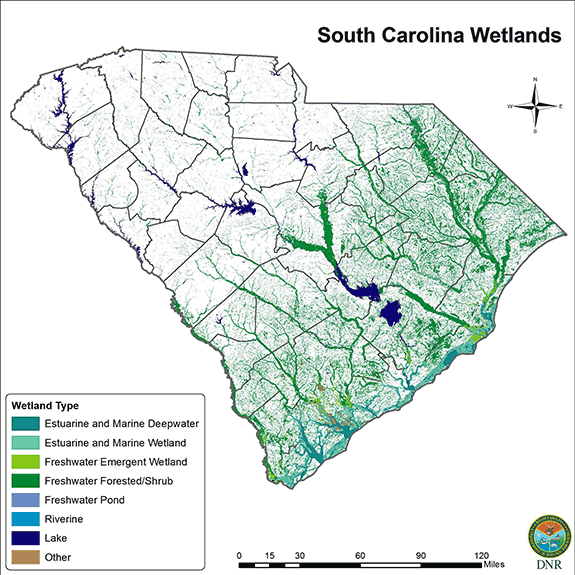

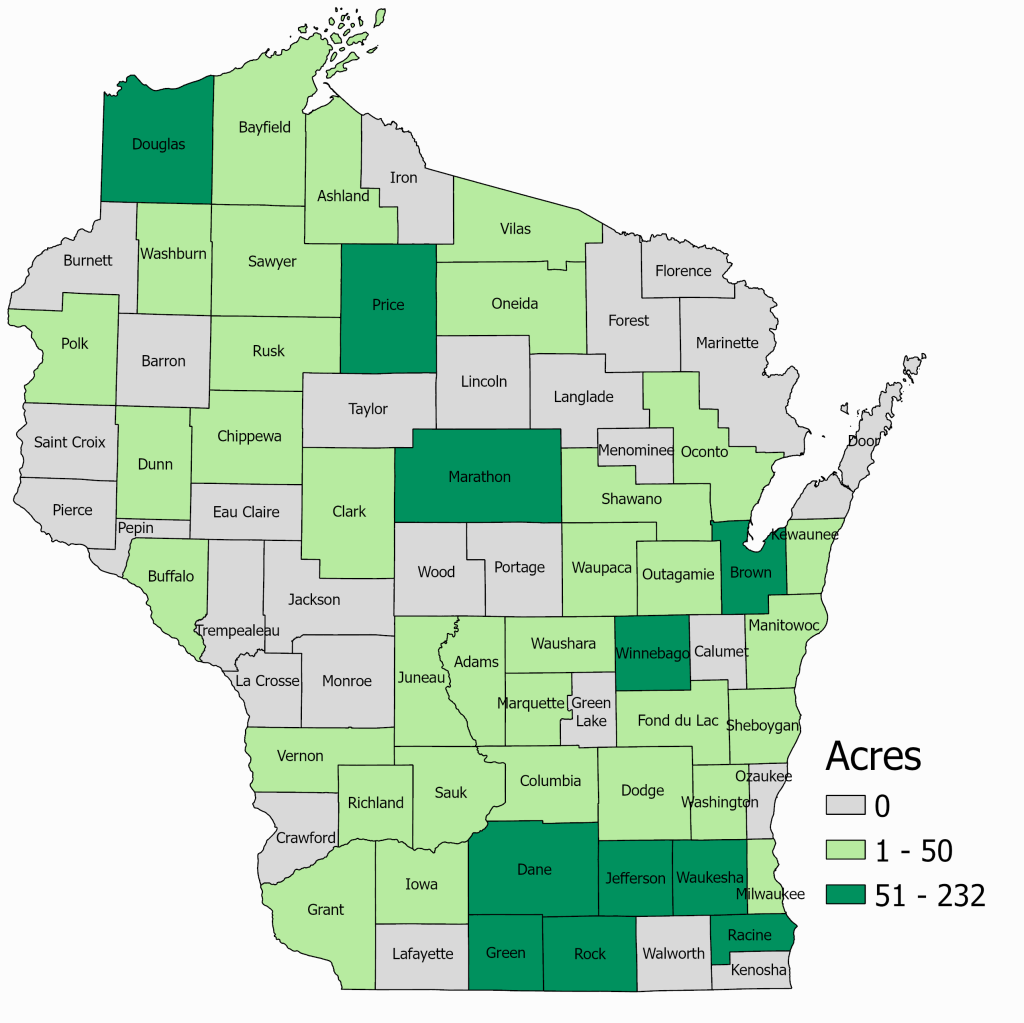


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Vital Role of Wetlands: A Comprehensive Guide to DNR Wetland Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!