Unveiling the World from Above: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Applications
Related Articles: Unveiling the World from Above: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Applications
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World from Above: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World from Above: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Applications

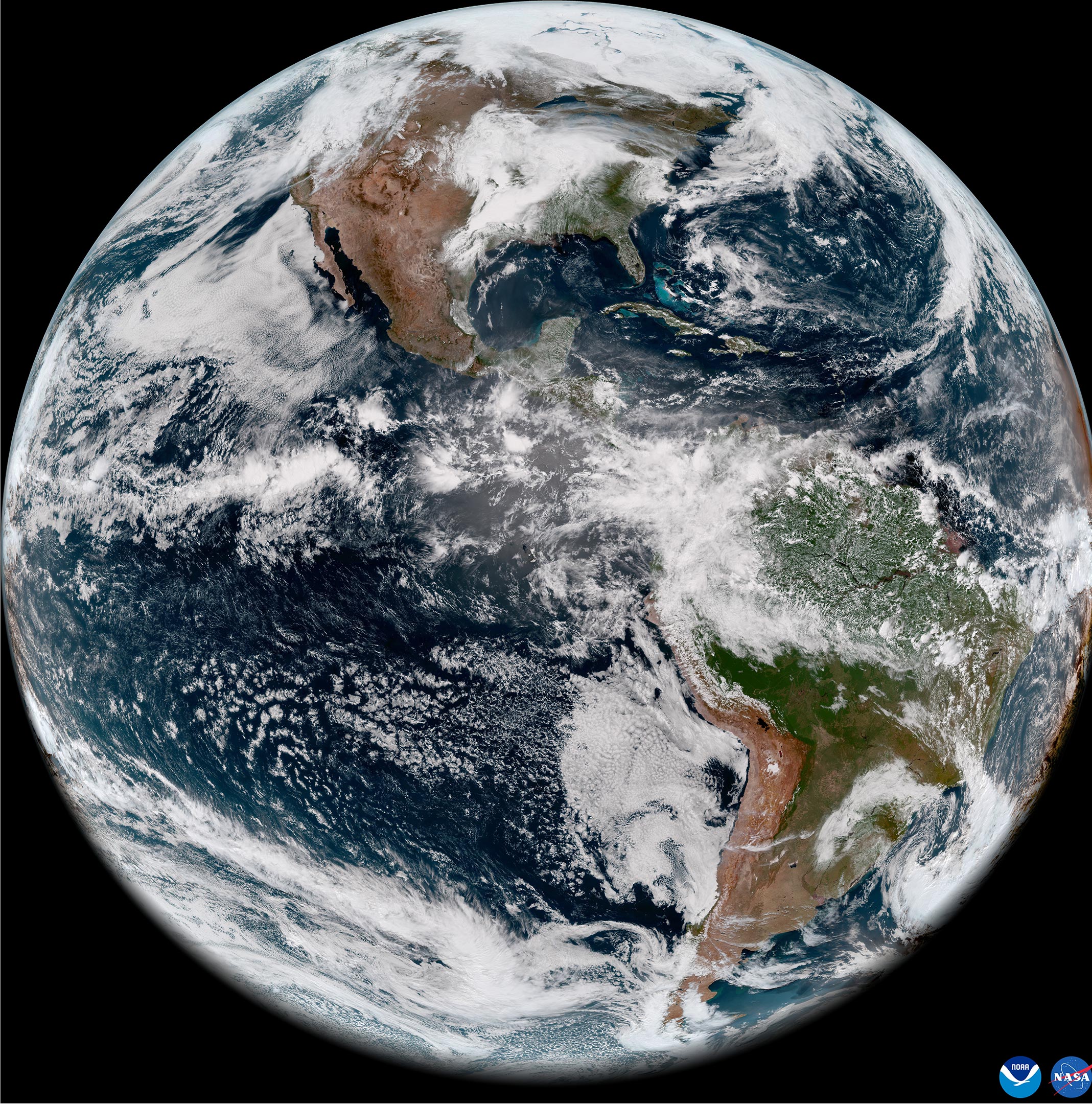
The Earth, a vibrant tapestry of landscapes, oceans, and human settlements, has long captivated our curiosity. However, our understanding of the planet has been revolutionized by a technological marvel: satellite imagery. This powerful tool, capturing breathtaking views of our world from space, has become an indispensable resource across a vast array of disciplines, from scientific research to everyday life.
The Genesis of Satellite Imagery
The journey of satellite imagery began in the early days of the space race. The first satellite images, captured by the American Explorer 6 in 1959, were rudimentary, showcasing only the Earth’s cloud cover. However, these early attempts paved the way for the development of sophisticated imaging systems that would revolutionize our perception of the planet.
Types of Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery is broadly categorized based on the type of sensor used to capture data:
- Optical Imagery: This type of imagery uses visible light to capture images of the Earth’s surface. It provides detailed information about land cover, vegetation, and urban development. Popular examples include Landsat and Sentinel satellites.
- Radar Imagery: Utilizing radio waves, radar imagery is capable of penetrating clouds and darkness, making it invaluable for weather monitoring, disaster response, and mapping terrain. The Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system is a prime example.
- Infrared Imagery: Sensitive to heat radiation, infrared imagery allows for the detection of thermal anomalies and the mapping of surface temperature variations. This is particularly useful for monitoring wildfires, volcanic activity, and urban heat islands.
The Power of Satellite Imagery: A Multifaceted Tool
The versatility of satellite imagery is truly remarkable. It plays a critical role in various fields, including:
1. Environmental Monitoring and Resource Management:
- Climate Change: Satellite data helps track changes in sea level, ice sheet melting, and global temperatures, providing crucial insights into the impact of climate change.
- Deforestation: By monitoring forest cover over time, satellite imagery aids in combating deforestation and promoting sustainable forestry practices.
- Water Resource Management: Satellite data is used to assess water quality, monitor drought conditions, and manage irrigation systems.
- Natural Disaster Management: Satellite imagery is essential for assessing the impact of natural disasters like floods, earthquakes, and wildfires, enabling rapid response and recovery efforts.
2. Agriculture and Food Security:
- Crop Monitoring: Satellite imagery allows farmers to monitor crop health, identify disease outbreaks, and optimize fertilizer application, leading to increased crop yields.
- Precision Agriculture: Satellite data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
- Food Security: Satellite imagery plays a crucial role in monitoring food production, identifying areas at risk of food shortages, and supporting humanitarian aid efforts.
3. Urban Planning and Development:
- Urban Growth Monitoring: Satellite imagery tracks urban sprawl and helps planners manage urban development, ensuring sustainable growth and infrastructure development.
- Traffic Management: Satellite data can be used to monitor traffic patterns, identify congestion hotspots, and optimize traffic flow.
- Infrastructure Planning: Satellite imagery aids in planning new infrastructure projects, like roads, railways, and power lines, minimizing environmental impact and optimizing resource utilization.
4. Security and Defense:
- Military Intelligence: Satellite imagery provides real-time information on troop movements, military installations, and potential threats, supporting national security efforts.
- Border Security: Satellite data helps monitor borders, detect illegal activities, and enhance border security.
- Disaster Response: Satellite imagery is crucial for coordinating search and rescue efforts, assessing damage, and providing humanitarian assistance in disaster zones.
5. Navigation and Mapping:
- Global Positioning System (GPS): Satellite-based navigation systems like GPS are used for navigation, mapping, and location tracking.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): Satellite imagery is used to create detailed 3D models of the Earth’s surface, providing valuable information for terrain analysis, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Satellite data is integrated into GIS software, enabling the creation of interactive maps and spatial analysis for various applications.
The Future of Satellite Imagery
The field of satellite imagery continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for its applications. Some key trends shaping the future include:
- Higher Resolution Imagery: New satellites are being launched with higher resolution sensors, providing even more detailed information about the Earth’s surface.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI algorithms are being used to analyze satellite data, enabling faster and more accurate interpretations of images.
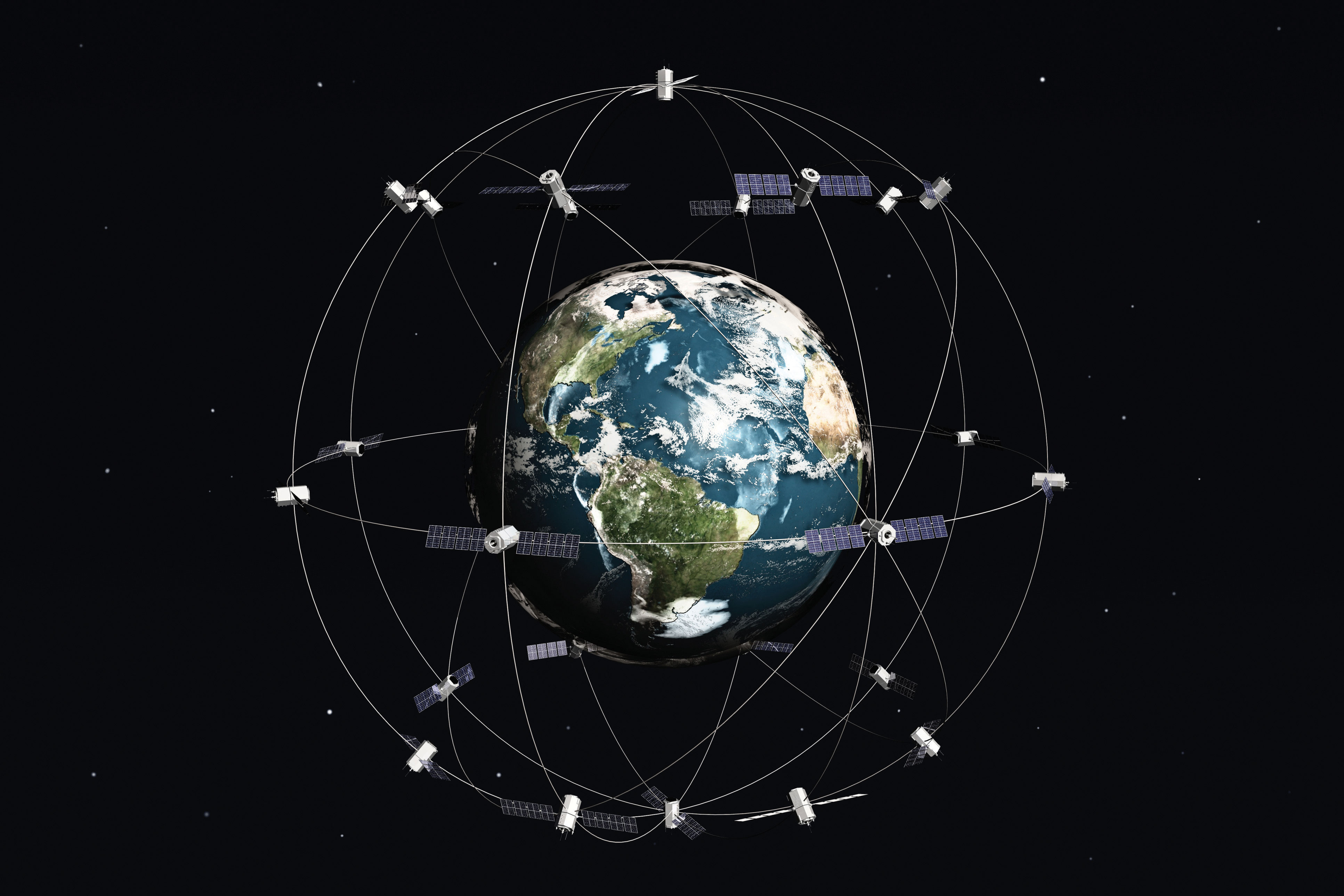
- Constellations of Satellites: Networks of interconnected satellites are being deployed, providing continuous coverage of the Earth’s surface and enabling real-time data collection.
- CubeSats and Small Satellites: The emergence of smaller, more affordable satellites is making space technology more accessible, leading to a proliferation of satellite imagery providers.
FAQs about Satellite Imagery
1. How does satellite imagery work?
Satellite imagery relies on sensors that capture electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from the Earth’s surface. These sensors are typically mounted on satellites orbiting the Earth. Different types of sensors capture different wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, providing information about various aspects of the Earth’s surface, such as land cover, vegetation, and temperature.
2. What are the benefits of using satellite imagery?
Satellite imagery offers several advantages, including:
- Global Coverage: Satellites provide a comprehensive view of the Earth, enabling the monitoring of vast areas.
- Regular Updates: Satellites can capture images frequently, allowing for the tracking of changes over time.
- Objectivity: Satellite data is not influenced by human perception, providing an objective view of the Earth’s surface.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Satellite imagery can be a cost-effective way to gather information compared to traditional methods like aerial photography.
3. What are the limitations of satellite imagery?
While powerful, satellite imagery has certain limitations:
- Cloud Cover: Clouds can obscure the Earth’s surface, limiting the visibility of certain areas.
- Resolution: The resolution of satellite images can vary, and some images may not be detailed enough for specific applications.
- Data Processing: Processing and analyzing satellite data can be complex and time-consuming.
- Cost: Accessing high-resolution satellite imagery can be expensive.
4. Who uses satellite imagery?
A wide range of users benefit from satellite imagery, including:
- Governments: For environmental monitoring, disaster response, and national security.
- Businesses: For market analysis, resource management, and infrastructure planning.
- Researchers: For scientific studies on climate change, land use, and environmental impact.
- Non-governmental organizations (NGOs): For humanitarian aid, conservation efforts, and development projects.
- Individuals: For navigation, mapping, and personal use.
5. How can I access satellite imagery?
Satellite imagery is available from various sources, including:
- Government Agencies: Agencies like NASA and the European Space Agency provide free and open access to satellite data.
- Commercial Providers: Companies like Planet Labs, DigitalGlobe, and Maxar Technologies offer high-resolution satellite imagery for purchase.
- Online Platforms: Websites like Google Earth and ArcGIS Online provide access to satellite imagery and mapping tools.
Tips for Using Satellite Imagery
- Identify your specific needs: Define the purpose of your analysis and choose the appropriate type of satellite imagery.
- Consider resolution and coverage: Select imagery with the necessary resolution and coverage for your area of interest.
- Explore data processing options: Utilize software tools and techniques for processing and analyzing satellite data.
- Combine satellite data with other sources: Integrate satellite imagery with other data sources, such as ground-based measurements and historical data.
- Stay updated on advancements: Keep abreast of new technologies and applications in the field of satellite imagery.
Conclusion
Satellite imagery has transformed our understanding of the Earth, providing invaluable insights into the planet’s dynamics, human impact, and potential future. From monitoring environmental changes to guiding development strategies, satellite imagery has become an indispensable tool across a wide range of fields. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of satellite imagery are vast and ever-expanding, promising to revolutionize our interaction with the world and drive progress towards a sustainable future.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-155439194-58b73fd35f9b5880804c1963.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World from Above: A Comprehensive Look at Satellite Imagery and its Applications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!